Compare commits
151 Commits
release_wo
...
v0.13.2
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
6476f8ade7 | ||
|
|
42bf614131 | ||
|
|
616eb5f96a | ||
|
|
bad80a64ef | ||
|
|
e93e5ed931 | ||
|
|
77e77775b2 | ||
|
|
f4a44fd93c | ||
|
|
89f4db617a | ||
|
|
b5aaa6759a | ||
|
|
54bbad12f8 | ||
|
|
dc2e8f7f70 | ||
|
|
86341c3172 | ||
|
|
91cdf64602 | ||
|
|
00804a0f81 | ||
|
|
a33f2f117e | ||
|
|
50563eef8d | ||
|
|
97a619eaf0 | ||
|
|
34fb1c2ef5 | ||
|
|
bf23a21486 | ||
|
|
01e2d209d0 | ||
|
|
27567b49db | ||
|
|
d15ab0922b | ||
|
|
64a91f552f | ||
|
|
b1a034fbd4 | ||
|
|
61d285ba13 | ||
|
|
65c47531f6 | ||
|
|
393f44aac6 | ||
|
|
700c0fb410 | ||
|
|
346524c660 | ||
|
|
487c626e00 | ||
|
|
c5ccc0fb08 | ||
|
|
66701b9cf9 | ||
|
|
4c1d34f0e9 | ||
|
|
86cd97609d | ||
|
|
8e419132ea | ||
|
|
49814b34d3 | ||
|
|
7b71c21c12 | ||
|
|
c35c7da82a | ||
|
|
e390533760 | ||
|
|
64bee7a64f | ||
|
|
ca4e0dbc75 | ||
|
|
ee7eaff965 | ||
|
|
e512406764 | ||
|
|
a4f5ad3a94 | ||
|
|
a47068922f | ||
|
|
f8153bdacc | ||
|
|
0de800a8e5 | ||
|
|
ebcf25741b | ||
|
|
eed08f534f | ||
|
|
da5cf1867b | ||
|
|
cc5297f180 | ||
|
|
f27025aef3 | ||
|
|
595fa3d111 | ||
|
|
89051c1b90 | ||
|
|
f00ced5a33 | ||
|
|
9b003e175d | ||
|
|
a490c375f4 | ||
|
|
15644a2b0c | ||
|
|
27cf1cdf15 | ||
|
|
fef6a7ca74 | ||
|
|
5c4501efbc | ||
|
|
614a36af9f | ||
|
|
a0bc3a3626 | ||
|
|
18062eca06 | ||
|
|
1dc42d2904 | ||
|
|
500d369c50 | ||
|
|
3dd0192fe6 | ||
|
|
1eb5105b24 | ||
|
|
463865db55 | ||
|
|
ea247ca816 | ||
|
|
8864e33d1c | ||
|
|
934b16723b | ||
|
|
fc186e4d5f | ||
|
|
7d157dfeb0 | ||
|
|
977eef9138 | ||
|
|
678f1201c6 | ||
|
|
4879de263b | ||
|
|
c6208b266b | ||
|
|
2da99c2308 | ||
|
|
9ac40cd953 | ||
|
|
7522bb6fab | ||
|
|
7b520e8a9d | ||
|
|
cadb1a6a5b | ||
|
|
97c15f7ef3 | ||
|
|
9fa70c3455 | ||
|
|
8c7f6d4a76 | ||
|
|
266b4099b5 | ||
|
|
a1e68a62d0 | ||
|
|
8a010fc1f5 | ||
|
|
563fdec211 | ||
|
|
3457dcddfe | ||
|
|
57a06d2220 | ||
|
|
aa93d4fbdd | ||
|
|
d0036b2f77 | ||
|
|
1b57f8c7e2 | ||
|
|
fa96ec64e4 | ||
|
|
e89db13282 | ||
|
|
fe6577736e | ||
|
|
64537672e6 | ||
|
|
ef36aabd30 | ||
|
|
ca84732574 | ||
|
|
0b828ef1ec | ||
|
|
3359123364 | ||
|
|
cc5357a31a | ||
|
|
f1b60f76eb | ||
|
|
f29e152619 | ||
|
|
92906a500a | ||
|
|
257bd89733 | ||
|
|
1d99bb908d | ||
|
|
591b91194a | ||
|
|
2b2c831253 | ||
|
|
08777100b5 | ||
|
|
a482160691 | ||
|
|
89dd114da1 | ||
|
|
4c05ef48a7 | ||
|
|
14c89c9b63 | ||
|
|
65e3e67a83 | ||
|
|
63233a5830 | ||
|
|
4f7b710112 | ||
|
|
ac53993f70 | ||
|
|
ef750e73a2 | ||
|
|
7270eef6bf | ||
|
|
b54aaad382 | ||
|
|
fc36be4f88 | ||
|
|
aefecad4c0 | ||
|
|
c57528cbcf | ||
|
|
090294e89b | ||
|
|
a6279a0337 | ||
|
|
37b82c0d60 | ||
|
|
0dd3dd23aa | ||
|
|
4bd29b2ee8 | ||
|
|
cc79cbcadc | ||
|
|
89366d7b12 | ||
|
|
6eff08eb2d | ||
|
|
8b6b83bd62 | ||
|
|
8b6e3a0d37 | ||
|
|
8a9b26df4e | ||
|
|
fd6a3bd5d2 | ||
|
|
8085ad4b4c | ||
|
|
af24eb7dbf | ||
|
|
d1620b4e39 | ||
|
|
ba603c1937 | ||
|
|
e89dafa82e | ||
|
|
9d717b371c | ||
|
|
3d70d29672 | ||
|
|
f1efd8dbe2 | ||
|
|
159fb51518 | ||
|
|
cd64399fe5 | ||
|
|
d72e1c38ae | ||
|
|
979c49fd35 | ||
|
|
ac41b6e181 |
@@ -42,7 +42,6 @@
|
||||
"extensions": [
|
||||
"ms-python.python",
|
||||
"ms-python.vscode-pylance",
|
||||
"ms-python.black-formatter",
|
||||
"visualstudioexptteam.vscodeintellicode",
|
||||
"mhutchie.git-graph",
|
||||
"ms-azuretools.vscode-docker",
|
||||
@@ -53,13 +52,10 @@
|
||||
"csstools.postcss",
|
||||
"blanu.vscode-styled-jsx",
|
||||
"bradlc.vscode-tailwindcss",
|
||||
"ms-python.isort",
|
||||
"charliermarsh.ruff"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"settings": {
|
||||
"remote.autoForwardPorts": false,
|
||||
"python.linting.pylintEnabled": true,
|
||||
"python.linting.enabled": true,
|
||||
"python.formatting.provider": "none",
|
||||
"python.languageServer": "Pylance",
|
||||
"editor.formatOnPaste": false,
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +68,7 @@
|
||||
"eslint.workingDirectories": ["./web"],
|
||||
"isort.args": ["--settings-path=./pyproject.toml"],
|
||||
"[python]": {
|
||||
"editor.defaultFormatter": "ms-python.black-formatter",
|
||||
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff",
|
||||
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
|
||||
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
|
||||
"source.fixAll": true,
|
||||
|
||||
21
.github/actions/setup/action.yml
vendored
@@ -11,11 +11,22 @@ outputs:
|
||||
runs:
|
||||
using: "composite"
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Remove unnecessary files
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /opt/ghc
|
||||
# Stop docker so we can mount more space at /var/lib/docker
|
||||
- name: Stop docker
|
||||
run: sudo systemctl stop docker
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# This creates a virtual volume at /var/lib/docker to maximize the size
|
||||
# As of 2/14/2024, this results in 97G for docker images
|
||||
- name: Maximize build space
|
||||
uses: easimon/maximize-build-space@master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
remove-dotnet: 'true'
|
||||
remove-android: 'true'
|
||||
remove-haskell: 'true'
|
||||
remove-codeql: 'true'
|
||||
build-mount-path: '/var/lib/docker'
|
||||
- name: Start docker
|
||||
run: sudo systemctl start docker
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
- id: lowercaseRepo
|
||||
uses: ASzc/change-string-case-action@v5
|
||||
|
||||
6
.github/dependabot.yml
vendored
@@ -18,6 +18,12 @@ updates:
|
||||
interval: daily
|
||||
open-pull-requests-limit: 10
|
||||
target-branch: dev
|
||||
- package-ecosystem: "pip"
|
||||
directory: "/docker/tensorrt"
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
interval: daily
|
||||
open-pull-requests-limit: 10
|
||||
target-branch: dev
|
||||
- package-ecosystem: "npm"
|
||||
directory: "/web"
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
|
||||
11
.github/workflows/ci.yml
vendored
@@ -79,6 +79,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
rpi.tags=${{ steps.setup.outputs.image-name }}-rpi
|
||||
*.cache-from=type=registry,ref=${{ steps.setup.outputs.cache-name }}-arm64
|
||||
*.cache-to=type=registry,ref=${{ steps.setup.outputs.cache-name }}-arm64,mode=max
|
||||
- name: Build and push RockChip build
|
||||
uses: docker/bake-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
targets: rk
|
||||
files: docker/rockchip/rk.hcl
|
||||
set: |
|
||||
rk.tags=${{ steps.setup.outputs.image-name }}-rk
|
||||
*.cache-from=type=gha
|
||||
jetson_jp4_build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
name: Jetson Jetpack 4
|
||||
@@ -141,7 +150,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- arm64_build
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- id: lowercaseRepo
|
||||
uses: ASzc/change-string-case-action@v5
|
||||
uses: ASzc/change-string-case-action@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
string: ${{ github.repository }}
|
||||
- name: Log in to the Container registry
|
||||
|
||||
11
.github/workflows/pull_request.yml
vendored
@@ -65,20 +65,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Check out the repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Set up Python ${{ env.DEFAULT_PYTHON }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4.7.1
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5.0.0
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: ${{ env.DEFAULT_PYTHON }}
|
||||
- name: Install requirements
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U pip
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -r docker/main/requirements-dev.txt
|
||||
- name: Check black
|
||||
- name: Check formatting
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
black --check --diff frigate migrations docker *.py
|
||||
- name: Check isort
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
isort --check --diff frigate migrations docker *.py
|
||||
- name: Check ruff
|
||||
ruff format --check --diff frigate migrations docker *.py
|
||||
- name: Check lint
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
ruff check frigate migrations docker *.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
37
.github/workflows/release.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
name: On release
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
types: [published]
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- id: lowercaseRepo
|
||||
uses: ASzc/change-string-case-action@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
string: ${{ github.repository }}
|
||||
- name: Log in to the Container registry
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@343f7c4344506bcbf9b4de18042ae17996df046d
|
||||
with:
|
||||
registry: ghcr.io
|
||||
username: ${{ github.actor }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Create tag variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
BRANCH=$([[ "${{ github.ref_name }}" =~ ^v[0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+$ ]] && echo "master" || echo "dev")
|
||||
echo "BASE=ghcr.io/${{ steps.lowercaseRepo.outputs.lowercase }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "BUILD_TAG=${BRANCH}-${GITHUB_SHA::7}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "CLEAN_VERSION=$(echo ${GITHUB_REF##*/} | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | sed 's/^[v]//')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
- name: Tag and push the main image
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
VERSION_TAG=${BASE}:${CLEAN_VERSION}
|
||||
PULL_TAG=${BASE}:${BUILD_TAG}
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $HOME/.docker/config.json:/config.json quay.io/skopeo/stable:latest copy --authfile /config.json --multi-arch all docker://${PULL_TAG} docker://${VERSION_TAG}
|
||||
for variant in standard-arm64 tensorrt tensorrt-jp4 tensorrt-jp5 rk; do
|
||||
docker run --rm -v $HOME/.docker/config.json:/config.json quay.io/skopeo/stable:latest copy --authfile /config.json --multi-arch all docker://${PULL_TAG}-${variant} docker://${VERSION_TAG}-${variant}
|
||||
done
|
||||
@@ -2,3 +2,5 @@
|
||||
/docker/tensorrt/ @madsciencetist @NateMeyer
|
||||
/docker/tensorrt/*arm64* @madsciencetist
|
||||
/docker/tensorrt/*jetson* @madsciencetist
|
||||
|
||||
/docker/rockchip/ @MarcA711
|
||||
|
||||
2
Makefile
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
default_target: local
|
||||
|
||||
COMMIT_HASH := $(shell git log -1 --pretty=format:"%h"|tail -1)
|
||||
VERSION = 0.13.0
|
||||
VERSION = 0.13.2
|
||||
IMAGE_REPO ?= ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate
|
||||
GITHUB_REF_NAME ?= $(shell git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD)
|
||||
CURRENT_UID := $(shell id -u)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,13 +14,14 @@ services:
|
||||
dockerfile: docker/main/Dockerfile
|
||||
# Use target devcontainer-trt for TensorRT dev
|
||||
target: devcontainer
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
resources:
|
||||
reservations:
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- driver: nvidia
|
||||
count: 1
|
||||
capabilities: [gpu]
|
||||
## Uncomment this block for nvidia gpu support
|
||||
# deploy:
|
||||
# resources:
|
||||
# reservations:
|
||||
# devices:
|
||||
# - driver: nvidia
|
||||
# count: 1
|
||||
# capabilities: [gpu]
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
YOLO_MODELS: yolov7-320
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ RUN --mount=type=tmpfs,target=/tmp --mount=type=tmpfs,target=/var/cache/apt \
|
||||
FROM scratch AS go2rtc
|
||||
ARG TARGETARCH
|
||||
WORKDIR /rootfs/usr/local/go2rtc/bin
|
||||
ADD --link --chmod=755 "https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/releases/download/v1.8.1/go2rtc_linux_${TARGETARCH}" go2rtc
|
||||
ADD --link --chmod=755 "https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/releases/download/v1.8.4/go2rtc_linux_${TARGETARCH}" go2rtc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
####
|
||||
@@ -215,13 +215,13 @@ COPY docker/main/fake_frigate_run /etc/s6-overlay/s6-rc.d/frigate/run
|
||||
RUN mkdir -p /opt/frigate \
|
||||
&& ln -svf /workspace/frigate/frigate /opt/frigate/frigate
|
||||
|
||||
# Install Node 16
|
||||
RUN apt-get update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install wget -y \
|
||||
&& wget -qO- https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_16.x | bash - \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y nodejs \
|
||||
# Install Node 20
|
||||
RUN curl -SLO https://deb.nodesource.com/nsolid_setup_deb.sh && \
|
||||
chmod 500 nsolid_setup_deb.sh && \
|
||||
./nsolid_setup_deb.sh 20 && \
|
||||
apt-get install nodejs -y \
|
||||
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* \
|
||||
&& npm install -g npm@9
|
||||
&& npm install -g npm@10
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /workspace/frigate
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
set -euxo pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
NGINX_VERSION="1.25.2"
|
||||
NGINX_VERSION="1.25.3"
|
||||
VOD_MODULE_VERSION="1.31"
|
||||
SECURE_TOKEN_MODULE_VERSION="1.5"
|
||||
RTMP_MODULE_VERSION="1.2.2"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1 @@
|
||||
black == 23.10.*
|
||||
isort
|
||||
ruff
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,9 +13,9 @@ psutil == 5.9.*
|
||||
pydantic == 1.10.*
|
||||
git+https://github.com/fbcotter/py3nvml#egg=py3nvml
|
||||
PyYAML == 6.0.*
|
||||
pytz == 2023.3
|
||||
ruamel.yaml == 0.17.*
|
||||
tzlocal == 5.1
|
||||
pytz == 2023.3.post1
|
||||
ruamel.yaml == 0.18.*
|
||||
tzlocal == 5.2
|
||||
types-PyYAML == 6.0.*
|
||||
requests == 2.31.*
|
||||
types-requests == 2.31.*
|
||||
@@ -23,6 +23,7 @@ scipy == 1.11.*
|
||||
norfair == 2.2.*
|
||||
setproctitle == 1.3.*
|
||||
ws4py == 0.5.*
|
||||
unidecode == 1.3.*
|
||||
# Openvino Library - Custom built with MYRIAD support
|
||||
openvino @ https://github.com/NateMeyer/openvino-wheels/releases/download/multi-arch_2022.3.1/openvino-2022.3.1-1-cp39-cp39-manylinux_2_31_x86_64.whl; platform_machine == 'x86_64'
|
||||
openvino @ https://github.com/NateMeyer/openvino-wheels/releases/download/multi-arch_2022.3.1/openvino-2022.3.1-1-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl; platform_machine == 'aarch64'
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,8 +45,13 @@ function get_ip_and_port_from_supervisor() {
|
||||
|
||||
export LIBAVFORMAT_VERSION_MAJOR=$(ffmpeg -version | grep -Po 'libavformat\W+\K\d+')
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -f "/dev/shm/go2rtc.yaml" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "[INFO] Removing stale config from last run..."
|
||||
rm /dev/shm/go2rtc.yaml
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ ! -f "/dev/shm/go2rtc.yaml" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "[INFO] Preparing go2rtc config..."
|
||||
echo "[INFO] Preparing new go2rtc config..."
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -n "${SUPERVISOR_TOKEN:-}" ]]; then
|
||||
# Running as a Home Assistant add-on, infer the IP address and port
|
||||
@@ -54,6 +59,8 @@ if [[ ! -f "/dev/shm/go2rtc.yaml" ]]; then
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
python3 /usr/local/go2rtc/create_config.py
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "[WARNING] Unable to remove existing go2rtc config. Changes made to your frigate config file may not be recognized. Please remove the /dev/shm/go2rtc.yaml from your docker host manually."
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
readonly config_path="/config"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import yaml
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,6 +17,14 @@ sys.path.remove("/opt/frigate")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
FRIGATE_ENV_VARS = {k: v for k, v in os.environ.items() if k.startswith("FRIGATE_")}
|
||||
# read docker secret files as env vars too
|
||||
if os.path.isdir("/run/secrets"):
|
||||
for secret_file in os.listdir("/run/secrets"):
|
||||
if secret_file.startswith("FRIGATE_"):
|
||||
FRIGATE_ENV_VARS[secret_file] = Path(
|
||||
os.path.join("/run/secrets", secret_file)
|
||||
).read_text()
|
||||
|
||||
config_file = os.environ.get("CONFIG_FILE", "/config/config.yml")
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if we can use .yaml instead of .yml
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +58,15 @@ if go2rtc_config.get("log") is None:
|
||||
elif go2rtc_config["log"].get("format") is None:
|
||||
go2rtc_config["log"]["format"] = "text"
|
||||
|
||||
if not go2rtc_config.get("webrtc", {}).get("candidates", []):
|
||||
# ensure there is a default webrtc config
|
||||
if not go2rtc_config.get("webrtc"):
|
||||
go2rtc_config["webrtc"] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# go2rtc should listen on 8555 tcp & udp by default
|
||||
if not go2rtc_config["webrtc"].get("listen"):
|
||||
go2rtc_config["webrtc"]["listen"] = ":8555"
|
||||
|
||||
if not go2rtc_config["webrtc"].get("candidates", []):
|
||||
default_candidates = []
|
||||
# use internal candidate if it was discovered when running through the add-on
|
||||
internal_candidate = os.environ.get(
|
||||
@@ -96,6 +113,20 @@ if int(os.environ["LIBAVFORMAT_VERSION_MAJOR"]) < 59:
|
||||
"rtsp"
|
||||
] = "-fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -stimeout 5000000 -user_agent go2rtc/ffmpeg -rtsp_transport tcp -i {input}"
|
||||
|
||||
# add hardware acceleration presets for rockchip devices
|
||||
# may be removed if frigate uses a go2rtc version that includes these presets
|
||||
if go2rtc_config.get("ffmpeg") is None:
|
||||
go2rtc_config["ffmpeg"] = {
|
||||
"h264/rk": "-c:v h264_rkmpp_encoder -g 50 -bf 0",
|
||||
"h265/rk": "-c:v hevc_rkmpp_encoder -g 50 -bf 0",
|
||||
}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if go2rtc_config["ffmpeg"].get("h264/rk") is None:
|
||||
go2rtc_config["ffmpeg"]["h264/rk"] = "-c:v h264_rkmpp_encoder -g 50 -bf 0"
|
||||
|
||||
if go2rtc_config["ffmpeg"].get("h265/rk") is None:
|
||||
go2rtc_config["ffmpeg"]["h265/rk"] = "-c:v hevc_rkmpp_encoder -g 50 -bf 0"
|
||||
|
||||
for name in go2rtc_config.get("streams", {}):
|
||||
stream = go2rtc_config["streams"][name]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,6 +10,8 @@ events {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
http {
|
||||
map_hash_bucket_size 256;
|
||||
|
||||
include mime.types;
|
||||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,6 +34,13 @@ http {
|
||||
gzip_proxied no-cache no-store private expired auth;
|
||||
gzip_vary on;
|
||||
|
||||
proxy_cache_path /dev/shm/nginx_cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=api_cache:10m max_size=10m inactive=1m use_temp_path=off;
|
||||
|
||||
map $sent_http_content_type $should_not_cache {
|
||||
'application/json' 0;
|
||||
default 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
upstream frigate_api {
|
||||
server 127.0.0.1:5001;
|
||||
keepalive 1024;
|
||||
@@ -157,19 +166,47 @@ http {
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location /live/mse/ {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/;
|
||||
# frigate lovelace card uses this path
|
||||
location /live/mse/api/ws {
|
||||
limit_except GET {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/api/ws;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location /live/webrtc/ {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/;
|
||||
location /live/webrtc/api/ws {
|
||||
limit_except GET {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/api/ws;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location ~* /api/go2rtc([/]?.*)$ {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc;
|
||||
rewrite ^/api/go2rtc(.*)$ /api$1 break;
|
||||
# pass through go2rtc player
|
||||
location /live/webrtc/webrtc.html {
|
||||
limit_except GET {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/webrtc.html;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# frontend uses this to fetch the version
|
||||
location /api/go2rtc/api {
|
||||
limit_except GET {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/api;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# integration uses this to add webrtc candidate
|
||||
location /api/go2rtc/webrtc {
|
||||
limit_except POST {
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
proxy_pass http://go2rtc/api/webrtc;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -185,6 +222,20 @@ http {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://frigate_api/;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
|
||||
proxy_cache api_cache;
|
||||
proxy_cache_lock on;
|
||||
proxy_cache_use_stale updating;
|
||||
proxy_cache_valid 200 5s;
|
||||
proxy_cache_bypass $http_x_cache_bypass;
|
||||
proxy_no_cache $should_not_cache;
|
||||
add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status;
|
||||
|
||||
location /api/vod/ {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://frigate_api/vod/;
|
||||
include proxy.conf;
|
||||
proxy_cache off;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location /api/stats {
|
||||
access_log off;
|
||||
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ $1 break;
|
||||
@@ -240,4 +291,4 @@ rtmp {
|
||||
meta copy;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
32
docker/rockchip/Dockerfile
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1.6
|
||||
|
||||
# https://askubuntu.com/questions/972516/debian-frontend-environment-variable
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
FROM wheels as rk-wheels
|
||||
COPY docker/main/requirements-wheels.txt /requirements-wheels.txt
|
||||
COPY docker/rockchip/requirements-wheels-rk.txt /requirements-wheels-rk.txt
|
||||
RUN sed -i "/https:\/\//d" /requirements-wheels.txt
|
||||
RUN pip3 wheel --wheel-dir=/rk-wheels -c /requirements-wheels.txt -r /requirements-wheels-rk.txt
|
||||
|
||||
FROM deps AS rk-deps
|
||||
ARG TARGETARCH
|
||||
|
||||
RUN --mount=type=bind,from=rk-wheels,source=/rk-wheels,target=/deps/rk-wheels \
|
||||
pip3 install -U /deps/rk-wheels/*.whl
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /opt/frigate/
|
||||
COPY --from=rootfs / /
|
||||
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknpu2/releases/download/v1.5.2/librknnrt_rk356x.so /usr/lib/
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknpu2/releases/download/v1.5.2/librknnrt_rk3588.so /usr/lib/
|
||||
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases/download/v1.5.2-rk3562/yolov8n-320x320-rk3562.rknn /models/rknn/
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases/download/v1.5.2-rk3566/yolov8n-320x320-rk3566.rknn /models/rknn/
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases/download/v1.5.2-rk3568/yolov8n-320x320-rk3568.rknn /models/rknn/
|
||||
ADD https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases/download/v1.5.2-rk3588/yolov8n-320x320-rk3588.rknn /models/rknn/
|
||||
|
||||
RUN rm -rf /usr/lib/btbn-ffmpeg/bin/ffmpeg
|
||||
RUN rm -rf /usr/lib/btbn-ffmpeg/bin/ffprobe
|
||||
ADD --chmod=111 https://github.com/MarcA711/Rockchip-FFmpeg-Builds/releases/download/6.0-1/ffmpeg /usr/lib/btbn-ffmpeg/bin/
|
||||
ADD --chmod=111 https://github.com/MarcA711/Rockchip-FFmpeg-Builds/releases/download/6.0-1/ffprobe /usr/lib/btbn-ffmpeg/bin/
|
||||
2
docker/rockchip/requirements-wheels-rk.txt
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
hide-warnings == 0.17
|
||||
rknn-toolkit-lite2 @ https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-toolkit2/releases/download/v1.5.2/rknn_toolkit_lite2-1.5.2-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl
|
||||
34
docker/rockchip/rk.hcl
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
target wget {
|
||||
dockerfile = "docker/main/Dockerfile"
|
||||
platforms = ["linux/arm64"]
|
||||
target = "wget"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
target wheels {
|
||||
dockerfile = "docker/main/Dockerfile"
|
||||
platforms = ["linux/arm64"]
|
||||
target = "wheels"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
target deps {
|
||||
dockerfile = "docker/main/Dockerfile"
|
||||
platforms = ["linux/arm64"]
|
||||
target = "deps"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
target rootfs {
|
||||
dockerfile = "docker/main/Dockerfile"
|
||||
platforms = ["linux/arm64"]
|
||||
target = "rootfs"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
target rk {
|
||||
dockerfile = "docker/rockchip/Dockerfile"
|
||||
contexts = {
|
||||
wget = "target:wget",
|
||||
wheels = "target:wheels",
|
||||
deps = "target:deps",
|
||||
rootfs = "target:rootfs"
|
||||
}
|
||||
platforms = ["linux/arm64"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
10
docker/rockchip/rk.mk
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
BOARDS += rk
|
||||
|
||||
local-rk: version
|
||||
docker buildx bake --load --file=docker/rockchip/rk.hcl --set rk.tags=frigate:latest-rk rk
|
||||
|
||||
build-rk: version
|
||||
docker buildx bake --file=docker/rockchip/rk.hcl --set rk.tags=$(IMAGE_REPO):${GITHUB_REF_NAME}-$(COMMIT_HASH)-rk rk
|
||||
|
||||
push-rk: build-rk
|
||||
docker buildx bake --push --file=docker/rockchip/rk.hcl --set rk.tags=$(IMAGE_REPO):${GITHUB_REF_NAME}-$(COMMIT_HASH)-rk rk
|
||||
@@ -23,8 +23,8 @@ else
|
||||
fi
|
||||
tar xaf jetson_multimedia_api.tbz2 -C / && rm jetson_multimedia_api.tbz2
|
||||
|
||||
wget -q https://github.com/madsciencetist/jetson-ffmpeg/archive/refs/heads/master.zip
|
||||
unzip master.zip && rm master.zip && cd jetson-ffmpeg-master
|
||||
wget -q https://github.com/AndBobsYourUncle/jetson-ffmpeg/archive/9c17b09.zip -O jetson-ffmpeg.zip
|
||||
unzip jetson-ffmpeg.zip && rm jetson-ffmpeg.zip && mv jetson-ffmpeg-* jetson-ffmpeg && cd jetson-ffmpeg
|
||||
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$(pwd)/stubs:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH # tegra multimedia libs aren't available in image, so use stubs for ffmpeg build
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ cd ../ && rm -rf nv-codec-headers-master
|
||||
# Build ffmpeg with nvmpi patch
|
||||
wget -q https://ffmpeg.org/releases/ffmpeg-6.0.tar.xz
|
||||
tar xaf ffmpeg-*.tar.xz && rm ffmpeg-*.tar.xz && cd ffmpeg-*
|
||||
patch -p1 < ../jetson-ffmpeg-master/ffmpeg_patches/ffmpeg6.0_nvmpi.patch
|
||||
patch -p1 < ../jetson-ffmpeg/ffmpeg_patches/ffmpeg6.0_nvmpi.patch
|
||||
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$INSTALL_PREFIX/lib/pkgconfig
|
||||
# enable Jetson codecs but disable dGPU codecs
|
||||
./configure --cc='ccache gcc' --cxx='ccache g++' \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ NOTE: The folder that is mapped from the host needs to be the folder that contai
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom go2rtc version
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate currently includes go2rtc v1.8.1, there may be certain cases where you want to run a different version of go2rtc.
|
||||
Frigate currently includes go2rtc v1.8.4, there may be certain cases where you want to run a different version of go2rtc.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ First, set up a PTZ preset in your camera's firmware and give it a name. If you'
|
||||
|
||||
Edit your Frigate configuration file and enter the ONVIF parameters for your camera. Specify the object types to track, a required zone the object must enter to begin autotracking, and the camera preset name you configured in your camera's firmware to return to when tracking has ended. Optionally, specify a delay in seconds before Frigate returns the camera to the preset.
|
||||
|
||||
An [ONVIF connection](cameras.md) is required for autotracking to function.
|
||||
An [ONVIF connection](cameras.md) is required for autotracking to function. Also, a [motion mask](masks.md) over your camera's timestamp and any overlay text is recommended to ensure they are completely excluded from scene change calculations when the camera is moving.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `autotracking` is disabled by default but can be enabled in the configuration or by MQTT.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ If you initially calibrate with zooming disabled and then enable zooming at a la
|
||||
|
||||
Every PTZ camera is different, so autotracking may not perform ideally in every situation. This experimental feature was initially developed using an EmpireTech/Dahua SD1A404XB-GNR.
|
||||
|
||||
The object tracker in Frigate estimates the motion of the PTZ so that tracked objects are preserved when the camera moves. In most cases (especially for faster moving objects), the default 5 fps is insufficient for the motion estimator to perform accurately. 10 fps is the current recommendation. Higher frame rates will likely not be more performant and will only slow down Frigate and the motion estimator. Adjust your camera to output at least 10 frames per second and change the `fps` parameter in the [detect configuration](index.md) of your configuration file.
|
||||
The object tracker in Frigate estimates the motion of the PTZ so that tracked objects are preserved when the camera moves. In most cases 5 fps is sufficient, but if you plan to track faster moving objects, you may want to increase this slightly. Higher frame rates (> 10fps) will only slow down Frigate and the motion estimator and may lead to dropped frames, especially if you are using experimental zooming.
|
||||
|
||||
A fast [detector](object_detectors.md) is recommended. CPU detectors will not perform well or won't work at all. You can watch Frigate's debug viewer for your camera to see a thicker colored box around the object currently being autotracked.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# Birdseye
|
||||
|
||||
Birdseye allows a heads-up view of your cameras to see what is going on around your property / space without having to watch all cameras that may have nothing happening. Birdseye allows specific modes that intelligently show and disappear based on what you care about.
|
||||
Birdseye allows a heads-up view of your cameras to see what is going on around your property / space without having to watch all cameras that may have nothing happening. Birdseye allows specific modes that intelligently show and disappear based on what you care about.
|
||||
|
||||
## Birdseye Behavior
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Modes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,6 +36,29 @@ cameras:
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Inactivity
|
||||
|
||||
By default birdseye shows all cameras that have had the configured activity in the last 30 seconds, this can be configured:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
inactivity_threshold: 15
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Birdseye Layout
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Dimensions
|
||||
|
||||
The resolution and aspect ratio of birdseye can be configured. Resolution will increase the quality but does not affect the layout. Changing the aspect ratio of birdseye does affect how cameras are laid out.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Sorting cameras in the Birdseye view
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to override the order of cameras that are being shown in the Birdseye view.
|
||||
@@ -55,3 +80,27 @@ cameras:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*Note*: Cameras are sorted by default using their name to ensure a constant view inside Birdseye.
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Cameras
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to limit the number of cameras shown on birdseye at one time. When this is enabled, birdseye will show the cameras with most recent activity. There is a cooldown to ensure that cameras do not switch too frequently.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, this can be configured to only show the most recently active camera.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
layout:
|
||||
max_cameras: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Scaling
|
||||
|
||||
By default birdseye tries to fit 2 cameras in each row and then double in size until a suitable layout is found. The scaling can be configured with a value between 1.0 and 5.0 depending on use case.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
layout:
|
||||
scaling_factor: 3.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,6 +105,15 @@ If available, recommended settings are:
|
||||
|
||||
According to [this discussion](https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/issues/3235#issuecomment-1135876973), the http video streams seem to be the most reliable for Reolink.
|
||||
|
||||
Cameras connected via a Reolink NVR can be connected with the http stream, use `channel[0..15]` in the stream url for the additional channels.
|
||||
The setup of main stream can be also done via RTSP, but isn't always reliable on all hardware versions. The example configuration is working with the oldest HW version RLN16-410 device with multiple types of cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
The below configuration only works for reolink cameras with stream resolution of 5MP or lower, 8MP+ cameras need to use RTSP as http-flv is not supported in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
streams:
|
||||
@@ -112,6 +121,11 @@ go2rtc:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel0_main.bcs&user=username&password=password#video=copy#audio=copy#audio=opus"
|
||||
your_reolink_camera_sub:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel0_ext.bcs&user=username&password=password"
|
||||
your_reolink_camera_via_nvr:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_nvr_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel3_main.bcs&user=username&password=password" # channel numbers are 0-15
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:your_reolink_camera_via_nvr#audio=aac"
|
||||
your_reolink_camera_via_nvr_sub:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_nvr_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel3_ext.bcs&user=username&password=password"
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
your_reolink_camera:
|
||||
@@ -125,6 +139,31 @@ cameras:
|
||||
input_args: preset-rtsp-restream
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
reolink_via_nvr:
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://127.0.0.1:8554/your_reolink_camera_via_nvr?video=copy&audio=aac
|
||||
input_args: preset-rtsp-restream
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- path: rtsp://127.0.0.1:8554/your_reolink_camera_via_nvr_sub?video=copy
|
||||
input_args: preset-rtsp-restream
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Reolink Doorbell
|
||||
|
||||
The reolink doorbell supports 2-way audio via go2rtc and other applications. It is important that the http-flv stream is still used for stability, a secondary rtsp stream can be added that will be using for the two way audio only.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
streams:
|
||||
your_reolink_doorbell:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel0_main.bcs&user=username&password=password#video=copy#audio=copy#audio=opus"
|
||||
- rtsp://reolink_ip/Preview_01_sub
|
||||
your_reolink_doorbell_sub:
|
||||
- "ffmpeg:http://reolink_ip/flv?port=1935&app=bcs&stream=channel0_ext.bcs&user=username&password=password"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Unifi Protect Cameras
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +179,7 @@ go2rtc:
|
||||
- rtspx://192.168.1.1:7441/abcdefghijk
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[See the go2rtc docs for more information](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#source-rtsp)
|
||||
[See the go2rtc docs for more information](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#source-rtsp)
|
||||
|
||||
In the Unifi 2.0 update Unifi Protect Cameras had a change in audio sample rate which causes issues for ffmpeg. The input rate needs to be set for record and rtmp if used directly with unifi protect.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -90,6 +90,7 @@ This list of working and non-working PTZ cameras is based on user feedback.
|
||||
| Reolink 511WA | ✅ | ❌ | Zoom only |
|
||||
| Reolink E1 Pro | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| Reolink E1 Zoom | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| Reolink RLC-823A 16x | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| Sunba 405-D20X | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| Tapo C200 | ✅ | ❌ | Incomplete ONVIF support |
|
||||
| Tapo C210 | ❌ | ❌ | Incomplete ONVIF support |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,8 +13,8 @@ See [the hwaccel docs](/configuration/hardware_acceleration.md) for more info on
|
||||
|
||||
| Preset | Usage | Other Notes |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| preset-rpi-32-h264 | 32 bit Rpi with h264 stream | |
|
||||
| preset-rpi-64-h264 | 64 bit Rpi with h264 stream | |
|
||||
| preset-rpi-64-h265 | 64 bit Rpi with h265 stream | |
|
||||
| preset-vaapi | Intel & AMD VAAPI | Check hwaccel docs to ensure correct driver is chosen |
|
||||
| preset-intel-qsv-h264 | Intel QSV with h264 stream | If issues occur recommend using vaapi preset instead |
|
||||
| preset-intel-qsv-h265 | Intel QSV with h265 stream | If issues occur recommend using vaapi preset instead |
|
||||
@@ -23,6 +23,8 @@ See [the hwaccel docs](/configuration/hardware_acceleration.md) for more info on
|
||||
| preset-nvidia-mjpeg | Nvidia GPU with mjpeg stream | Recommend restreaming mjpeg and using nvidia-h264 |
|
||||
| preset-jetson-h264 | Nvidia Jetson with h264 stream | |
|
||||
| preset-jetson-h265 | Nvidia Jetson with h265 stream | |
|
||||
| preset-rk-h264 | Rockchip MPP with h264 stream | Use image with *-rk suffix and privileged mode |
|
||||
| preset-rk-h265 | Rockchip MPP with h265 stream | Use image with *-rk suffix and privileged mode |
|
||||
|
||||
### Input Args Presets
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -74,8 +76,8 @@ Output args presets help make the config more readable and handle use cases for
|
||||
| Preset | Usage | Other Notes |
|
||||
| -------------------------------- | --------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| preset-record-generic | Record WITHOUT audio | This is the default when nothing is specified |
|
||||
| preset-record-generic-audio-aac | Record WITH aac audio | Use this to enable audio in recordings |
|
||||
| preset-record-generic-audio-copy | Record WITH original audio | Use this to enable audio in recordings |
|
||||
| preset-record-generic-audio-aac | Record WITH transcoded aac audio | Use this to transcode to aac audio. If your source is already aac, use preset-record-generic-audio-copy instead to avoid re-encoding |
|
||||
| preset-record-mjpeg | Record an mjpeg stream | Recommend restreaming mjpeg stream instead |
|
||||
| preset-record-jpeg | Record live jpeg | Recommend restreaming live jpeg instead |
|
||||
| preset-record-ubiquiti | Record ubiquiti stream with audio | Recordings with ubiquiti non-standard audio |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,32 +3,62 @@ id: hardware_acceleration
|
||||
title: Hardware Acceleration
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Hardware Acceleration
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to update your configuration to enable hardware accelerated decoding in ffmpeg. Depending on your system, these parameters may not be compatible. More information on hardware accelerated decoding for ffmpeg can be found here: https://trac.ffmpeg.org/wiki/HWAccelIntro
|
||||
|
||||
# Officially Supported
|
||||
|
||||
## Raspberry Pi 3/4
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you increase the allocated RAM for your GPU to at least 128 (raspi-config > Performance Options > GPU Memory).
|
||||
**NOTICE**: If you are using the addon, you may need to turn off `Protection mode` for hardware acceleration.
|
||||
Ensure you increase the allocated RAM for your GPU to at least 128 (`raspi-config` > Performance Options > GPU Memory).
|
||||
If you are using the HA addon, you may need to use the full access variant and turn off `Protection mode` for hardware acceleration.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# if you want to decode a h264 stream
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-rpi-64-h264
|
||||
|
||||
# if you want to decode a h265 (hevc) stream
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-rpi-64-h265
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
If running Frigate in docker, you either need to run in priviliged mode or be sure to map the /dev/video1x devices to Frigate
|
||||
If running Frigate in Docker, you either need to run in privileged mode or
|
||||
map the `/dev/video*` devices to Frigate. With Docker compose add:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
services:
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
...
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/video11:/dev/video11
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or with `docker run`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -d \
|
||||
--name frigate \
|
||||
...
|
||||
--device /dev/video10 \
|
||||
--device /dev/video11 \
|
||||
ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`/dev/video11` is the correct device (on Raspberry Pi 4B). You can check
|
||||
by running the following and looking for `H264`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
for d in /dev/video*; do
|
||||
echo -e "---\n$d"
|
||||
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext -d $d
|
||||
done
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or map in all the `/dev/video*` devices.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Intel-based CPUs
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +72,11 @@ ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-vaapi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTICE**: With some of the processors, like the J4125, the default driver `iHD` doesn't seem to work correctly for hardware acceleration. You may need to change the driver to `i965` by adding the following environment variable `LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=i965` to your docker-compose file or [in the `frigate.yaml` for HA OS users](advanced.md#environment_vars).
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
With some of the processors, like the J4125, the default driver `iHD` doesn't seem to work correctly for hardware acceleration. You may need to change the driver to `i965` by adding the following environment variable `LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=i965` to your docker-compose file or [in the `frigate.yaml` for HA OS users](advanced.md#environment_vars).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Via Quicksync (>=10th Generation only)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -130,7 +164,11 @@ Depending on your OS and kernel configuration, you may need to change the `/proc
|
||||
|
||||
VAAPI supports automatic profile selection so it will work automatically with both H.264 and H.265 streams.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** You also need to set `LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=radeonsi` as an environment variable on the container.
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
You need to change the driver to `radeonsi` by adding the following environment variable `LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=radeonsi` to your docker-compose file or [in the `frigate.yaml` for HA OS users](advanced.md#environment_vars).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
@@ -246,7 +284,7 @@ These instructions were originally based on the [Jellyfin documentation](https:/
|
||||
|
||||
# Community Supported
|
||||
|
||||
## NVIDIA Jetson (Orin AGX, Orin NX, Orin Nano*, Xavier AGX, Xavier NX, TX2, TX1, Nano)
|
||||
## NVIDIA Jetson (Orin AGX, Orin NX, Orin Nano\*, Xavier AGX, Xavier NX, TX2, TX1, Nano)
|
||||
|
||||
A separate set of docker images is available that is based on Jetpack/L4T. They comes with an `ffmpeg` build
|
||||
with codecs that use the Jetson's dedicated media engine. If your Jetson host is running Jetpack 4.6, use the
|
||||
@@ -319,3 +357,57 @@ ffmpeg:
|
||||
If everything is working correctly, you should see a significant reduction in ffmpeg CPU load and power consumption.
|
||||
Verify that hardware decoding is working by running `jtop` (`sudo pip3 install -U jetson-stats`), which should show
|
||||
that NVDEC/NVDEC1 are in use.
|
||||
|
||||
## Rockchip platform
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware accelerated video de-/encoding is supported on all Rockchip SoCs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Use a frigate docker image with `-rk` suffix and enable privileged mode by adding the `--privileged` flag to your docker run command or `privileged: true` to your `docker-compose.yml` file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Add one of the following ffmpeg presets to your `config.yaml` to enable hardware acceleration:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# if you try to decode a h264 encoded stream
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-rk-h264
|
||||
|
||||
# if you try to decode a h265 (hevc) encoded stream
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-rk-h265
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that your SoC supports hardware acceleration for your input stream. For example, if your camera streams with h265 encoding and a 4k resolution, your SoC must be able to de- and encode h265 with a 4k resolution or higher. If you are unsure whether your SoC meets the requirements, take a look at the datasheet.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### go2rtc presets for hardware accelerated transcoding
|
||||
|
||||
If your input stream is to be transcoded using hardware acceleration, there are these presets for go2rtc: `h264/rk` and `h265/rk`. You can use them this way:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
streams:
|
||||
Cam_h264: ffmpeg:rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0#video=h264/rk
|
||||
Cam_h265: ffmpeg:rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0#video=h265/rk
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
||||
The go2rtc docs may suggest the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
streams:
|
||||
Cam_h264: ffmpeg:rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0#video=h264#hardware=rk
|
||||
Cam_h265: ffmpeg:rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0#video=h265#hardware=rk
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, this does not currently work.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,46 +1,35 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: index
|
||||
title: Frigate Configuration Reference
|
||||
title: Frigate Configuration
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
For Home Assistant Addon installations, the config file needs to be in the root of your Home Assistant config directory (same location as `configuration.yaml`). It can be named `frigate.yaml` or `frigate.yml`, but if both files exist `frigate.yaml` will be preferred and `frigate.yml` will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
For all other installation types, the config file should be mapped to `/config/config.yml` inside the container.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to start with a minimal configuration and add to it as described in [this guide](../guides/getting_started.md):
|
||||
It is recommended to start with a minimal configuration and add to it as described in [this guide](../guides/getting_started.md) and use the built in configuration editor in Frigate's UI which supports validation.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
host: mqtt.server.com
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
back:
|
||||
dummy_camera: # <--- this will be changed to your actual camera later
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://viewer:{FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD}@10.0.10.10:554/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=2
|
||||
- path: rtsp://127.0.0.1:554/rtsp
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### VSCode Configuration Schema
|
||||
## VSCode Configuration Schema
|
||||
|
||||
VSCode (and VSCode addon) supports the JSON schemas which will automatically validate the config. This can be added by adding `# yaml-language-server: $schema=http://frigate_host:5000/api/config/schema.json` to the top of the config file. `frigate_host` being the IP address of Frigate or `ccab4aaf-frigate` if running in the addon.
|
||||
VSCode supports JSON schemas for automatically validating configuration files. You can enable this feature by adding `# yaml-language-server: $schema=http://frigate_host:5000/api/config/schema.json` to the beginning of the configuration file. Replace `frigate_host` with the IP address or hostname of your Frigate server. If you're using both VSCode and Frigate as an add-on, you should use `ccab4aaf-frigate` instead. Make sure to expose port `5000` for the Web Interface when accessing the config from VSCode on another machine.
|
||||
|
||||
### Full configuration reference:
|
||||
## Environment Variable Substitution
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
It is not recommended to copy this full configuration file. Only specify values that are different from the defaults. Configuration options and default values may change in future versions.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The following values will be replaced at runtime by using environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
- `{FRIGATE_MQTT_USER}`
|
||||
- `{FRIGATE_MQTT_PASSWORD}`
|
||||
- `{FRIGATE_RTSP_USER}`
|
||||
- `{FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD}`
|
||||
|
||||
for example:
|
||||
Frigate supports the use of environment variables starting with `FRIGATE_` **only** where specifically indicated in the [reference config](./reference.md). For example, the following values can be replaced at runtime by using environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
@@ -61,617 +50,187 @@ onvif:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable mqtt server (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Required: host name
|
||||
host: mqtt.server.com
|
||||
# Optional: port (default: shown below)
|
||||
port: 1883
|
||||
# Optional: topic prefix (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: must be unique if you are running multiple instances
|
||||
topic_prefix: frigate
|
||||
# Optional: client id (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: must be unique if you are running multiple instances
|
||||
client_id: frigate
|
||||
# Optional: user
|
||||
# NOTE: MQTT user can be specified with an environment variables that must begin with 'FRIGATE_'.
|
||||
# e.g. user: '{FRIGATE_MQTT_USER}'
|
||||
user: mqtt_user
|
||||
# Optional: password
|
||||
# NOTE: MQTT password can be specified with an environment variables that must begin with 'FRIGATE_'.
|
||||
# e.g. password: '{FRIGATE_MQTT_PASSWORD}'
|
||||
password: password
|
||||
# Optional: tls_ca_certs for enabling TLS using self-signed certs (default: None)
|
||||
tls_ca_certs: /path/to/ca.crt
|
||||
# Optional: tls_client_cert and tls_client key in order to use self-signed client
|
||||
# certificates (default: None)
|
||||
# NOTE: certificate must not be password-protected
|
||||
# do not set user and password when using a client certificate
|
||||
tls_client_cert: /path/to/client.crt
|
||||
tls_client_key: /path/to/client.key
|
||||
# Optional: tls_insecure (true/false) for enabling TLS verification of
|
||||
# the server hostname in the server certificate (default: None)
|
||||
tls_insecure: false
|
||||
# Optional: interval in seconds for publishing stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
stats_interval: 60
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Detectors configuration. Defaults to a single CPU detector
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
# Required: name of the detector
|
||||
detector_name:
|
||||
# Required: type of the detector
|
||||
# Frigate provided types include 'cpu', 'edgetpu', 'openvino' and 'tensorrt' (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Additional detector types can also be plugged in.
|
||||
# Detectors may require additional configuration.
|
||||
# Refer to the Detectors configuration page for more information.
|
||||
type: cpu
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Database configuration
|
||||
database:
|
||||
# The path to store the SQLite DB (default: shown below)
|
||||
path: /config/frigate.db
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: model modifications
|
||||
model:
|
||||
# Optional: path to the model (default: automatic based on detector)
|
||||
path: /edgetpu_model.tflite
|
||||
# Optional: path to the labelmap (default: shown below)
|
||||
labelmap_path: /labelmap.txt
|
||||
# Required: Object detection model input width (default: shown below)
|
||||
width: 320
|
||||
# Required: Object detection model input height (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 320
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model input colorspace
|
||||
# Valid values are rgb, bgr, or yuv. (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_pixel_format: rgb
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model input tensor format
|
||||
# Valid values are nhwc or nchw (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_tensor: nhwc
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model type, currently only used with the OpenVINO detector
|
||||
# Valid values are ssd, yolox, yolov5, or yolov8 (default: shown below)
|
||||
model_type: ssd
|
||||
# Optional: Label name modifications. These are merged into the standard labelmap.
|
||||
labelmap:
|
||||
2: vehicle
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Audio Events Configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
audio:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable audio events (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: Configure the amount of seconds without detected audio to end the event (default: shown below)
|
||||
max_not_heard: 30
|
||||
# Optional: Configure the min rms volume required to run audio detection (default: shown below)
|
||||
# As a rule of thumb:
|
||||
# - 200 - high sensitivity
|
||||
# - 500 - medium sensitivity
|
||||
# - 1000 - low sensitivity
|
||||
min_volume: 500
|
||||
# Optional: Types of audio to listen for (default: shown below)
|
||||
listen:
|
||||
- bark
|
||||
- fire_alarm
|
||||
- scream
|
||||
- speech
|
||||
- yell
|
||||
# Optional: Filters to configure detection.
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
# Label that matches label in listen config.
|
||||
speech:
|
||||
# Minimum score that triggers an audio event (default: shown below)
|
||||
threshold: 0.8
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: logger verbosity settings
|
||||
logger:
|
||||
# Optional: Default log verbosity (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: info
|
||||
# Optional: Component specific logger overrides
|
||||
logs:
|
||||
frigate.event: debug
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: set environment variables
|
||||
environment_vars:
|
||||
EXAMPLE_VAR: value
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: birdseye configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can (enabled, mode) be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable birdseye view (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: Restream birdseye via RTSP (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Enabling this will set birdseye to run 24/7 which may increase CPU usage somewhat.
|
||||
restream: False
|
||||
# Optional: Width of the output resolution (default: shown below)
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
# Optional: Height of the output resolution (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: Encoding quality of the mpeg1 feed (default: shown below)
|
||||
# 1 is the highest quality, and 31 is the lowest. Lower quality feeds utilize less CPU resources.
|
||||
quality: 8
|
||||
# Optional: Mode of the view. Available options are: objects, motion, and continuous
|
||||
# objects - cameras are included if they have had a tracked object within the last 30 seconds
|
||||
# motion - cameras are included if motion was detected in the last 30 seconds
|
||||
# continuous - all cameras are included always
|
||||
mode: objects
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: ffmpeg configuration
|
||||
# More information about presets at https://docs.frigate.video/configuration/ffmpeg_presets
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
# Optional: global ffmpeg args (default: shown below)
|
||||
global_args: -hide_banner -loglevel warning -threads 2
|
||||
# Optional: global hwaccel args (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: See hardware acceleration docs for your specific device
|
||||
hwaccel_args: []
|
||||
# Optional: global input args (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_args: preset-rtsp-generic
|
||||
# Optional: global output args
|
||||
output_args:
|
||||
# Optional: output args for detect streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
detect: -threads 2 -f rawvideo -pix_fmt yuv420p
|
||||
# Optional: output args for record streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
record: preset-record-generic
|
||||
# Optional: output args for rtmp streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
rtmp: preset-rtmp-generic
|
||||
# Optional: Time in seconds to wait before ffmpeg retries connecting to the camera. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# If set too low, frigate will retry a connection to the camera's stream too frequently, using up the limited streams some cameras can allow at once
|
||||
# If set too high, then if a ffmpeg crash or camera stream timeout occurs, you could potentially lose up to a maximum of retry_interval second(s) of footage
|
||||
# NOTE: this can be a useful setting for Wireless / Battery cameras to reduce how much footage is potentially lost during a connection timeout.
|
||||
retry_interval: 10
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Detect configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
detect:
|
||||
# Optional: width of the frame for the input with the detect role (default: shown below)
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
# Optional: height of the frame for the input with the detect role (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: desired fps for your camera for the input with the detect role (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Recommended value of 5. Ideally, try and reduce your FPS on the camera.
|
||||
fps: 5
|
||||
# Optional: enables detection for the camera (default: True)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: Number of frames without a detection before Frigate considers an object to be gone. (default: 5x the frame rate)
|
||||
max_disappeared: 25
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for stationary object tracking
|
||||
stationary:
|
||||
# Optional: Frequency for confirming stationary objects (default: same as threshold)
|
||||
# When set to 1, object detection will run to confirm the object still exists on every frame.
|
||||
# If set to 10, object detection will run to confirm the object still exists on every 10th frame.
|
||||
interval: 50
|
||||
# Optional: Number of frames without a position change for an object to be considered stationary (default: 10x the frame rate or 10s)
|
||||
threshold: 50
|
||||
# Optional: Define a maximum number of frames for tracking a stationary object (default: not set, track forever)
|
||||
# This can help with false positives for objects that should only be stationary for a limited amount of time.
|
||||
# It can also be used to disable stationary object tracking. For example, you may want to set a value for person, but leave
|
||||
# car at the default.
|
||||
# WARNING: Setting these values overrides default behavior and disables stationary object tracking.
|
||||
# There are very few situations where you would want it disabled. It is NOT recommended to
|
||||
# copy these values from the example config into your config unless you know they are needed.
|
||||
max_frames:
|
||||
# Optional: Default for all object types (default: not set, track forever)
|
||||
default: 3000
|
||||
# Optional: Object specific values
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 1000
|
||||
# Optional: Milliseconds to offset detect annotations by (default: shown below).
|
||||
# There can often be latency between a recording and the detect process,
|
||||
# especially when using separate streams for detect and record.
|
||||
# Use this setting to make the timeline bounding boxes more closely align
|
||||
# with the recording. The value can be positive or negative.
|
||||
# TIP: Imagine there is an event clip with a person walking from left to right.
|
||||
# If the event timeline bounding box is consistently to the left of the person
|
||||
# then the value should be decreased. Similarly, if a person is walking from
|
||||
# left to right and the bounding box is consistently ahead of the person
|
||||
# then the value should be increased.
|
||||
# TIP: This offset is dynamic so you can change the value and it will update existing
|
||||
# events, this makes it easy to tune.
|
||||
# WARNING: Fast moving objects will likely not have the bounding box align.
|
||||
annotation_offset: 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Object configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
# Optional: list of objects to track from labelmap.txt (default: shown below)
|
||||
track:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: mask to prevent all object types from being detected in certain areas (default: no mask)
|
||||
# Checks based on the bottom center of the bounding box of the object.
|
||||
# NOTE: This mask is COMBINED with the object type specific mask below
|
||||
mask: 0,0,1000,0,1000,200,0,200
|
||||
# Optional: filters to reduce false positives for specific object types
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
person:
|
||||
# Optional: minimum width*height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 0)
|
||||
min_area: 5000
|
||||
# Optional: maximum width*height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 24000000)
|
||||
max_area: 100000
|
||||
# Optional: minimum width/height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 0)
|
||||
min_ratio: 0.5
|
||||
# Optional: maximum width/height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 24000000)
|
||||
max_ratio: 2.0
|
||||
# Optional: minimum score for the object to initiate tracking (default: shown below)
|
||||
min_score: 0.5
|
||||
# Optional: minimum decimal percentage for tracked object's computed score to be considered a true positive (default: shown below)
|
||||
threshold: 0.7
|
||||
# Optional: mask to prevent this object type from being detected in certain areas (default: no mask)
|
||||
# Checks based on the bottom center of the bounding box of the object
|
||||
mask: 0,0,1000,0,1000,200,0,200
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Motion configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
# Optional: The threshold passed to cv2.threshold to determine if a pixel is different enough to be counted as motion. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection less sensitive and decreasing it will make motion detection more sensitive.
|
||||
# The value should be between 1 and 255.
|
||||
threshold: 30
|
||||
# Optional: The percentage of the image used to detect lightning or other substantial changes where motion detection
|
||||
# needs to recalibrate. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection more likely to consider lightning or ir mode changes as valid motion.
|
||||
# Decreasing this value will make motion detection more likely to ignore large amounts of motion such as a person approaching
|
||||
# a doorbell camera.
|
||||
lightning_threshold: 0.8
|
||||
# Optional: Minimum size in pixels in the resized motion image that counts as motion (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will prevent smaller areas of motion from being detected. Decreasing will
|
||||
# make motion detection more sensitive to smaller moving objects.
|
||||
# As a rule of thumb:
|
||||
# - 10 - high sensitivity
|
||||
# - 30 - medium sensitivity
|
||||
# - 50 - low sensitivity
|
||||
contour_area: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Alpha value passed to cv2.accumulateWeighted when averaging frames to determine the background (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Higher values mean the current frame impacts the average a lot, and a new object will be averaged into the background faster.
|
||||
# Low values will cause things like moving shadows to be detected as motion for longer.
|
||||
# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/background-subtraction-in-an-image-using-concept-of-running-average/
|
||||
frame_alpha: 0.01
|
||||
# Optional: Height of the resized motion frame (default: 100)
|
||||
# Higher values will result in more granular motion detection at the expense of higher CPU usage.
|
||||
# Lower values result in less CPU, but small changes may not register as motion.
|
||||
frame_height: 100
|
||||
# Optional: motion mask
|
||||
# NOTE: see docs for more detailed info on creating masks
|
||||
mask: 0,900,1080,900,1080,1920,0,1920
|
||||
# Optional: improve contrast (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Enables dynamic contrast improvement. This should help improve night detections at the cost of making motion detection more sensitive
|
||||
# for daytime.
|
||||
improve_contrast: True
|
||||
# Optional: Delay when updating camera motion through MQTT from ON -> OFF (default: shown below).
|
||||
mqtt_off_delay: 30
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Record configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
record:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable recording (default: shown below)
|
||||
# WARNING: If recording is disabled in the config, turning it on via
|
||||
# the UI or MQTT later will have no effect.
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: Number of minutes to wait between cleanup runs (default: shown below)
|
||||
# This can be used to reduce the frequency of deleting recording segments from disk if you want to minimize i/o
|
||||
expire_interval: 60
|
||||
# Optional: Sync recordings with disk on startup (default: shown below).
|
||||
sync_on_startup: False
|
||||
# Optional: Retention settings for recording
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Optional: Number of days to retain recordings regardless of events (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: This should be set to 0 and retention should be defined in events section below
|
||||
# if you only want to retain recordings of events.
|
||||
days: 0
|
||||
# Optional: Mode for retention. Available options are: all, motion, and active_objects
|
||||
# all - save all recording segments regardless of activity
|
||||
# motion - save all recordings segments with any detected motion
|
||||
# active_objects - save all recording segments with active/moving objects
|
||||
# NOTE: this mode only applies when the days setting above is greater than 0
|
||||
mode: all
|
||||
# Optional: Recording Export Settings
|
||||
export:
|
||||
# Optional: Timelapse Output Args (default: shown below).
|
||||
# NOTE: The default args are set to fit 24 hours of recording into 1 hour playback.
|
||||
# See https://stackoverflow.com/a/58268695 for more info on how these args work.
|
||||
# As an example: if you wanted to go from 24 hours to 30 minutes that would be going
|
||||
# from 86400 seconds to 1800 seconds which would be 1800 / 86400 = 0.02.
|
||||
# The -r (framerate) dictates how smooth the output video is.
|
||||
# So the args would be -vf setpts=0.02*PTS -r 30 in that case.
|
||||
timelapse_args: "-vf setpts=0.04*PTS -r 30"
|
||||
# Optional: Event recording settings
|
||||
events:
|
||||
# Optional: Number of seconds before the event to include (default: shown below)
|
||||
pre_capture: 5
|
||||
# Optional: Number of seconds after the event to include (default: shown below)
|
||||
post_capture: 5
|
||||
# Optional: Objects to save recordings for. (default: all tracked objects)
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict recordings to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
# Optional: Retention settings for recordings of events
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Required: Default retention days (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Mode for retention. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# all - save all recording segments for events regardless of activity
|
||||
# motion - save all recordings segments for events with any detected motion
|
||||
# active_objects - save all recording segments for event with active/moving objects
|
||||
#
|
||||
# NOTE: If the retain mode for the camera is more restrictive than the mode configured
|
||||
# here, the segments will already be gone by the time this mode is applied.
|
||||
# For example, if the camera retain mode is "motion", the segments without motion are
|
||||
# never stored, so setting the mode to "all" here won't bring them back.
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
# Optional: Per object retention days
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 15
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for the jpg snapshots written to the clips directory for each event
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
snapshots:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable writing jpg snapshot to /media/frigate/clips (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: save a clean PNG copy of the snapshot image (default: shown below)
|
||||
clean_copy: True
|
||||
# Optional: print a timestamp on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
timestamp: False
|
||||
# Optional: draw bounding box on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
bounding_box: False
|
||||
# Optional: crop the snapshot (default: shown below)
|
||||
crop: False
|
||||
# Optional: height to resize the snapshot to (default: original size)
|
||||
height: 175
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict snapshots to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
# Optional: Camera override for retention settings (default: global values)
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Required: Default retention days (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Per object retention days
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 15
|
||||
# Optional: quality of the encoded jpeg, 0-100 (default: shown below)
|
||||
quality: 70
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: RTMP configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: RTMP is deprecated in favor of restream
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
rtmp:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable the RTMP stream (default: False)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Restream configuration
|
||||
# Uses https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc (v1.8.1)
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: jsmpeg stream configuration for WebUI
|
||||
live:
|
||||
# Optional: Set the name of the stream that should be used for live view
|
||||
# in frigate WebUI. (default: name of camera)
|
||||
stream_name: camera_name
|
||||
# Optional: Set the height of the jsmpeg stream. (default: 720)
|
||||
# This must be less than or equal to the height of the detect stream. Lower resolutions
|
||||
# reduce bandwidth required for viewing the jsmpeg stream. Width is computed to match known aspect ratio.
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: Set the encode quality of the jsmpeg stream (default: shown below)
|
||||
# 1 is the highest quality, and 31 is the lowest. Lower quality feeds utilize less CPU resources.
|
||||
quality: 8
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: in-feed timestamp style configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
timestamp_style:
|
||||
# Optional: Position of the timestamp (default: shown below)
|
||||
# "tl" (top left), "tr" (top right), "bl" (bottom left), "br" (bottom right)
|
||||
position: "tl"
|
||||
# Optional: Format specifier conform to the Python package "datetime" (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Additional Examples:
|
||||
# german: "%d.%m.%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
format: "%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
# Optional: Color of font
|
||||
color:
|
||||
# All Required when color is specified (default: shown below)
|
||||
red: 255
|
||||
green: 255
|
||||
blue: 255
|
||||
# Optional: Line thickness of font (default: shown below)
|
||||
thickness: 2
|
||||
# Optional: Effect of lettering (default: shown below)
|
||||
# None (No effect),
|
||||
# "solid" (solid background in inverse color of font)
|
||||
# "shadow" (shadow for font)
|
||||
effect: None
|
||||
|
||||
# Required
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
# Required: name of the camera
|
||||
back:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable/Disable the camera (default: shown below).
|
||||
# If disabled: config is used but no live stream and no capture etc.
|
||||
# Events/Recordings are still viewable.
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Required: ffmpeg settings for the camera
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
# Required: A list of input streams for the camera. See documentation for more information.
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
# Required: the path to the stream
|
||||
# NOTE: path may include environment variables, which must begin with 'FRIGATE_' and be referenced in {}
|
||||
- path: rtsp://viewer:{FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD}@10.0.10.10:554/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=2
|
||||
# Required: list of roles for this stream. valid values are: audio,detect,record,rtmp
|
||||
# NOTICE: In addition to assigning the audio, record, and rtmp roles,
|
||||
# they must also be enabled in the camera config.
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- audio
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- rtmp
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific global args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# global_args:
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific hwaccel args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# hwaccel_args:
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific input args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# input_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific global args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# global_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific hwaccel args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# hwaccel_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific input args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# input_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific output args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# output_args:
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: timeout for highest scoring image before allowing it
|
||||
# to be replaced by a newer image. (default: shown below)
|
||||
best_image_timeout: 60
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: zones for this camera
|
||||
zones:
|
||||
# Required: name of the zone
|
||||
# NOTE: This must be different than any camera names, but can match with another zone on another
|
||||
# camera.
|
||||
front_steps:
|
||||
# Required: List of x,y coordinates to define the polygon of the zone.
|
||||
# NOTE: Presence in a zone is evaluated only based on the bottom center of the objects bounding box.
|
||||
coordinates: 545,1077,747,939,788,805
|
||||
# Optional: Number of consecutive frames required for object to be considered present in the zone (default: shown below).
|
||||
inertia: 3
|
||||
# Optional: List of objects that can trigger this zone (default: all tracked objects)
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: Zone level object filters.
|
||||
# NOTE: The global and camera filters are applied upstream.
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
person:
|
||||
min_area: 5000
|
||||
max_area: 100000
|
||||
threshold: 0.7
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for the jpg snapshots published via MQTT
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable publishing snapshot via mqtt for camera (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Only applies to publishing image data to MQTT via 'frigate/<camera_name>/<object_name>/snapshot'.
|
||||
# All other messages will still be published.
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: print a timestamp on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
timestamp: True
|
||||
# Optional: draw bounding box on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
bounding_box: True
|
||||
# Optional: crop the snapshot (default: shown below)
|
||||
crop: True
|
||||
# Optional: height to resize the snapshot to (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 270
|
||||
# Optional: jpeg encode quality (default: shown below)
|
||||
quality: 70
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict mqtt messages to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for how camera is handled in the GUI.
|
||||
ui:
|
||||
# Optional: Adjust sort order of cameras in the UI. Larger numbers come later (default: shown below)
|
||||
# By default the cameras are sorted alphabetically.
|
||||
order: 0
|
||||
# Optional: Whether or not to show the camera in the Frigate UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
dashboard: True
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: connect to ONVIF camera
|
||||
# to enable PTZ controls.
|
||||
onvif:
|
||||
# Required: host of the camera being connected to.
|
||||
host: 0.0.0.0
|
||||
# Optional: ONVIF port for device (default: shown below).
|
||||
port: 8000
|
||||
# Optional: username for login.
|
||||
# NOTE: Some devices require admin to access ONVIF.
|
||||
user: admin
|
||||
# Optional: password for login.
|
||||
password: admin
|
||||
# Optional: PTZ camera object autotracking. Keeps a moving object in
|
||||
# the center of the frame by automatically moving the PTZ camera.
|
||||
autotracking:
|
||||
# Optional: enable/disable object autotracking. (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: calibrate the camera on startup (default: shown below)
|
||||
# A calibration will move the PTZ in increments and measure the time it takes to move.
|
||||
# The results are used to help estimate the position of tracked objects after a camera move.
|
||||
# Frigate will update your config file automatically after a calibration with
|
||||
# a "movement_weights" entry for the camera. You should then set calibrate_on_startup to False.
|
||||
calibrate_on_startup: False
|
||||
# Optional: the mode to use for zooming in/out on objects during autotracking. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Available options are: disabled, absolute, and relative
|
||||
# disabled - don't zoom in/out on autotracked objects, use pan/tilt only
|
||||
# absolute - use absolute zooming (supported by most PTZ capable cameras)
|
||||
# relative - use relative zooming (not supported on all PTZs, but makes concurrent pan/tilt/zoom movements)
|
||||
zooming: disabled
|
||||
# Optional: A value to change the behavior of zooming on autotracked objects. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# A lower value will keep more of the scene in view around a tracked object.
|
||||
# A higher value will zoom in more on a tracked object, but Frigate may lose tracking more quickly.
|
||||
# The value should be between 0.1 and 0.75
|
||||
zoom_factor: 0.3
|
||||
# Optional: list of objects to track from labelmap.txt (default: shown below)
|
||||
track:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Required: Begin automatically tracking an object when it enters any of the listed zones.
|
||||
required_zones:
|
||||
- zone_name
|
||||
# Required: Name of ONVIF preset in camera's firmware to return to when tracking is over. (default: shown below)
|
||||
return_preset: home
|
||||
# Optional: Seconds to delay before returning to preset. (default: shown below)
|
||||
timeout: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Values generated automatically by a camera calibration. Do not modify these manually. (default: shown below)
|
||||
movement_weights: []
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for how to sort the cameras in the Birdseye view.
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
# Optional: Adjust sort order of cameras in the Birdseye view. Larger numbers come later (default: shown below)
|
||||
# By default the cameras are sorted alphabetically.
|
||||
order: 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional
|
||||
ui:
|
||||
# Optional: Set the default live mode for cameras in the UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
live_mode: mse
|
||||
# Optional: Set a timezone to use in the UI (default: use browser local time)
|
||||
# timezone: America/Denver
|
||||
# Optional: Use an experimental recordings / camera view UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
use_experimental: False
|
||||
# Optional: Set the time format used.
|
||||
# Options are browser, 12hour, or 24hour (default: shown below)
|
||||
time_format: browser
|
||||
# Optional: Set the date style for a specified length.
|
||||
# Options are: full, long, medium, short
|
||||
# Examples:
|
||||
# short: 2/11/23
|
||||
# medium: Feb 11, 2023
|
||||
# full: Saturday, February 11, 2023
|
||||
# (default: shown below).
|
||||
date_style: short
|
||||
# Optional: Set the time style for a specified length.
|
||||
# Options are: full, long, medium, short
|
||||
# Examples:
|
||||
# short: 8:14 PM
|
||||
# medium: 8:15:22 PM
|
||||
# full: 8:15:22 PM Mountain Standard Time
|
||||
# (default: shown below).
|
||||
time_style: medium
|
||||
# Optional: Ability to manually override the date / time styling to use strftime format
|
||||
# https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Formatting-Calendar-Time.html
|
||||
# possible values are shown above (default: not set)
|
||||
strftime_fmt: "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M"
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Telemetry configuration
|
||||
telemetry:
|
||||
# Optional: Enabled network interfaces for bandwidth stats monitoring (default: empty list, let nethogs search all)
|
||||
network_interfaces:
|
||||
- eth
|
||||
- enp
|
||||
- eno
|
||||
- ens
|
||||
- wl
|
||||
- lo
|
||||
# Optional: Configure system stats
|
||||
stats:
|
||||
# Enable AMD GPU stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
amd_gpu_stats: True
|
||||
# Enable Intel GPU stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
intel_gpu_stats: True
|
||||
# Enable network bandwidth stats monitoring for camera ffmpeg processes, go2rtc, and object detectors. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: The container must either be privileged or have cap_net_admin, cap_net_raw capabilities enabled.
|
||||
network_bandwidth: False
|
||||
# Optional: Enable the latest version outbound check (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: If you use the HomeAssistant integration, disabling this will prevent it from reporting new versions
|
||||
version_check: True
|
||||
rtsp:
|
||||
username: "{FRIGATE_GO2RTC_RTSP_USERNAME}"
|
||||
password: "{FRIGATE_GO2RTC_RTSP_PASSWORD}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Common configuration examples
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some common starter configuration examples. Refer to the [reference config](./reference.md) for detailed information about all the config values.
|
||||
|
||||
### Raspberry Pi Home Assistant Addon with USB Coral
|
||||
|
||||
- Single camera with 720p, 5fps stream for detect
|
||||
- MQTT connected to home assistant mosquitto addon
|
||||
- Hardware acceleration for decoding video
|
||||
- USB Coral detector
|
||||
- Save all video with any detectable motion for 7 days regardless of whether any objects were detected or not
|
||||
- Continue to keep all video if it was during any event for 30 days
|
||||
- Save snapshots for 30 days
|
||||
- Motion mask for the camera timestamp
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
host: core-mosquitto
|
||||
user: mqtt-user
|
||||
password: xxxxxxxxxx
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-rpi-64-h264
|
||||
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
coral:
|
||||
type: edgetpu
|
||||
device: usb
|
||||
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 7
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
|
||||
snapshots:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
name_of_your_camera:
|
||||
detect:
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
fps: 5
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://10.0.10.10:554/rtsp
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
mask:
|
||||
- 0,461,3,0,1919,0,1919,843,1699,492,1344,458,1346,336,973,317,869,375,866,432
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Standalone Intel Mini PC with USB Coral
|
||||
|
||||
- Single camera with 720p, 5fps stream for detect
|
||||
- MQTT disabled (not integrated with home assistant)
|
||||
- VAAPI hardware acceleration for decoding video
|
||||
- USB Coral detector
|
||||
- Save all video with any detectable motion for 7 days regardless of whether any objects were detected or not
|
||||
- Continue to keep all video if it was during any event for 30 days
|
||||
- Save snapshots for 30 days
|
||||
- Motion mask for the camera timestamp
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-vaapi
|
||||
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
coral:
|
||||
type: edgetpu
|
||||
device: usb
|
||||
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 7
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
|
||||
snapshots:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
name_of_your_camera:
|
||||
detect:
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
fps: 5
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://10.0.10.10:554/rtsp
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
mask:
|
||||
- 0,461,3,0,1919,0,1919,843,1699,492,1344,458,1346,336,973,317,869,375,866,432
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Home Assistant integrated Intel Mini PC with OpenVino
|
||||
|
||||
- Single camera with 720p, 5fps stream for detect
|
||||
- MQTT connected to same mqtt server as home assistant
|
||||
- VAAPI hardware acceleration for decoding video
|
||||
- OpenVino detector
|
||||
- Save all video with any detectable motion for 7 days regardless of whether any objects were detected or not
|
||||
- Continue to keep all video if it was during any event for 30 days
|
||||
- Save snapshots for 30 days
|
||||
- Motion mask for the camera timestamp
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
host: 192.168.X.X # <---- same mqtt broker that home assistant uses
|
||||
user: mqtt-user
|
||||
password: xxxxxxxxxx
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
hwaccel_args: preset-vaapi
|
||||
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
ov:
|
||||
type: openvino
|
||||
device: AUTO
|
||||
model:
|
||||
path: /openvino-model/ssdlite_mobilenet_v2.xml
|
||||
|
||||
model:
|
||||
width: 300
|
||||
height: 300
|
||||
input_tensor: nhwc
|
||||
input_pixel_format: bgr
|
||||
labelmap_path: /openvino-model/coco_91cl_bkgr.txt
|
||||
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 7
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
|
||||
snapshots:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
name_of_your_camera:
|
||||
detect:
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
fps: 5
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://10.0.10.10:554/rtsp
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
mask:
|
||||
- 0,461,3,0,1919,0,1919,843,1699,492,1344,458,1346,336,973,317,869,375,866,432
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,11 +9,11 @@ Frigate has different live view options, some of which require the bundled `go2r
|
||||
|
||||
Live view options can be selected while viewing the live stream. The options are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Source | Latency | Frame Rate | Resolution | Audio | Requires go2rtc | Other Limitations |
|
||||
| ------ | ------- | ------------------------------------- | -------------- | ---------------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| jsmpeg | low | same as `detect -> fps`, capped at 10 | same as detect | no | no | none |
|
||||
| mse | low | native | native | yes (depends on audio codec) | yes | iPhone requires iOS 17.1+, Firefox is h.264 only |
|
||||
| webrtc | lowest | native | native | yes (depends on audio codec) | yes | requires extra config, doesn't support h.265 |
|
||||
| Source | Latency | Frame Rate | Resolution | Audio | Requires go2rtc | Other Limitations |
|
||||
| ------ | ------- | ------------------------------------- | -------------- | ---------------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| jsmpeg | low | same as `detect -> fps`, capped at 10 | same as detect | no | no | none |
|
||||
| mse | low | native | native | yes (depends on audio codec) | yes | iPhone requires iOS 17.1+, Firefox is h.264 only |
|
||||
| webrtc | lowest | native | native | yes (depends on audio codec) | yes | requires extra config, doesn't support h.265 |
|
||||
|
||||
### Audio Support
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -104,6 +104,7 @@ If you are having difficulties getting WebRTC to work and you are running Frigat
|
||||
If not running in host mode, port 8555 will need to be mapped for the container:
|
||||
|
||||
docker-compose.yml
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
services:
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
@@ -115,4 +116,4 @@ services:
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
See [go2rtc WebRTC docs](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#module-webrtc) for more information about this.
|
||||
See [go2rtc WebRTC docs](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.3#module-webrtc) for more information about this.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,11 +3,19 @@ id: masks
|
||||
title: Masks
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
There are two types of masks available:
|
||||
## Motion masks
|
||||
|
||||
**Motion masks**: Motion masks are used to prevent unwanted types of motion from triggering detection. Try watching the debug feed with `Motion Boxes` enabled to see what may be regularly detected as motion. For example, you want to mask out your timestamp, the sky, rooftops, etc. Keep in mind that this mask only prevents motion from being detected and does not prevent objects from being detected if object detection was started due to motion in unmasked areas. Motion is also used during object tracking to refine the object detection area in the next frame. Over masking will make it more difficult for objects to be tracked. To see this effect, create a mask, and then watch the video feed with `Motion Boxes` enabled again.
|
||||
Motion masks are used to prevent unwanted types of motion from triggering detection. Try watching the debug feed with `Motion Boxes` enabled to see what may be regularly detected as motion. For example, you want to mask out your timestamp, the sky, rooftops, etc. Keep in mind that this mask only prevents motion from being detected and does not prevent objects from being detected if object detection was started due to motion in unmasked areas. Motion is also used during object tracking to refine the object detection area in the next frame. Over masking will make it more difficult for objects to be tracked. To see this effect, create a mask, and then watch the video feed with `Motion Boxes` enabled again.
|
||||
|
||||
**Object filter masks**: Object filter masks are used to filter out false positives for a given object type based on location. These should be used to filter any areas where it is not possible for an object of that type to be. The bottom center of the detected object's bounding box is evaluated against the mask. If it is in a masked area, it is assumed to be a false positive. For example, you may want to mask out rooftops, walls, the sky, treetops for people. For cars, masking locations other than the street or your driveway will tell Frigate that anything in your yard is a false positive.
|
||||
## Object filter masks
|
||||
|
||||
Object filter masks are used to filter out false positives for a given object type based on location. These should be used to filter any areas where it is not possible for an object of that type to be. The bottom center of the detected object's bounding box is evaluated against the mask. If it is in a masked area, it is assumed to be a false positive. For example, you may want to mask out rooftops, walls, the sky, treetops for people. For cars, masking locations other than the street or your driveway will tell Frigate that anything in your yard is a false positive.
|
||||
|
||||
Object filter masks can be used to filter out stubborn false positives in fixed locations. For example, the base of this tree may be frequently detected as a person. The following image shows an example of an object filter mask (shaded red area) over the location where the bottom center is typically located to filter out person detections in a precise location.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Using the mask creator
|
||||
|
||||
To create a poly mask:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
103
docs/docs/configuration/motion_detection.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: motion_detection
|
||||
title: Motion Detection
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Tuning Motion Detection
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate uses motion detection as a first line check to see if there is anything happening in the frame worth checking with object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
Once motion is detected, it tries to group up nearby areas of motion together in hopes of identifying a rectangle in the image that will capture the area worth inspecting. These are the red "motion boxes" you see in the debug viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Goal
|
||||
|
||||
The default motion settings should work well for the majority of cameras, however there are cases where tuning motion detection can lead to better and more optimal results. Each camera has its own environment with different variables that affect motion, this means that the same motion settings will not fit all of your cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
Before tuning motion it is important to understand the goal. In an optimal configuration, motion from people and cars would be detected, but not grass moving, lighting changes, timestamps, etc. If your motion detection is too sensitive, you will experience higher CPU loads and greater false positives from the increased rate of object detection. If it is not sensitive enough, you will miss events.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Motion Masks
|
||||
|
||||
First, mask areas with regular motion not caused by the objects you want to detect. The best way to find candidates for motion masks is by watching the debug stream with motion boxes enabled. Good use cases for motion masks are timestamps or tree limbs and large bushes that regularly move due to wind. When possible, avoid creating motion masks that would block motion detection for objects you want to track **even if they are in locations where you don't want events**. Motion masks should not be used to avoid detecting objects in specific areas. More details can be found [in the masks docs.](/configuration/masks.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare For Testing
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to tune motion detection is to do it live, have one window / screen open with the frigate debug view and motion boxes enabled with another window / screen open allowing for configuring the motion settings. It is recommended to use Home Assistant or MQTT as they offer live configuration of some motion settings meaning that Frigate does not need to be restarted when values are changed.
|
||||
|
||||
In Home Assistant the `Improve Contrast`, `Contour Area`, and `Threshold` configuration entities are disabled by default but can easily be enabled and used to tune live, otherwise MQTT can be used.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tuning Motion Detection During The Day
|
||||
|
||||
Now that things are set up, find a time to tune that represents normal circumstances. For example, if you tune your motion on a day that is sunny and windy you may find later that the motion settings are not sensitive enough on a cloudy and still day.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that motion detection is just used to determine when object detection should be used. You should aim to have motion detection sensitive enough that you won't miss events from objects you want to detect with object detection. The goal is to prevent object detection from running constantly for every small pixel change in the image. Windy days are still going to result in lots of motion being detected.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Threshold
|
||||
|
||||
The threshold value dictates how much of a change in a pixels luminance is required to be considered motion.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# default threshold value
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
# Optional: The threshold passed to cv2.threshold to determine if a pixel is different enough to be counted as motion. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection less sensitive and decreasing it will make motion detection more sensitive.
|
||||
# The value should be between 1 and 255.
|
||||
threshold: 30
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lower values mean motion detection is more sensitive to changes in color, making it more likely for example to detect motion when a brown dogs blends in with a brown fence or a person wearing a red shirt blends in with a red car. If the threshold is too low however, it may detect things like grass blowing in the wind, shadows, etc. to be detected as motion.
|
||||
|
||||
Watching the motion boxes in the debug view, increase the threshold until you only see motion that is visible to the eye. Once this is done, it is important to test and ensure that desired motion is still detected.
|
||||
|
||||
### Contour Area
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# default contour_area value
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
# Optional: Minimum size in pixels in the resized motion image that counts as motion (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will prevent smaller areas of motion from being detected. Decreasing will
|
||||
# make motion detection more sensitive to smaller moving objects.
|
||||
# As a rule of thumb:
|
||||
# - 10 - high sensitivity
|
||||
# - 30 - medium sensitivity
|
||||
# - 50 - low sensitivity
|
||||
contour_area: 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once the threshold calculation is run, the pixels that have changed are grouped together. The contour area value is used to decide which groups of changed pixels qualify as motion. Smaller values are more sensitive meaning people that are far away, small animals, etc. are more likely to be detected as motion, but it also means that small changes in shadows, leaves, etc. are detected as motion. Higher values are less sensitive meaning these things won't be detected as motion but with the risk that desired motion won't be detected until closer to the camera.
|
||||
|
||||
Watching the motion boxes in the debug view, adjust the contour area until there are no motion boxes smaller than the smallest you'd expect frigate to detect something moving.
|
||||
|
||||
### Improve Contrast
|
||||
|
||||
At this point if motion is working as desired there is no reason to continue with tuning for the day. If you were unable to find a balance between desired and undesired motion being detected, you can try disabling improve contrast and going back to the threshold and contour area steps.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tuning Motion Detection During The Night
|
||||
|
||||
Once daytime motion detection is tuned, there is a chance that the settings will work well for motion detection during the night as well. If this is the case then the preferred settings can be written to the config file and left alone.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if the preferred day settings do not work well at night it is recommended to use HomeAssistant or some other solution to automate changing the settings. That way completely separate sets of motion settings can be used for optimal day and night motion detection.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tuning For Large Changes In Motion
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# default lightning_threshold:
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
# Optional: The percentage of the image used to detect lightning or other substantial changes where motion detection
|
||||
# needs to recalibrate. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection more likely to consider lightning or ir mode changes as valid motion.
|
||||
# Decreasing this value will make motion detection more likely to ignore large amounts of motion such as a person approaching
|
||||
# a doorbell camera.
|
||||
lightning_threshold: 0.8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
Some cameras like doorbell cameras may have missed detections when someone walks directly in front of the camera and the lightning_threshold causes motion detection to be re-calibrated. In this case, it may be desirable to increase the `lightning_threshold` to ensure these events are not missed.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Large changes in motion like PTZ moves and camera switches between Color and IR mode should result in no motion detection. This is done via the `lightning_threshold` configuration. It is defined as the percentage of the image used to detect lightning or other substantial changes where motion detection needs to recalibrate. Increasing this value will make motion detection more likely to consider lightning or IR mode changes as valid motion. Decreasing this value will make motion detection more likely to ignore large amounts of motion such as a person approaching a doorbell camera.
|
||||
@@ -5,12 +5,18 @@ title: Object Detectors
|
||||
|
||||
# Officially Supported Detectors
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate provides the following builtin detector types: `cpu`, `edgetpu`, `openvino`, and `tensorrt`. By default, Frigate will use a single CPU detector. Other detectors may require additional configuration as described below. When using multiple detectors they will run in dedicated processes, but pull from a common queue of detection requests from across all cameras.
|
||||
Frigate provides the following builtin detector types: `cpu`, `edgetpu`, `openvino`, `tensorrt`, and `rknn`. By default, Frigate will use a single CPU detector. Other detectors may require additional configuration as described below. When using multiple detectors they will run in dedicated processes, but pull from a common queue of detection requests from across all cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
## CPU Detector (not recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
The CPU detector type runs a TensorFlow Lite model utilizing the CPU without hardware acceleration. It is recommended to use a hardware accelerated detector type instead for better performance. To configure a CPU based detector, set the `"type"` attribute to `"cpu"`.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not have GPU or Edge TPU hardware, using the [OpenVINO Detector](#openvino-detector) is often more efficient than using the CPU detector.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
The number of threads used by the interpreter can be specified using the `"num_threads"` attribute, and defaults to `3.`
|
||||
|
||||
A TensorFlow Lite model is provided in the container at `/cpu_model.tflite` and is used by this detector type by default. To provide your own model, bind mount the file into the container and provide the path with `model.path`.
|
||||
@@ -29,14 +35,20 @@ detectors:
|
||||
|
||||
When using CPU detectors, you can add one CPU detector per camera. Adding more detectors than the number of cameras should not improve performance.
|
||||
|
||||
## Edge-TPU Detector
|
||||
## Edge TPU Detector
|
||||
|
||||
The EdgeTPU detector type runs a TensorFlow Lite model utilizing the Google Coral delegate for hardware acceleration. To configure an EdgeTPU detector, set the `"type"` attribute to `"edgetpu"`.
|
||||
The Edge TPU detector type runs a TensorFlow Lite model utilizing the Google Coral delegate for hardware acceleration. To configure an Edge TPU detector, set the `"type"` attribute to `"edgetpu"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The EdgeTPU device can be specified using the `"device"` attribute according to the [Documentation for the TensorFlow Lite Python API](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/multiple-edgetpu/#using-the-tensorflow-lite-python-api). If not set, the delegate will use the first device it finds.
|
||||
The Edge TPU device can be specified using the `"device"` attribute according to the [Documentation for the TensorFlow Lite Python API](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/multiple-edgetpu/#using-the-tensorflow-lite-python-api). If not set, the delegate will use the first device it finds.
|
||||
|
||||
A TensorFlow Lite model is provided in the container at `/edgetpu_model.tflite` and is used by this detector type by default. To provide your own model, bind mount the file into the container and provide the path with `model.path`.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
See [common Edge TPU troubleshooting steps](/troubleshooting/edgetpu) if the Edge TPU is not detected.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Single USB Coral
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
@@ -95,11 +107,11 @@ detectors:
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenVINO Detector
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenVINO detector type runs an OpenVINO IR model on Intel CPU, GPU and VPU hardware. To configure an OpenVINO detector, set the `"type"` attribute to `"openvino"`.
|
||||
The OpenVINO detector type runs an OpenVINO IR model on AMD and Intel CPUs, Intel GPUs and Intel VPU hardware. To configure an OpenVINO detector, set the `"type"` attribute to `"openvino"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenVINO device to be used is specified using the `"device"` attribute according to the naming conventions in the [Device Documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/openvino_docs_OV_UG_Working_with_devices.html). Other supported devices could be `AUTO`, `CPU`, `GPU`, `MYRIAD`, etc. If not specified, the default OpenVINO device will be selected by the `AUTO` plugin.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVINO is supported on 6th Gen Intel platforms (Skylake) and newer. A supported Intel platform is required to use the `GPU` device with OpenVINO. The `MYRIAD` device may be run on any platform, including Arm devices. For detailed system requirements, see [OpenVINO System Requirements](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/openvino-toolkit/system-requirements.html)
|
||||
OpenVINO is supported on 6th Gen Intel platforms (Skylake) and newer. It will also run on AMD CPUs despite having no official support for it. A supported Intel platform is required to use the `GPU` device with OpenVINO. The `MYRIAD` device may be run on any platform, including Arm devices. For detailed system requirements, see [OpenVINO System Requirements](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/openvino-toolkit/system-requirements.html)
|
||||
|
||||
An OpenVINO model is provided in the container at `/openvino-model/ssdlite_mobilenet_v2.xml` and is used by this detector type by default. The model comes from Intel's Open Model Zoo [SSDLite MobileNet V2](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/open_model_zoo/tree/master/models/public/ssdlite_mobilenet_v2) and is converted to an FP16 precision IR model. Use the model configuration shown below when using the OpenVINO detector with the default model.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -119,7 +131,7 @@ model:
|
||||
labelmap_path: /openvino-model/coco_91cl_bkgr.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This detector also supports some YOLO variants: YOLOX, YOLOv5, and YOLOv8 specifically. Other YOLO variants are not officially supported/tested. Frigate does not come with any yolo models preloaded, so you will need to supply your own models. This detector has been verified to work with the [yolox_tiny](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/open_model_zoo/tree/master/models/public/yolox-tiny) model from Intel's Open Model Zoo. You can follow [these instructions](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/open_model_zoo/tree/master/models/public/yolox-tiny#download-a-model-and-convert-it-into-openvino-ir-format) to retrieve the OpenVINO-compatible `yolox_tiny` model. Make sure that the model input dimensions match the `width` and `height` parameters, and `model_type` is set accordingly. See [Full Configuration Reference](/configuration/index.md#full-configuration-reference) for a list of possible `model_type` options. Below is an example of how `yolox_tiny` can be used in Frigate:
|
||||
This detector also supports some YOLO variants: YOLOX, YOLOv5, and YOLOv8 specifically. Other YOLO variants are not officially supported/tested. Frigate does not come with any yolo models preloaded, so you will need to supply your own models. This detector has been verified to work with the [yolox_tiny](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/open_model_zoo/tree/master/models/public/yolox-tiny) model from Intel's Open Model Zoo. You can follow [these instructions](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/open_model_zoo/tree/master/models/public/yolox-tiny#download-a-model-and-convert-it-into-openvino-ir-format) to retrieve the OpenVINO-compatible `yolox_tiny` model. Make sure that the model input dimensions match the `width` and `height` parameters, and `model_type` is set accordingly. See [Full Configuration Reference](/configuration/reference.md) for a list of possible `model_type` options. Below is an example of how `yolox_tiny` can be used in Frigate:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
@@ -170,7 +182,7 @@ volumes:
|
||||
|
||||
## NVidia TensorRT Detector
|
||||
|
||||
NVidia GPUs may be used for object detection using the TensorRT libraries. Due to the size of the additional libraries, this detector is only provided in images with the `-tensorrt` tag suffix. This detector is designed to work with Yolo models for object detection.
|
||||
Nvidia GPUs may be used for object detection using the TensorRT libraries. Due to the size of the additional libraries, this detector is only provided in images with the `-tensorrt` tag suffix, e.g. `ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-tensorrt`. This detector is designed to work with Yolo models for object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Minimum Hardware Support
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +204,7 @@ There are improved capabilities in newer GPU architectures that TensorRT can ben
|
||||
|
||||
The model used for TensorRT must be preprocessed on the same hardware platform that they will run on. This means that each user must run additional setup to generate a model file for the TensorRT library. A script is included that will build several common models.
|
||||
|
||||
The Frigate image will generate model files during startup if the specified model is not found. Processed models are stored in the `/config/model_cache` folder. Typically the `/config` path is mapped to a directory on the host already and the `model_cache` does not need to be mapped separately unless the user wants to store it in a different location on the host.
|
||||
The Frigate image will generate model files during startup if the specified model is not found. Processed models are stored in the `/config/model_cache` folder. Typically the `/config` path is mapped to a directory on the host already and the `model_cache` does not need to be mapped separately unless the user wants to store it in a different location on the host.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the `yolov7-320` model will be generated, but this can be overridden by specifying the `YOLO_MODELS` environment variable in Docker. One or more models may be listed in a comma-separated format, and each one will be generated. To select no model generation, set the variable to an empty string, `YOLO_MODELS=""`. Models will only be generated if the corresponding `{model}.trt` file is not present in the `model_cache` folder, so you can force a model to be regenerated by deleting it from your Frigate data folder.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +251,7 @@ frigate:
|
||||
- USE_FP16=false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have multiple GPUs passed through to Frigate, you can specify which one to use for the model conversion. The conversion script will use the first visible GPU, however in systems with mixed GPU models you may not want to use the default index for object detection. Add the `TRT_MODEL_PREP_DEVICE` environment variable to select a specific GPU.
|
||||
If you have multiple GPUs passed through to Frigate, you can specify which one to use for the model conversion. The conversion script will use the first visible GPU, however in systems with mixed GPU models you may not want to use the default index for object detection. Add the `TRT_MODEL_PREP_DEVICE` environment variable to select a specific GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
@@ -289,5 +301,105 @@ Replace `<your_codeproject_ai_server_ip>` and `<port>` with the IP address and p
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that the integration is working correctly, start Frigate and observe the logs for any error messages related to CodeProject.AI. Additionally, you can check the Frigate web interface to see if the objects detected by CodeProject.AI are being displayed and tracked properly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Community Supported Detectors
|
||||
|
||||
## Rockchip RKNN-Toolkit-Lite2
|
||||
|
||||
This detector is only available if one of the following Rockchip SoCs is used:
|
||||
|
||||
- RK3588/RK3588S
|
||||
- RK3568
|
||||
- RK3566
|
||||
- RK3562
|
||||
|
||||
These SoCs come with a NPU that will highly speed up detection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Use a frigate docker image with `-rk` suffix and enable privileged mode by adding the `--privileged` flag to your docker run command or `privileged: true` to your `docker-compose.yml` file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This `config.yml` shows all relevant options to configure the detector and explains them. All values shown are the default values (except for one). Lines that are required at least to use the detector are labeled as required, all other lines are optional.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
detectors: # required
|
||||
rknn: # required
|
||||
type: rknn # required
|
||||
# core mask for npu
|
||||
core_mask: 0
|
||||
|
||||
model: # required
|
||||
# name of yolov8 model or path to your own .rknn model file
|
||||
# possible values are:
|
||||
# - default-yolov8n
|
||||
# - default-yolov8s
|
||||
# - default-yolov8m
|
||||
# - default-yolov8l
|
||||
# - default-yolov8x
|
||||
# - /config/model_cache/rknn/your_custom_model.rknn
|
||||
path: default-yolov8n
|
||||
# width and height of detection frames
|
||||
width: 320
|
||||
height: 320
|
||||
# pixel format of detection frame
|
||||
# default value is rgb but yolov models usually use bgr format
|
||||
input_pixel_format: bgr # required
|
||||
# shape of detection frame
|
||||
input_tensor: nhwc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation for rknn specific options:
|
||||
|
||||
- **core mask** controls which cores of your NPU should be used. This option applies only to SoCs with a multicore NPU (at the time of writing this in only the RK3588/S). The easiest way is to pass the value as a binary number. To do so, use the prefix `0b` and write a `0` to disable a core and a `1` to enable a core, whereas the last digit coresponds to core0, the second last to core1, etc. You also have to use the cores in ascending order (so you can't use core0 and core2; but you can use core0 and core1). Enabling more cores can reduce the inference speed, especially when using bigger models (see section below). Examples:
|
||||
- `core_mask: 0b000` or just `core_mask: 0` let the NPU decide which cores should be used. Default and recommended value.
|
||||
- `core_mask: 0b001` use only core0.
|
||||
- `core_mask: 0b011` use core0 and core1.
|
||||
- `core_mask: 0b110` use core1 and core2. **This does not** work, since core0 is disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choosing a model
|
||||
|
||||
There are 5 default yolov8 models that differ in size and therefore load the NPU more or less. In ascending order, with the top one being the smallest and least computationally intensive model:
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Size in mb |
|
||||
| ------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| yolov8n | 9 |
|
||||
| yolov8s | 25 |
|
||||
| yolov8m | 54 |
|
||||
| yolov8l | 90 |
|
||||
| yolov8x | 136 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
You can get the load of your NPU with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ cat /sys/kernel/debug/rknpu/load
|
||||
>> NPU load: Core0: 0%, Core1: 0%, Core2: 0%,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
- By default the rknn detector uses the yolov8n model (`model: path: default-yolov8n`). This model comes with the image, so no further steps than those mentioned above are necessary.
|
||||
- If you want to use a more precise model, you can pass `default-yolov8s`, `default-yolov8m`, `default-yolov8l` or `default-yolov8x` as `model: path:` option.
|
||||
- If the model does not exist, it will be automatically downloaded to `/config/model_cache/rknn`.
|
||||
- If your server has no internet connection, you can download the model from [this Github repository](https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases) using another device and place it in the `config/model_cache/rknn` on your system.
|
||||
- Finally, you can also provide your own model. Note that only yolov8 models are currently supported. Moreover, you will need to convert your model to the rknn format using `rknn-toolkit2` on a x86 machine. Afterwards, you can place your `.rknn` model file in the `config/model_cache/rknn` directory on your system. Then you need to pass the path to your model using the `path` option of your `model` block like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
model:
|
||||
path: /config/model_cache/rknn/my-rknn-model.rknn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
When you have a multicore NPU, you can enable all cores to reduce inference times. You should consider activating all cores if you use a larger model like yolov8l. If your NPU has 3 cores (like rk3588/S SoCs), you can enable all 3 cores using:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
rknn:
|
||||
type: rknn
|
||||
core_mask: 0b111
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: false_positives
|
||||
title: Reducing false positives
|
||||
id: object_filters
|
||||
title: Filters
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
There are several types of object filters that can be used to reduce false positive rates.
|
||||
|
||||
## Object Scores
|
||||
|
||||
For object filters in your configuration, any single detection below `min_score` will be ignored as a false positive. `threshold` is based on the median of the history of scores (padded to 3 values) for a tracked object. Consider the following frames when `min_score` is set to 0.6 and threshold is set to 0.85:
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +20,8 @@ For object filters in your configuration, any single detection below `min_score`
|
||||
|
||||
In frame 2, the score is below the `min_score` value, so Frigate ignores it and it becomes a 0.0. The computed score is the median of the score history (padding to at least 3 values), and only when that computed score crosses the `threshold` is the object marked as a true positive. That happens in frame 4 in the example.
|
||||
|
||||
show image of snapshot vs event with differing scores
|
||||
|
||||
### Minimum Score
|
||||
|
||||
Any detection below `min_score` will be immediately thrown out and never tracked because it is considered a false positive. If `min_score` is too low then false positives may be detected and tracked which can confuse the object tracker and may lead to wasted resources. If `min_score` is too high then lower scoring true positives like objects that are further away or partially occluded may be thrown out which can also confuse the tracker and cause valid events to be lost or disjointed.
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +40,13 @@ False positives can also be reduced by filtering a detection based on its shape.
|
||||
|
||||
### Object Proportions
|
||||
|
||||
`min_ratio` and `max_ratio` filter on the ratio of width / height of an objects bounding box and can be used to reduce false positives. For example if a false positive is detected as very tall for a dog which is often wider, a `min_ratio` filter can be used to filter out these false positives.
|
||||
`min_ratio` and `max_ratio` values are compared against a given detected object's width/height ratio (in pixels). If the ratio is outside this range, the object will be ignored as a false positive. This allows objects that are proportionally too short-and-wide (higher ratio) or too tall-and-narrow (smaller ratio) to be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
Conceptually, a ratio of 1 is a square, 0.5 is a "tall skinny" box, and 2 is a "wide flat" box. If `min_ratio` is 1.0, any object that is taller than it is wide will be ignored. Similarly, if `max_ratio` is 1.0, then any object that is wider than it is tall will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Tools
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: objects
|
||||
title: Objects
|
||||
title: Available Objects
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
import labels from "../../../labelmap.txt";
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate includes the object models listed below from the Google Coral test data.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note:
|
||||
- `car` is listed twice because `truck` has been renamed to `car` by default. These object types are frequently confused.
|
||||
- `person` is the only tracked object by default. See the [full configuration reference](index.md#full-configuration-reference) for an example of expanding the list of tracked objects.
|
||||
Please note:
|
||||
|
||||
- `car` is listed twice because `truck` has been renamed to `car` by default. These object types are frequently confused.
|
||||
- `person` is the only tracked object by default. See the [full configuration reference](reference.md) for an example of expanding the list of tracked objects.
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
{labels.split("\n").map((label) => (
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,17 +3,90 @@ id: record
|
||||
title: Recording
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Recordings can be enabled and are stored at `/media/frigate/recordings`. The folder structure for the recordings is `YYYY-MM-DD/HH/<camera_name>/MM.SS.mp4`. These recordings are written directly from your camera stream without re-encoding. Each camera supports a configurable retention policy in the config. Frigate chooses the largest matching retention value between the recording retention and the event retention when determining if a recording should be removed.
|
||||
Recordings can be enabled and are stored at `/media/frigate/recordings`. The folder structure for the recordings is `YYYY-MM-DD/HH/<camera_name>/MM.SS.mp4` in **UTC time**. These recordings are written directly from your camera stream without re-encoding. Each camera supports a configurable retention policy in the config. Frigate chooses the largest matching retention value between the recording retention and the event retention when determining if a recording should be removed.
|
||||
|
||||
New recording segments are written from the camera stream to cache, they are only moved to disk if they match the setup recording retention policy.
|
||||
|
||||
H265 recordings can be viewed in Chrome 108+, Edge and Safari only. All other browsers require recordings to be encoded with H264.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common recording configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Most conservative: Ensure all video is saved
|
||||
|
||||
For users deploying Frigate in environments where it is important to have contiguous video stored even if there was no detectable motion, the following config will store all video for 3 days. After 3 days, only video containing motion and overlapping with events will be retained until 30 days have passed.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 3
|
||||
mode: all
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reduced storage: Only saving video when motion is detected
|
||||
|
||||
In order to reduce storage requirements, you can adjust your config to only retain video where motion was detected.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 3
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Minimum: Events only
|
||||
|
||||
If you only want to retain video that occurs during an event, this config will discard video unless an event is ongoing.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 0
|
||||
mode: all
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 30
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Will Frigate delete old recordings if my storage runs out?
|
||||
|
||||
As of Frigate 0.12 if there is less than an hour left of storage, the oldest 2 hours of recordings will be deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
## What if I don't want 24/7 recordings?
|
||||
## Configuring Recording Retention
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate supports both continuous and event based recordings with separate retention modes and retention periods.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
Retention configs support decimals meaning they can be configured to retain `0.5` days, for example.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Continuous Recording
|
||||
|
||||
The number of days to retain continuous recordings can be set via the following config where X is a number, by default continuous recording is disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
days: 1 # <- number of days to keep continuous recordings
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Continuous recording supports different retention modes [which are described below](#what-do-the-different-retain-modes-mean)
|
||||
|
||||
### Event Recording
|
||||
|
||||
If you only used clips in previous versions with recordings disabled, you can use the following config to get the same behavior. This is also the default behavior when recordings are enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,34 +95,31 @@ record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
events:
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
default: 10
|
||||
default: 10 # <- number of days to keep event recordings
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This configuration will retain recording segments that overlap with events and have active tracked objects for 10 days. Because multiple events can reference the same recording segments, this avoids storing duplicate footage for overlapping events and reduces overall storage needs.
|
||||
|
||||
When `retain -> days` is set to `0`, segments will be deleted from the cache if no events are in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
## Can I have "24/7" recordings, but only at certain times?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Frigate UI, HomeAssistant, or MQTT, cameras can be automated to only record in certain situations or at certain times.
|
||||
|
||||
**WARNING**: Recordings still must be enabled in the config. If a camera has recordings disabled in the config, enabling via the methods listed above will have no effect.
|
||||
|
||||
## What do the different retain modes mean?
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate saves from the stream with the `record` role in 10 second segments. These options determine which recording segments are kept for 24/7 recording (but can also affect events).
|
||||
Frigate saves from the stream with the `record` role in 10 second segments. These options determine which recording segments are kept for continuous recording (but can also affect events).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you have Frigate configured so that your doorbell camera would retain the last **2** days of continuous recording.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you have Frigate configured so that your doorbell camera would retain the last **2** days of 24/7 recording.
|
||||
- With the `all` option all 48 hours of those two days would be kept and viewable.
|
||||
- With the `motion` option the only parts of those 48 hours would be segments that Frigate detected motion. This is the middle ground option that won't keep all 48 hours, but will likely keep all segments of interest along with the potential for some extra segments.
|
||||
- With the `active_objects` option the only segments that would be kept are those where there was a true positive object that was not considered stationary.
|
||||
|
||||
The same options are available with events. Let's consider a scenario where you drive up and park in your driveway, go inside, then come back out 4 hours later.
|
||||
|
||||
- With the `all` option all segments for the duration of the event would be saved for the event. This event would have 4 hours of footage.
|
||||
- With the `motion` option all segments for the duration of the event with motion would be saved. This means any segment where a car drove by in the street, person walked by, lighting changed, etc. would be saved.
|
||||
- With the `active_objects` it would only keep segments where the object was active. In this case the only segments that would be saved would be the ones where the car was driving up, you going inside, you coming outside, and the car driving away. Essentially reducing the 4 hours to a minute or two of event footage.
|
||||
|
||||
A configuration example of the above retain modes where all `motion` segments are stored for 7 days and `active objects` are stored for 14 days would be as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
@@ -61,11 +131,13 @@ record:
|
||||
default: 14
|
||||
mode: active_objects
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above configuration example can be added globally or on a per camera basis.
|
||||
|
||||
### Object Specific Retention
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set specific retention length for an object type. The below configuration example builds on from above but also specifies that recordings of dogs only need to be kept for 2 days and recordings of cars should be kept for 7 days.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
@@ -81,17 +153,40 @@ record:
|
||||
car: 7
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Can I have "continuous" recordings, but only at certain times?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Frigate UI, HomeAssistant, or MQTT, cameras can be automated to only record in certain situations or at certain times.
|
||||
|
||||
## How do I export recordings?
|
||||
|
||||
The export page in the Frigate WebUI allows for exporting real time clips with a designated start and stop time as well as exporting a timelapse for a designated start and stop time. These exports can take a while so it is important to leave the file until it is no longer in progress.
|
||||
The export page in the Frigate WebUI allows for exporting real time clips with a designated start and stop time as well as exporting a time-lapse for a designated start and stop time. These exports can take a while so it is important to leave the file until it is no longer in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
## Syncing Recordings With Disk
|
||||
### Time-lapse export
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases the recordings files may be deleted but Frigate will not know this has happened. Sync on startup can be enabled which will tell Frigate to check the file system and delete any db entries for files which don't exist.
|
||||
When exporting a time-lapse the default speed-up is 25x with 30 FPS. This means that every 25 seconds of (real-time) recording is condensed into 1 second of time-lapse video (always without audio) with a smoothness of 30 FPS.
|
||||
To configure the speed-up factor, the frame rate and further custom settings, the configuration parameter `timelapse_args` can be used. The below configuration example would change the time-lapse speed to 60x (for fitting 1 hour of recording into 1 minute of time-lapse) with 25 FPS:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
sync_on_startup: True
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
export:
|
||||
timelapse_args: "-vf setpts=PTS/60 -r 25"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
When using `hwaccel_args` globally hardware encoding is used for time lapse generation. The encoder determines its own behavior so the resulting file size may be undesirably large.
|
||||
To reduce the output file size the ffmpeg parameter `-qp n` can be utilized (where `n` stands for the value of the quantisation parameter). The value can be adjusted to get an acceptable tradeoff between quality and file size for the given scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Syncing Recordings With Disk
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases the recordings files may be deleted but Frigate will not know this has happened. Recordings sync can be enabled which will tell Frigate to check the file system and delete any db entries for files which don't exist.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
record:
|
||||
sync_recordings: True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
||||
641
docs/docs/configuration/reference.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,641 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: reference
|
||||
title: Full Reference Config
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Full configuration reference:
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
It is not recommended to copy this full configuration file. Only specify values that are different from the defaults. Configuration options and default values may change in future versions.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable mqtt server (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Required: host name
|
||||
host: mqtt.server.com
|
||||
# Optional: port (default: shown below)
|
||||
port: 1883
|
||||
# Optional: topic prefix (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: must be unique if you are running multiple instances
|
||||
topic_prefix: frigate
|
||||
# Optional: client id (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: must be unique if you are running multiple instances
|
||||
client_id: frigate
|
||||
# Optional: user
|
||||
# NOTE: MQTT user can be specified with an environment variable or docker secrets that must begin with 'FRIGATE_'.
|
||||
# e.g. user: '{FRIGATE_MQTT_USER}'
|
||||
user: mqtt_user
|
||||
# Optional: password
|
||||
# NOTE: MQTT password can be specified with an environment variable or docker secrets that must begin with 'FRIGATE_'.
|
||||
# e.g. password: '{FRIGATE_MQTT_PASSWORD}'
|
||||
password: password
|
||||
# Optional: tls_ca_certs for enabling TLS using self-signed certs (default: None)
|
||||
tls_ca_certs: /path/to/ca.crt
|
||||
# Optional: tls_client_cert and tls_client key in order to use self-signed client
|
||||
# certificates (default: None)
|
||||
# NOTE: certificate must not be password-protected
|
||||
# do not set user and password when using a client certificate
|
||||
tls_client_cert: /path/to/client.crt
|
||||
tls_client_key: /path/to/client.key
|
||||
# Optional: tls_insecure (true/false) for enabling TLS verification of
|
||||
# the server hostname in the server certificate (default: None)
|
||||
tls_insecure: false
|
||||
# Optional: interval in seconds for publishing stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
stats_interval: 60
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Detectors configuration. Defaults to a single CPU detector
|
||||
detectors:
|
||||
# Required: name of the detector
|
||||
detector_name:
|
||||
# Required: type of the detector
|
||||
# Frigate provided types include 'cpu', 'edgetpu', 'openvino' and 'tensorrt' (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Additional detector types can also be plugged in.
|
||||
# Detectors may require additional configuration.
|
||||
# Refer to the Detectors configuration page for more information.
|
||||
type: cpu
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Database configuration
|
||||
database:
|
||||
# The path to store the SQLite DB (default: shown below)
|
||||
path: /config/frigate.db
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: model modifications
|
||||
model:
|
||||
# Optional: path to the model (default: automatic based on detector)
|
||||
path: /edgetpu_model.tflite
|
||||
# Optional: path to the labelmap (default: shown below)
|
||||
labelmap_path: /labelmap.txt
|
||||
# Required: Object detection model input width (default: shown below)
|
||||
width: 320
|
||||
# Required: Object detection model input height (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 320
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model input colorspace
|
||||
# Valid values are rgb, bgr, or yuv. (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_pixel_format: rgb
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model input tensor format
|
||||
# Valid values are nhwc or nchw (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_tensor: nhwc
|
||||
# Optional: Object detection model type, currently only used with the OpenVINO detector
|
||||
# Valid values are ssd, yolox, yolov5, or yolov8 (default: shown below)
|
||||
model_type: ssd
|
||||
# Optional: Label name modifications. These are merged into the standard labelmap.
|
||||
labelmap:
|
||||
2: vehicle
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Audio Events Configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
audio:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable audio events (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: Configure the amount of seconds without detected audio to end the event (default: shown below)
|
||||
max_not_heard: 30
|
||||
# Optional: Configure the min rms volume required to run audio detection (default: shown below)
|
||||
# As a rule of thumb:
|
||||
# - 200 - high sensitivity
|
||||
# - 500 - medium sensitivity
|
||||
# - 1000 - low sensitivity
|
||||
min_volume: 500
|
||||
# Optional: Types of audio to listen for (default: shown below)
|
||||
listen:
|
||||
- bark
|
||||
- fire_alarm
|
||||
- scream
|
||||
- speech
|
||||
- yell
|
||||
# Optional: Filters to configure detection.
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
# Label that matches label in listen config.
|
||||
speech:
|
||||
# Minimum score that triggers an audio event (default: shown below)
|
||||
threshold: 0.8
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: logger verbosity settings
|
||||
logger:
|
||||
# Optional: Default log verbosity (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: info
|
||||
# Optional: Component specific logger overrides
|
||||
logs:
|
||||
frigate.event: debug
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: set environment variables
|
||||
environment_vars:
|
||||
EXAMPLE_VAR: value
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: birdseye configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can (enabled, mode) be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable birdseye view (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: Restream birdseye via RTSP (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Enabling this will set birdseye to run 24/7 which may increase CPU usage somewhat.
|
||||
restream: False
|
||||
# Optional: Width of the output resolution (default: shown below)
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
# Optional: Height of the output resolution (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: Encoding quality of the mpeg1 feed (default: shown below)
|
||||
# 1 is the highest quality, and 31 is the lowest. Lower quality feeds utilize less CPU resources.
|
||||
quality: 8
|
||||
# Optional: Mode of the view. Available options are: objects, motion, and continuous
|
||||
# objects - cameras are included if they have had a tracked object within the last 30 seconds
|
||||
# motion - cameras are included if motion was detected in the last 30 seconds
|
||||
# continuous - all cameras are included always
|
||||
mode: objects
|
||||
# Optional: Threshold for camera activity to stop showing camera (default: shown below)
|
||||
inactivity_threshold: 30
|
||||
# Optional: Configure the birdseye layout
|
||||
layout:
|
||||
# Optional: Scaling factor for the layout calculator (default: shown below)
|
||||
scaling_factor: 2.0
|
||||
# Optional: Maximum number of cameras to show at one time, showing the most recent (default: show all cameras)
|
||||
max_cameras: 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: ffmpeg configuration
|
||||
# More information about presets at https://docs.frigate.video/configuration/ffmpeg_presets
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
# Optional: global ffmpeg args (default: shown below)
|
||||
global_args: -hide_banner -loglevel warning -threads 2
|
||||
# Optional: global hwaccel args (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: See hardware acceleration docs for your specific device
|
||||
hwaccel_args: []
|
||||
# Optional: global input args (default: shown below)
|
||||
input_args: preset-rtsp-generic
|
||||
# Optional: global output args
|
||||
output_args:
|
||||
# Optional: output args for detect streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
detect: -threads 2 -f rawvideo -pix_fmt yuv420p
|
||||
# Optional: output args for record streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
record: preset-record-generic
|
||||
# Optional: output args for rtmp streams (default: shown below)
|
||||
rtmp: preset-rtmp-generic
|
||||
# Optional: Time in seconds to wait before ffmpeg retries connecting to the camera. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# If set too low, frigate will retry a connection to the camera's stream too frequently, using up the limited streams some cameras can allow at once
|
||||
# If set too high, then if a ffmpeg crash or camera stream timeout occurs, you could potentially lose up to a maximum of retry_interval second(s) of footage
|
||||
# NOTE: this can be a useful setting for Wireless / Battery cameras to reduce how much footage is potentially lost during a connection timeout.
|
||||
retry_interval: 10
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Detect configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
detect:
|
||||
# Optional: width of the frame for the input with the detect role (default: use native stream resolution)
|
||||
width: 1280
|
||||
# Optional: height of the frame for the input with the detect role (default: use native stream resolution)
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: desired fps for your camera for the input with the detect role (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Recommended value of 5. Ideally, try and reduce your FPS on the camera.
|
||||
fps: 5
|
||||
# Optional: enables detection for the camera (default: True)
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: Number of consecutive detection hits required for an object to be initialized in the tracker. (default: 1/2 the frame rate)
|
||||
min_initialized: 2
|
||||
# Optional: Number of frames without a detection before Frigate considers an object to be gone. (default: 5x the frame rate)
|
||||
max_disappeared: 25
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for stationary object tracking
|
||||
stationary:
|
||||
# Optional: Frequency for confirming stationary objects (default: same as threshold)
|
||||
# When set to 1, object detection will run to confirm the object still exists on every frame.
|
||||
# If set to 10, object detection will run to confirm the object still exists on every 10th frame.
|
||||
interval: 50
|
||||
# Optional: Number of frames without a position change for an object to be considered stationary (default: 10x the frame rate or 10s)
|
||||
threshold: 50
|
||||
# Optional: Define a maximum number of frames for tracking a stationary object (default: not set, track forever)
|
||||
# This can help with false positives for objects that should only be stationary for a limited amount of time.
|
||||
# It can also be used to disable stationary object tracking. For example, you may want to set a value for person, but leave
|
||||
# car at the default.
|
||||
# WARNING: Setting these values overrides default behavior and disables stationary object tracking.
|
||||
# There are very few situations where you would want it disabled. It is NOT recommended to
|
||||
# copy these values from the example config into your config unless you know they are needed.
|
||||
max_frames:
|
||||
# Optional: Default for all object types (default: not set, track forever)
|
||||
default: 3000
|
||||
# Optional: Object specific values
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 1000
|
||||
# Optional: Milliseconds to offset detect annotations by (default: shown below).
|
||||
# There can often be latency between a recording and the detect process,
|
||||
# especially when using separate streams for detect and record.
|
||||
# Use this setting to make the timeline bounding boxes more closely align
|
||||
# with the recording. The value can be positive or negative.
|
||||
# TIP: Imagine there is an event clip with a person walking from left to right.
|
||||
# If the event timeline bounding box is consistently to the left of the person
|
||||
# then the value should be decreased. Similarly, if a person is walking from
|
||||
# left to right and the bounding box is consistently ahead of the person
|
||||
# then the value should be increased.
|
||||
# TIP: This offset is dynamic so you can change the value and it will update existing
|
||||
# events, this makes it easy to tune.
|
||||
# WARNING: Fast moving objects will likely not have the bounding box align.
|
||||
annotation_offset: 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Object configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
# Optional: list of objects to track from labelmap.txt (default: shown below)
|
||||
track:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: mask to prevent all object types from being detected in certain areas (default: no mask)
|
||||
# Checks based on the bottom center of the bounding box of the object.
|
||||
# NOTE: This mask is COMBINED with the object type specific mask below
|
||||
mask: 0,0,1000,0,1000,200,0,200
|
||||
# Optional: filters to reduce false positives for specific object types
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
person:
|
||||
# Optional: minimum width*height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 0)
|
||||
min_area: 5000
|
||||
# Optional: maximum width*height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 24000000)
|
||||
max_area: 100000
|
||||
# Optional: minimum width/height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 0)
|
||||
min_ratio: 0.5
|
||||
# Optional: maximum width/height of the bounding box for the detected object (default: 24000000)
|
||||
max_ratio: 2.0
|
||||
# Optional: minimum score for the object to initiate tracking (default: shown below)
|
||||
min_score: 0.5
|
||||
# Optional: minimum decimal percentage for tracked object's computed score to be considered a true positive (default: shown below)
|
||||
threshold: 0.7
|
||||
# Optional: mask to prevent this object type from being detected in certain areas (default: no mask)
|
||||
# Checks based on the bottom center of the bounding box of the object
|
||||
mask: 0,0,1000,0,1000,200,0,200
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Motion configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
motion:
|
||||
# Optional: The threshold passed to cv2.threshold to determine if a pixel is different enough to be counted as motion. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection less sensitive and decreasing it will make motion detection more sensitive.
|
||||
# The value should be between 1 and 255.
|
||||
threshold: 30
|
||||
# Optional: The percentage of the image used to detect lightning or other substantial changes where motion detection
|
||||
# needs to recalibrate. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will make motion detection more likely to consider lightning or ir mode changes as valid motion.
|
||||
# Decreasing this value will make motion detection more likely to ignore large amounts of motion such as a person approaching
|
||||
# a doorbell camera.
|
||||
lightning_threshold: 0.8
|
||||
# Optional: Minimum size in pixels in the resized motion image that counts as motion (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Increasing this value will prevent smaller areas of motion from being detected. Decreasing will
|
||||
# make motion detection more sensitive to smaller moving objects.
|
||||
# As a rule of thumb:
|
||||
# - 10 - high sensitivity
|
||||
# - 30 - medium sensitivity
|
||||
# - 50 - low sensitivity
|
||||
contour_area: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Alpha value passed to cv2.accumulateWeighted when averaging frames to determine the background (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Higher values mean the current frame impacts the average a lot, and a new object will be averaged into the background faster.
|
||||
# Low values will cause things like moving shadows to be detected as motion for longer.
|
||||
# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/background-subtraction-in-an-image-using-concept-of-running-average/
|
||||
frame_alpha: 0.01
|
||||
# Optional: Height of the resized motion frame (default: 100)
|
||||
# Higher values will result in more granular motion detection at the expense of higher CPU usage.
|
||||
# Lower values result in less CPU, but small changes may not register as motion.
|
||||
frame_height: 100
|
||||
# Optional: motion mask
|
||||
# NOTE: see docs for more detailed info on creating masks
|
||||
mask: 0,900,1080,900,1080,1920,0,1920
|
||||
# Optional: improve contrast (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Enables dynamic contrast improvement. This should help improve night detections at the cost of making motion detection more sensitive
|
||||
# for daytime.
|
||||
improve_contrast: True
|
||||
# Optional: Delay when updating camera motion through MQTT from ON -> OFF (default: shown below).
|
||||
mqtt_off_delay: 30
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Record configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
record:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable recording (default: shown below)
|
||||
# WARNING: If recording is disabled in the config, turning it on via
|
||||
# the UI or MQTT later will have no effect.
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: Number of minutes to wait between cleanup runs (default: shown below)
|
||||
# This can be used to reduce the frequency of deleting recording segments from disk if you want to minimize i/o
|
||||
expire_interval: 60
|
||||
# Optional: Sync recordings with disk on startup and once a day (default: shown below).
|
||||
sync_recordings: False
|
||||
# Optional: Retention settings for recording
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Optional: Number of days to retain recordings regardless of events (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: This should be set to 0 and retention should be defined in events section below
|
||||
# if you only want to retain recordings of events.
|
||||
days: 0
|
||||
# Optional: Mode for retention. Available options are: all, motion, and active_objects
|
||||
# all - save all recording segments regardless of activity
|
||||
# motion - save all recordings segments with any detected motion
|
||||
# active_objects - save all recording segments with active/moving objects
|
||||
# NOTE: this mode only applies when the days setting above is greater than 0
|
||||
mode: all
|
||||
# Optional: Recording Export Settings
|
||||
export:
|
||||
# Optional: Timelapse Output Args (default: shown below).
|
||||
# NOTE: The default args are set to fit 24 hours of recording into 1 hour playback.
|
||||
# See https://stackoverflow.com/a/58268695 for more info on how these args work.
|
||||
# As an example: if you wanted to go from 24 hours to 30 minutes that would be going
|
||||
# from 86400 seconds to 1800 seconds which would be 1800 / 86400 = 0.02.
|
||||
# The -r (framerate) dictates how smooth the output video is.
|
||||
# So the args would be -vf setpts=0.02*PTS -r 30 in that case.
|
||||
timelapse_args: "-vf setpts=0.04*PTS -r 30"
|
||||
# Optional: Event recording settings
|
||||
events:
|
||||
# Optional: Number of seconds before the event to include (default: shown below)
|
||||
pre_capture: 5
|
||||
# Optional: Number of seconds after the event to include (default: shown below)
|
||||
post_capture: 5
|
||||
# Optional: Objects to save recordings for. (default: all tracked objects)
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict recordings to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
# Optional: Retention settings for recordings of events
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Required: Default retention days (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Mode for retention. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# all - save all recording segments for events regardless of activity
|
||||
# motion - save all recordings segments for events with any detected motion
|
||||
# active_objects - save all recording segments for event with active/moving objects
|
||||
#
|
||||
# NOTE: If the retain mode for the camera is more restrictive than the mode configured
|
||||
# here, the segments will already be gone by the time this mode is applied.
|
||||
# For example, if the camera retain mode is "motion", the segments without motion are
|
||||
# never stored, so setting the mode to "all" here won't bring them back.
|
||||
mode: motion
|
||||
# Optional: Per object retention days
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 15
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for the jpg snapshots written to the clips directory for each event
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
snapshots:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable writing jpg snapshot to /media/frigate/clips (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: save a clean PNG copy of the snapshot image (default: shown below)
|
||||
clean_copy: True
|
||||
# Optional: print a timestamp on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
timestamp: False
|
||||
# Optional: draw bounding box on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
bounding_box: True
|
||||
# Optional: crop the snapshot (default: shown below)
|
||||
crop: False
|
||||
# Optional: height to resize the snapshot to (default: original size)
|
||||
height: 175
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict snapshots to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
# Optional: Camera override for retention settings (default: global values)
|
||||
retain:
|
||||
# Required: Default retention days (default: shown below)
|
||||
default: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Per object retention days
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
person: 15
|
||||
# Optional: quality of the encoded jpeg, 0-100 (default: shown below)
|
||||
quality: 70
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: RTMP configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: RTMP is deprecated in favor of restream
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
rtmp:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable the RTMP stream (default: False)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Restream configuration
|
||||
# Uses https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc (v1.8.3)
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: jsmpeg stream configuration for WebUI
|
||||
live:
|
||||
# Optional: Set the name of the stream that should be used for live view
|
||||
# in frigate WebUI. (default: name of camera)
|
||||
stream_name: camera_name
|
||||
# Optional: Set the height of the jsmpeg stream. (default: 720)
|
||||
# This must be less than or equal to the height of the detect stream. Lower resolutions
|
||||
# reduce bandwidth required for viewing the jsmpeg stream. Width is computed to match known aspect ratio.
|
||||
height: 720
|
||||
# Optional: Set the encode quality of the jsmpeg stream (default: shown below)
|
||||
# 1 is the highest quality, and 31 is the lowest. Lower quality feeds utilize less CPU resources.
|
||||
quality: 8
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: in-feed timestamp style configuration
|
||||
# NOTE: Can be overridden at the camera level
|
||||
timestamp_style:
|
||||
# Optional: Position of the timestamp (default: shown below)
|
||||
# "tl" (top left), "tr" (top right), "bl" (bottom left), "br" (bottom right)
|
||||
position: "tl"
|
||||
# Optional: Format specifier conform to the Python package "datetime" (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Additional Examples:
|
||||
# german: "%d.%m.%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
format: "%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
# Optional: Color of font
|
||||
color:
|
||||
# All Required when color is specified (default: shown below)
|
||||
red: 255
|
||||
green: 255
|
||||
blue: 255
|
||||
# Optional: Line thickness of font (default: shown below)
|
||||
thickness: 2
|
||||
# Optional: Effect of lettering (default: shown below)
|
||||
# None (No effect),
|
||||
# "solid" (solid background in inverse color of font)
|
||||
# "shadow" (shadow for font)
|
||||
effect: None
|
||||
|
||||
# Required
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
# Required: name of the camera
|
||||
back:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable/Disable the camera (default: shown below).
|
||||
# If disabled: config is used but no live stream and no capture etc.
|
||||
# Events/Recordings are still viewable.
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Required: ffmpeg settings for the camera
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
# Required: A list of input streams for the camera. See documentation for more information.
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
# Required: the path to the stream
|
||||
# NOTE: path may include environment variables or docker secrets, which must begin with 'FRIGATE_' and be referenced in {}
|
||||
- path: rtsp://viewer:{FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD}@10.0.10.10:554/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=2
|
||||
# Required: list of roles for this stream. valid values are: audio,detect,record,rtmp
|
||||
# NOTICE: In addition to assigning the audio, record, and rtmp roles,
|
||||
# they must also be enabled in the camera config.
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- audio
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- rtmp
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific global args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# global_args:
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific hwaccel args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# hwaccel_args:
|
||||
# Optional: stream specific input args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# input_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific global args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# global_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific hwaccel args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# hwaccel_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific input args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# input_args:
|
||||
# Optional: camera specific output args (default: inherit)
|
||||
# output_args:
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: timeout for highest scoring image before allowing it
|
||||
# to be replaced by a newer image. (default: shown below)
|
||||
best_image_timeout: 60
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: URL to visit the camera web UI directly from the system page. Might not be available on every camera.
|
||||
webui_url: ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: zones for this camera
|
||||
zones:
|
||||
# Required: name of the zone
|
||||
# NOTE: This must be different than any camera names, but can match with another zone on another
|
||||
# camera.
|
||||
front_steps:
|
||||
# Required: List of x,y coordinates to define the polygon of the zone.
|
||||
# NOTE: Presence in a zone is evaluated only based on the bottom center of the objects bounding box.
|
||||
coordinates: 545,1077,747,939,788,805
|
||||
# Optional: Number of consecutive frames required for object to be considered present in the zone (default: shown below).
|
||||
inertia: 3
|
||||
# Optional: List of objects that can trigger this zone (default: all tracked objects)
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Optional: Zone level object filters.
|
||||
# NOTE: The global and camera filters are applied upstream.
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
person:
|
||||
min_area: 5000
|
||||
max_area: 100000
|
||||
threshold: 0.7
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for the jpg snapshots published via MQTT
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
# Optional: Enable publishing snapshot via mqtt for camera (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: Only applies to publishing image data to MQTT via 'frigate/<camera_name>/<object_name>/snapshot'.
|
||||
# All other messages will still be published.
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
# Optional: print a timestamp on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
timestamp: True
|
||||
# Optional: draw bounding box on the snapshots (default: shown below)
|
||||
bounding_box: True
|
||||
# Optional: crop the snapshot (default: shown below)
|
||||
crop: True
|
||||
# Optional: height to resize the snapshot to (default: shown below)
|
||||
height: 270
|
||||
# Optional: jpeg encode quality (default: shown below)
|
||||
quality: 70
|
||||
# Optional: Restrict mqtt messages to objects that entered any of the listed zones (default: no required zones)
|
||||
required_zones: []
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for how camera is handled in the GUI.
|
||||
ui:
|
||||
# Optional: Adjust sort order of cameras in the UI. Larger numbers come later (default: shown below)
|
||||
# By default the cameras are sorted alphabetically.
|
||||
order: 0
|
||||
# Optional: Whether or not to show the camera in the Frigate UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
dashboard: True
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: connect to ONVIF camera
|
||||
# to enable PTZ controls.
|
||||
onvif:
|
||||
# Required: host of the camera being connected to.
|
||||
host: 0.0.0.0
|
||||
# Optional: ONVIF port for device (default: shown below).
|
||||
port: 8000
|
||||
# Optional: username for login.
|
||||
# NOTE: Some devices require admin to access ONVIF.
|
||||
user: admin
|
||||
# Optional: password for login.
|
||||
password: admin
|
||||
# Optional: PTZ camera object autotracking. Keeps a moving object in
|
||||
# the center of the frame by automatically moving the PTZ camera.
|
||||
autotracking:
|
||||
# Optional: enable/disable object autotracking. (default: shown below)
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
# Optional: calibrate the camera on startup (default: shown below)
|
||||
# A calibration will move the PTZ in increments and measure the time it takes to move.
|
||||
# The results are used to help estimate the position of tracked objects after a camera move.
|
||||
# Frigate will update your config file automatically after a calibration with
|
||||
# a "movement_weights" entry for the camera. You should then set calibrate_on_startup to False.
|
||||
calibrate_on_startup: False
|
||||
# Optional: the mode to use for zooming in/out on objects during autotracking. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# Available options are: disabled, absolute, and relative
|
||||
# disabled - don't zoom in/out on autotracked objects, use pan/tilt only
|
||||
# absolute - use absolute zooming (supported by most PTZ capable cameras)
|
||||
# relative - use relative zooming (not supported on all PTZs, but makes concurrent pan/tilt/zoom movements)
|
||||
zooming: disabled
|
||||
# Optional: A value to change the behavior of zooming on autotracked objects. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# A lower value will keep more of the scene in view around a tracked object.
|
||||
# A higher value will zoom in more on a tracked object, but Frigate may lose tracking more quickly.
|
||||
# The value should be between 0.1 and 0.75
|
||||
zoom_factor: 0.3
|
||||
# Optional: list of objects to track from labelmap.txt (default: shown below)
|
||||
track:
|
||||
- person
|
||||
# Required: Begin automatically tracking an object when it enters any of the listed zones.
|
||||
required_zones:
|
||||
- zone_name
|
||||
# Required: Name of ONVIF preset in camera's firmware to return to when tracking is over. (default: shown below)
|
||||
return_preset: home
|
||||
# Optional: Seconds to delay before returning to preset. (default: shown below)
|
||||
timeout: 10
|
||||
# Optional: Values generated automatically by a camera calibration. Do not modify these manually. (default: shown below)
|
||||
movement_weights: []
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Configuration for how to sort the cameras in the Birdseye view.
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
# Optional: Adjust sort order of cameras in the Birdseye view. Larger numbers come later (default: shown below)
|
||||
# By default the cameras are sorted alphabetically.
|
||||
order: 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional
|
||||
ui:
|
||||
# Optional: Set the default live mode for cameras in the UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
live_mode: mse
|
||||
# Optional: Set a timezone to use in the UI (default: use browser local time)
|
||||
# timezone: America/Denver
|
||||
# Optional: Use an experimental recordings / camera view UI (default: shown below)
|
||||
use_experimental: False
|
||||
# Optional: Set the time format used.
|
||||
# Options are browser, 12hour, or 24hour (default: shown below)
|
||||
time_format: browser
|
||||
# Optional: Set the date style for a specified length.
|
||||
# Options are: full, long, medium, short
|
||||
# Examples:
|
||||
# short: 2/11/23
|
||||
# medium: Feb 11, 2023
|
||||
# full: Saturday, February 11, 2023
|
||||
# (default: shown below).
|
||||
date_style: short
|
||||
# Optional: Set the time style for a specified length.
|
||||
# Options are: full, long, medium, short
|
||||
# Examples:
|
||||
# short: 8:14 PM
|
||||
# medium: 8:15:22 PM
|
||||
# full: 8:15:22 PM Mountain Standard Time
|
||||
# (default: shown below).
|
||||
time_style: medium
|
||||
# Optional: Ability to manually override the date / time styling to use strftime format
|
||||
# https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Formatting-Calendar-Time.html
|
||||
# possible values are shown above (default: not set)
|
||||
strftime_fmt: "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M"
|
||||
|
||||
# Optional: Telemetry configuration
|
||||
telemetry:
|
||||
# Optional: Enabled network interfaces for bandwidth stats monitoring (default: empty list, let nethogs search all)
|
||||
network_interfaces:
|
||||
- eth
|
||||
- enp
|
||||
- eno
|
||||
- ens
|
||||
- wl
|
||||
- lo
|
||||
# Optional: Configure system stats
|
||||
stats:
|
||||
# Enable AMD GPU stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
amd_gpu_stats: True
|
||||
# Enable Intel GPU stats (default: shown below)
|
||||
intel_gpu_stats: True
|
||||
# Enable network bandwidth stats monitoring for camera ffmpeg processes, go2rtc, and object detectors. (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: The container must either be privileged or have cap_net_admin, cap_net_raw capabilities enabled.
|
||||
network_bandwidth: False
|
||||
# Optional: Enable the latest version outbound check (default: shown below)
|
||||
# NOTE: If you use the HomeAssistant integration, disabling this will prevent it from reporting new versions
|
||||
version_check: True
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -7,17 +7,18 @@ title: Restream
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate can restream your video feed as an RTSP feed for other applications such as Home Assistant to utilize it at `rtsp://<frigate_host>:8554/<camera_name>`. Port 8554 must be open. [This allows you to use a video feed for detection in Frigate and Home Assistant live view at the same time without having to make two separate connections to the camera](#reduce-connections-to-camera). The video feed is copied from the original video feed directly to avoid re-encoding. This feed does not include any annotation by Frigate.
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate uses [go2rtc](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1) to provide its restream and MSE/WebRTC capabilities. The go2rtc config is hosted at the `go2rtc` in the config, see [go2rtc docs](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#configuration) for more advanced configurations and features.
|
||||
Frigate uses [go2rtc](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4) to provide its restream and MSE/WebRTC capabilities. The go2rtc config is hosted at the `go2rtc` in the config, see [go2rtc docs](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#configuration) for more advanced configurations and features.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
You can access the go2rtc webUI at `http://frigate_ip:5000/live/webrtc` which can be helpful to debug as well as provide useful information about your camera streams.
|
||||
You can access the go2rtc stream info at `http://frigate_ip:5000/api/go2rtc/streams` which can be helpful to debug as well as provide useful information about your camera streams.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdseye Restream
|
||||
|
||||
Birdseye RTSP restream can be accessed at `rtsp://<frigate_host>:8554/birdseye`. Enabling the birdseye restream will cause birdseye to run 24/7 which may increase CPU usage somewhat.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
birdseye:
|
||||
restream: true
|
||||
@@ -32,15 +33,14 @@ go2rtc:
|
||||
rtsp:
|
||||
username: "admin"
|
||||
password: "pass"
|
||||
streams:
|
||||
...
|
||||
streams: ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE:** This does not apply to localhost requests, there is no need to provide credentials when using the restream as a source for frigate cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
## RTMP (Deprecated)
|
||||
|
||||
In previous Frigate versions RTMP was used for re-streaming. RTMP has disadvantages however including being incompatible with H.265, high bitrates, and certain audio codecs. RTMP is deprecated and it is recommended to move to the new restream role.
|
||||
In previous Frigate versions RTMP was used for re-streaming. RTMP has disadvantages however including being incompatible with H.265, high bitrates, and certain audio codecs. RTMP is deprecated and it is recommended use the built in go2rtc config for restreaming.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reduce Connections To Camera
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ cameras:
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Restream Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
The [exec](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#source-exec) source in go2rtc can be used for custom ffmpeg commands. An example is below:
|
||||
The [exec](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#source-exec) source in go2rtc can be used for custom ffmpeg commands. An example is below:
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: The output will need to be passed with two curly braces `{{output}}`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,6 +23,34 @@ NOTE: There is no way to disable stationary object tracking with this value.
|
||||
|
||||
`threshold` is the number of frames an object needs to remain relatively still before it is considered stationary.
|
||||
|
||||
## Avoiding stationary objects
|
||||
## Handling stationary objects
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, like a driveway, you may prefer to only have an event when a car is coming & going vs a constant event of it stationary in the driveway. [This docs sections](../guides/stationary_objects.md) explains how to approach that scenario.
|
||||
In some cases, like a driveway, you may prefer to only have an event when a car is coming & going vs a constant event of it stationary in the driveway. You can reference [this guide](../guides/parked_cars.md) for recommended approaches.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why does Frigate track stationary objects?
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate didn't always track stationary objects. In fact, it didn't even track objects at all initially.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at an example use case: I want to record any cars that enter my driveway.
|
||||
|
||||
One might simply think "Why not just run object detection any time there is motion around the driveway area and notify if the bounding box is in that zone?"
|
||||
|
||||
With that approach, what video is related to the car that entered the driveway? Did it come from the left or right? Was it parked across the street for an hour before turning into the driveway? One approach is to just record 24/7 or for motion (on any changed changed pixels) and not attempt to do that at all. This is what most other NVRs do. Just don't even try to identify a start and end for that object since it's hard and you will be wrong some portion of the time.
|
||||
|
||||
Couldn't you just look at when motion stopped and started? Motion for a video feed is nothing more than looking for pixels that are different than they were in previous frames. If the car entered the driveway while someone was mowing the grass, how would you know which motion was for the car and which was for the person when they mow along the driveway or street? What if another car was driving the other direction on the street? Or what if its a windy day and the bush by your mailbox is blowing around?
|
||||
|
||||
In order to do it more accurately, you need to identify objects and track them with a unique id. In each subsequent frame, everything has moved a little and you need to determine which bounding boxes go with each object from the previous frame.
|
||||
|
||||
Tracking objects across frames is a challenging problem. Especially if you want to do it in real time. There are entire competitions for research algorithms to see which of them can do it the most accurately. Zero of them are accurate 100% of the time. Even the ones that can't do it in realtime. There is always an error rate in the algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
Now consider that the car is driving down a street that has other cars parked along it. It will drive behind some of these cars and in front of others. There may even be a car driving the opposite direction.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's assume for now that we are NOT already tracking two parked cars on the street or the car parked in the driveway, ie, there is no stationary object tracking.
|
||||
|
||||
As the car you are tracking approaches an area with 2 cars parked, the headlights reflect off the parked cars and the car parked in your driveway. The pixel values are different in that area, so there is motion detected. Object detection runs and identifies the remaining 3 cars. In the previous frame, you had a single bounding box from the car you are tracking. Now you have 4. The original object, the 2 cars on the street and the one in your driveway.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have to determine which of the bounding boxes in this frame should be matched to the tracking id from the previous frame where you only had one. Remember, you have never seen these additional 3 cars before, so you know nothing about them. On top of that the bounding box for the car you are tracking has now moved to a new location, so which of the 4 belongs to the car you were originally tracking? The algorithms here are fairly good. They use a Kalman filter to predict the next location of an object using the historical bounding boxes and the bounding box closest to the predicted location is linked. It's right sometimes, but the error rate is going to be high when there are 4 possible bounding boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's assume that those other 3 cars were already being tracked as stationary objects, so the car driving down the street is a new 4th car. The object tracker knows we have had 3 cars and we now have 4. As the new car approaches the parked cars, the bounding boxes for all 4 cars is predicted based on the previous frames. The predicted boxes for the parked cars is pretty much a 100% overlap with the bounding boxes in the new frame. The parked cars are slam dunk matches to the tracking ids they had before and the only one left is the remaining bounding box which gets assigned to the new car. This results in a much lower error rate. Not perfect, but better.
|
||||
|
||||
The most difficult scenario that causes IDs to be assigned incorrectly is when an object completely occludes another object. When a car drives in front of another car and its no longer visible, a bounding box disappeared and it's a bit of a toss up when assigning the id since it's difficult to know which one is in front of the other. This happens for cars passing in front of other cars fairly often. It's something that we want to improve in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,6 +5,9 @@ title: Zones
|
||||
|
||||
Zones allow you to define a specific area of the frame and apply additional filters for object types so you can determine whether or not an object is within a particular area. Presence in a zone is evaluated based on the bottom center of the bounding box for the object. It does not matter how much of the bounding box overlaps with the zone.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the cat in this image is currently in Zone 1, but **not** Zone 2.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Zones cannot have the same name as a camera. If desired, a single zone can include multiple cameras if you have multiple cameras covering the same area by configuring zones with the same name for each camera.
|
||||
|
||||
During testing, enable the Zones option for the debug feed so you can adjust as needed. The zone line will increase in thickness when any object enters the zone.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ The following commands are used inside the container to ensure hardware accelera
|
||||
|
||||
**Raspberry Pi (64bit)**
|
||||
|
||||
This should show <50% CPU in top, and ~80% CPU without `-c:v h264_v4l2m2m`.
|
||||
This should show less than 50% CPU in top, and ~80% CPU without `-c:v h264_v4l2m2m`.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ffmpeg -c:v h264_v4l2m2m -re -stream_loop -1 -i https://streams.videolan.org/ffmpeg/incoming/720p60.mp4 -f rawvideo -pix_fmt yuv420p pipe: > /dev/null
|
||||
@@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ ffmpeg -c:v h264_qsv -re -stream_loop -1 -i https://streams.videolan.org/ffmpeg/
|
||||
|
||||
- [Frigate source code](#frigate-core-web-and-docs)
|
||||
- All [core](#core) prerequisites _or_ another running Frigate instance locally available
|
||||
- Node.js 16
|
||||
- Node.js 20
|
||||
|
||||
### Making changes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -183,7 +183,7 @@ npm run test
|
||||
### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- [Frigate source code](#frigate-core-web-and-docs)
|
||||
- Node.js 16
|
||||
- Node.js 20
|
||||
|
||||
### Making changes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ npm run start
|
||||
|
||||
This command starts a local development server and open up a browser window. Most changes are reflected live without having to restart the server.
|
||||
|
||||
The docs are built using [Docusaurus v2](https://v2.docusaurus.io). Please refer to the Docusaurus docs for more information on how to modify Frigate's documentation.
|
||||
The docs are built using [Docusaurus v3](https://docusaurus.io). Please refer to the Docusaurus docs for more information on how to modify Frigate's documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Build (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
58
docs/docs/frigate/glossary.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: glossary
|
||||
title: Glossary
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The glossary explains terms commonly used in Frigate's documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Bounding Box
|
||||
|
||||
A box returned from the object detection model that outlines an object in the frame. These have multiple colors depending on object type in the debug live view.
|
||||
|
||||
## Event
|
||||
|
||||
The time period starting when a tracked object entered the frame and ending when it left the frame, including any time that the object remained still. Events are saved when it is considered a [true positive](#threshold) and meets the requirements for a snapshot or recording to be saved.
|
||||
|
||||
## False Positive
|
||||
|
||||
An incorrect detection of an object type. For example a dog being detected as a person, a chair being detected as a dog, etc. A person being detected in an area you want to ignore is not a false positive.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mask
|
||||
|
||||
There are two types of masks in Frigate. [See the mask docs for more info](/configuration/masks)
|
||||
|
||||
### Motion Mask
|
||||
|
||||
Motion masks prevent detection of [motion](#motion) in masked areas from triggering Frigate to run object detection, but do not prevent objects from being detected if object detection runs due to motion in nearby areas. For example: camera timestamps, skies, the tops of trees, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Object Mask
|
||||
|
||||
Object filter masks drop any bounding boxes where the bottom center (overlap doesn't matter) is in the masked area. It forces them to be considered a [false positive](#false_positive) so that they are ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
## Min Score
|
||||
|
||||
The lowest score that an object can be detected with during tracking, any detection with a lower score will be assumed to be a false positive
|
||||
|
||||
## Motion
|
||||
|
||||
When pixels in the current camera frame are different than previous frames. When many nearby pixels are different in the current frame they grouped together and indicated with a red motion box in the live debug view. [See the motion detection docs for more info](/configuration/motion_detection)
|
||||
|
||||
## Region
|
||||
|
||||
A portion of the camera frame that is sent to object detection, regions can be sent due to motion, active objects, or occasionally for stationary objects. These are represented by green boxes in the debug live view.
|
||||
|
||||
## Snapshot Score
|
||||
|
||||
The score shown in a snapshot is the score of that object at that specific moment in time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Threshold
|
||||
|
||||
The threshold is the median score that an object must reach in order to be considered a true positive.
|
||||
|
||||
## Top Score
|
||||
|
||||
The top score for an object is the highest median score for an object.
|
||||
|
||||
## Zone
|
||||
|
||||
Zones are areas of interest, zones can be used for notifications and for limiting the areas where Frigate will create an [event](#event). [See the zone docs for more info](/configuration/zones)
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Cameras that output H.264 video and AAC audio will offer the most compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
I recommend Dahua, Hikvision, and Amcrest in that order. Dahua edges out Hikvision because they are easier to find and order, not because they are better cameras. I personally use Dahua cameras because they are easier to purchase directly. In my experience Dahua and Hikvision both have multiple streams with configurable resolutions and frame rates and rock solid streams. They also both have models with large sensors well known for excellent image quality at night. Not all the models are equal. Larger sensors are better than higher resolutions; especially at night. Amcrest is the fallback recommendation because they are rebranded Dahuas. They are rebranding the lower end models with smaller sensors or less configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
Many users have reported various issues with Reolink cameras, so I do not recommend them. If you are using Reolink, I suggest the [Reolink specific configuration](../configuration/camera_specific.md#reolink-410520-possibly-others). Wifi cameras are also not recommended. Their streams are less reliable and cause connection loss and/or lost video data.
|
||||
Many users have reported various issues with Reolink cameras, so I do not recommend them. If you are using Reolink, I suggest the [Reolink specific configuration](../configuration/camera_specific.md#reolink-cameras). Wifi cameras are also not recommended. Their streams are less reliable and cause connection loss and/or lost video data.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the camera's I recommend:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,13 +21,12 @@ I may earn a small commission for my endorsement, recommendation, testimonial, o
|
||||
|
||||
## Server
|
||||
|
||||
My current favorite is the Minisforum GK41 because of the dual NICs that allow you to setup a dedicated private network for your cameras where they can be blocked from accessing the internet. There are many used workstation options on eBay that work very well. Anything with an Intel CPU and capable of running Debian should work fine. As a bonus, you may want to look for devices with a M.2 or PCIe express slot that is compatible with the Google Coral. I may earn a small commission for my endorsement, recommendation, testimonial, or link to any products or services from this website.
|
||||
My current favorite is the Beelink EQ12 because of the efficient N100 CPU and dual NICs that allow you to setup a dedicated private network for your cameras where they can be blocked from accessing the internet. There are many used workstation options on eBay that work very well. Anything with an Intel CPU and capable of running Debian should work fine. As a bonus, you may want to look for devices with a M.2 or PCIe express slot that is compatible with the Google Coral. I may earn a small commission for my endorsement, recommendation, testimonial, or link to any products or services from this website.
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Coral Inference Speed | Coral Compatibility | Notes |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Odyssey X86 Blue J4125 (<a href="https://amzn.to/3oH4BKi" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">Amazon</a>) (<a href="https://www.seeedstudio.com/Frigate-NVR-with-Odyssey-Blue-and-Coral-USB-Accelerator.html?utm_source=Frigate" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">SeeedStudio</a>) | 9-10ms | M.2 B+M, USB | Dual gigabit NICs for easy isolated camera network. Easily handles several 1080p cameras. |
|
||||
| Minisforum GK41 (<a href="https://amzn.to/3ptnb8D" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">Amazon</a>) | 9-10ms | USB | Dual gigabit NICs for easy isolated camera network. Easily handles several 1080p cameras. |
|
||||
| Intel NUC (<a href="https://amzn.to/3psFlHi" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">Amazon</a>) | 8-10ms | USB | Overkill for most, but great performance. Can handle many cameras at 5fps depending on typical amounts of motion. Requires extra parts. |
|
||||
| Name | Coral Inference Speed | Coral Compatibility | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Beelink EQ12 (<a href="https://amzn.to/3OlTMJY" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">Amazon</a>) | 5-10ms | USB | Dual gigabit NICs for easy isolated camera network. Easily handles several 1080p cameras. |
|
||||
| Intel NUC (<a href="https://amzn.to/3psFlHi" target="_blank" rel="nofollow noopener sponsored">Amazon</a>) | 5-10ms | USB | Overkill for most, but great performance. Can handle many cameras at 5fps depending on typical amounts of motion. Requires extra parts. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Detectors
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,14 +40,15 @@ The USB version is compatible with the widest variety of hardware and does not r
|
||||
|
||||
The PCIe and M.2 versions require installation of a driver on the host. Follow the instructions for your version from https://coral.ai
|
||||
|
||||
A single Coral can handle many cameras and will be sufficient for the majority of users. You can calculate the maximum performance of your Coral based on the inference speed reported by Frigate. With an inference speed of 10, your Coral will top out at `1000/10=100`, or 100 frames per second. If your detection fps is regularly getting close to that, you should first consider tuning motion masks. If those are already properly configured, a second Coral may be needed.
|
||||
A single Coral can handle many cameras using the default model and will be sufficient for the majority of users. You can calculate the maximum performance of your Coral based on the inference speed reported by Frigate. With an inference speed of 10, your Coral will top out at `1000/10=100`, or 100 frames per second. If your detection fps is regularly getting close to that, you should first consider tuning motion masks. If those are already properly configured, a second Coral may be needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenVino
|
||||
### OpenVINO
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenVINO detector type is able to run on:
|
||||
|
||||
- 6th Gen Intel Platforms and newer that have an iGPU
|
||||
- x86 & Arm64 hosts with VPU Hardware (ex: Intel NCS2)
|
||||
- Most modern AMD CPUs (though this is officially not supported by Intel)
|
||||
|
||||
More information is available [in the detector docs](/configuration/object_detectors#openvino-detector)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,6 +95,17 @@ Frigate supports all Jetson boards, from the inexpensive Jetson Nano to the powe
|
||||
|
||||
Inference speed will vary depending on the YOLO model, jetson platform and jetson nvpmodel (GPU/DLA/EMC clock speed). It is typically 20-40 ms for most models. The DLA is more efficient than the GPU, but not faster, so using the DLA will reduce power consumption but will slightly increase inference time.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Rockchip SoC
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate supports SBCs with the following Rockchip SoCs:
|
||||
|
||||
- RK3566/RK3568
|
||||
- RK3588/RK3588S
|
||||
- RV1103/RV1106
|
||||
- RK3562
|
||||
|
||||
Using the yolov8n model and an Orange Pi 5 Plus with RK3588 SoC inference speeds vary between 20 - 25 ms.
|
||||
|
||||
## What does Frigate use the CPU for and what does it use a detector for? (ELI5 Version)
|
||||
|
||||
This is taken from a [user question on reddit](https://www.reddit.com/r/homeassistant/comments/q8mgau/comment/hgqbxh5/?utm_source=share&utm_medium=web2x&context=3). Modified slightly for clarity.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,6 +47,12 @@ services:
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
Users of the Snapcraft build of Docker cannot use storage locations outside your $HOME folder.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Calculating required shm-size
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate utilizes shared memory to store frames during processing. The default `shm-size` provided by Docker is **64MB**.
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +78,6 @@ $ python -c 'print("{:.2f}MB".format(((1280 * 720 * 1.5 * 9 + 270480) / 1048576)
|
||||
|
||||
The shm size cannot be set per container for Home Assistant add-ons. However, this is probably not required since by default Home Assistant Supervisor allocates `/dev/shm` with half the size of your total memory. If your machine has 8GB of memory, chances are that Frigate will have access to up to 4GB without any additional configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Raspberry Pi 3/4
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the Raspberry Pi limits the amount of memory available to the GPU. In order to use ffmpeg hardware acceleration, you must increase the available memory by setting `gpu_mem` to the maximum recommended value in `config.txt` as described in the [official docs](https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/computers/config_txt.html#memory-options).
|
||||
@@ -81,22 +86,7 @@ Additionally, the USB Coral draws a considerable amount of power. If using any o
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Running in Docker with compose is the recommended install method:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
The following officially supported builds are available:
|
||||
|
||||
`ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable` - Standard Frigate build for amd64 & RPi Optimized Frigate build for arm64
|
||||
`ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-standard-arm64` - Standard Frigate build for arm64
|
||||
`ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-tensorrt` - Frigate build specific for amd64 devices running an nvidia GPU
|
||||
|
||||
The following community supported builds are available:
|
||||
|
||||
`ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-tensorrt-jp5` - Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 5
|
||||
`ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-tensorrt-jp4` - Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 4.6
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
Running in Docker with compose is the recommended install method.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3.9"
|
||||
@@ -108,9 +98,10 @@ services:
|
||||
image: ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
shm_size: "64mb" # update for your cameras based on calculation above
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb # passes the USB Coral, needs to be modified for other versions
|
||||
- /dev/apex_0:/dev/apex_0 # passes a PCIe Coral, follow driver instructions here https://coral.ai/docs/m2/get-started/#2a-on-linux
|
||||
- /dev/dri/renderD128 # for intel hwaccel, needs to be updated for your hardware
|
||||
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb # Passes the USB Coral, needs to be modified for other versions
|
||||
- /dev/apex_0:/dev/apex_0 # Passes a PCIe Coral, follow driver instructions here https://coral.ai/docs/m2/get-started/#2a-on-linux
|
||||
- /dev/video11:/dev/video11 # For Raspberry Pi 4B
|
||||
- /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128 # For intel hwaccel, needs to be updated for your hardware
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
|
||||
- /path/to/your/config:/config
|
||||
@@ -149,6 +140,18 @@ docker run -d \
|
||||
ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The official docker image tags for the current stable version are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `stable` - Standard Frigate build for amd64 & RPi Optimized Frigate build for arm64
|
||||
- `stable-standard-arm64` - Standard Frigate build for arm64
|
||||
- `stable-tensorrt` - Frigate build specific for amd64 devices running an nvidia GPU
|
||||
|
||||
The community supported docker image tags for the current stable version are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `stable-tensorrt-jp5` - Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 5
|
||||
- `stable-tensorrt-jp4` - Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 4.6
|
||||
- `stable-rk` - Frigate build for SBCs with Rockchip SoC
|
||||
|
||||
## Home Assistant Addon
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
@@ -156,6 +159,7 @@ docker run -d \
|
||||
As of HomeAssistant OS 10.2 and Core 2023.6 defining separate network storage for media is supported.
|
||||
|
||||
There are important limitations in Home Assistant Operating System to be aware of:
|
||||
|
||||
- Separate local storage for media is not yet supported by Home Assistant
|
||||
- AMD GPUs are not supported because HA OS does not include the mesa driver.
|
||||
- Nvidia GPUs are not supported because addons do not support the nvidia runtime.
|
||||
@@ -210,7 +214,6 @@ If you're running Frigate on a rack mounted server and want to passthough the Go
|
||||
|
||||
These settings were tested on DSM 7.1.1-42962 Update 4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**General:**
|
||||
|
||||
The `Execute container using high privilege` option needs to be enabled in order to give the frigate container the elevated privileges it may need.
|
||||
@@ -219,14 +222,12 @@ The `Enable auto-restart` option can be enabled if you want the container to aut
|
||||
|
||||
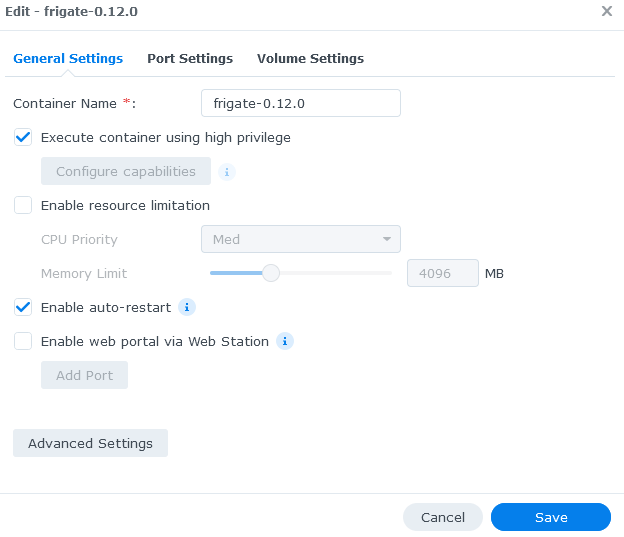
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Advanced Settings:**
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the password template feature, you should add the "FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD" environment variable and set it to your preferred password under advanced settings. The rest of the environment variables should be left as default for now.
|
||||
|
||||
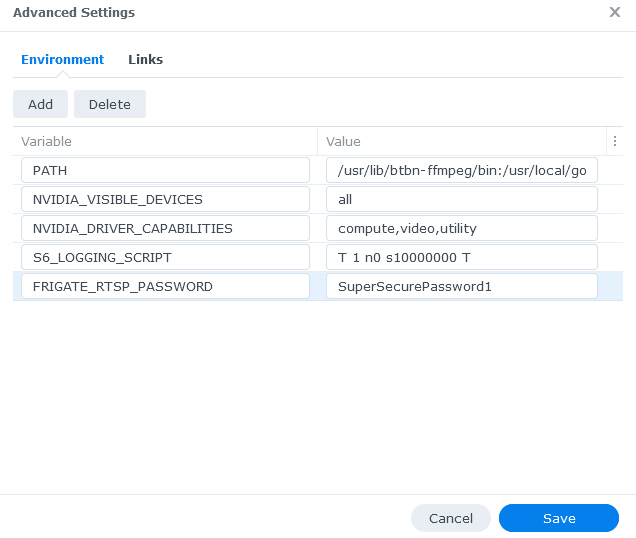
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Port Settings:**
|
||||
|
||||
The network mode should be set to `bridge`. You need to map the default frigate container ports to your local Synology NAS ports that you want to use to access Frigate.
|
||||
@@ -235,7 +236,6 @@ There may be other services running on your NAS that are using the same ports th
|
||||
|
||||
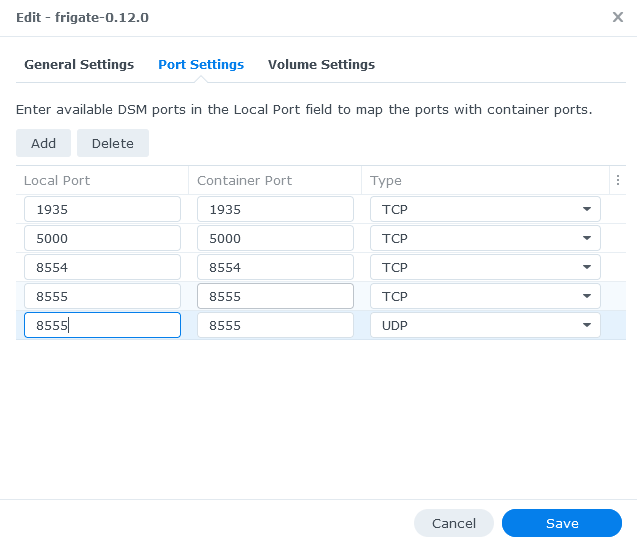
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Volume Settings:**
|
||||
|
||||
You need to configure 2 paths:
|
||||
@@ -249,14 +249,15 @@ You need to configure 2 paths:
|
||||
|
||||
These instructions were tested on a QNAP with an Intel J3455 CPU and 16G RAM, running QTS 4.5.4.2117.
|
||||
|
||||
QNAP has a graphic tool named Container Station to install and manage docker containers. However, there are two limitations with Container Station that make it unsuitable to install Frigate:
|
||||
QNAP has a graphic tool named Container Station to install and manage docker containers. However, there are two limitations with Container Station that make it unsuitable to install Frigate:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Container Station does not incorporate GitHub Container Registry (ghcr), which hosts Frigate docker image version 0.12.0 and above.
|
||||
2. Container Station uses default 64 Mb shared memory size (shm-size), and does not have a mechanism to adjust it. Frigate requires a larger shm-size to be able to work properly with more than two high resolution cameras.
|
||||
2. Container Station uses default 64 Mb shared memory size (shm-size), and does not have a mechanism to adjust it. Frigate requires a larger shm-size to be able to work properly with more than two high resolution cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
Because of above limitations, the installation has to be done from command line. Here are the steps:
|
||||
Because of above limitations, the installation has to be done from command line. Here are the steps:
|
||||
|
||||
**Preparation**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Container Station from QNAP App Center if it is not installed.
|
||||
2. Enable ssh on your QNAP (please do an Internet search on how to do this).
|
||||
3. Prepare Frigate config file, name it `config.yml`.
|
||||
@@ -267,7 +268,8 @@ Because of above limitations, the installation has to be done from command line.
|
||||
**Installation**
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following commands to install Frigate (using `stable` version as example):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# Download Frigate image
|
||||
docker pull ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
# Create directory to host Frigate config file on QNAP file system.
|
||||
@@ -308,6 +310,4 @@ docker run \
|
||||
ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Log into QNAP, open Container Station. Frigate docker container should be listed under 'Overview' and running. Visit Frigate Web UI by clicking Frigate docker, and then clicking the URL shown at the top of the detail page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Log into QNAP, open Container Station. Frigate docker container should be listed under 'Overview' and running. Visit Frigate Web UI by clicking Frigate docker, and then clicking the URL shown at the top of the detail page.
|
||||
|
||||
67
docs/docs/frigate/video_pipeline.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: video_pipeline
|
||||
title: Video pipeline
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate uses a sophisticated video pipeline that starts with the camera feed and progressively applies transformations to it (e.g. decoding, motion detection, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide provides an overview to help users understand some of the key Frigate concepts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
At a high level, there are five processing steps that could be applied to a camera feed
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
%%{init: {"themeVariables": {"edgeLabelBackground": "transparent"}}}%%
|
||||
|
||||
flowchart LR
|
||||
Feed(Feed\nacquisition) --> Decode(Video\ndecoding)
|
||||
Decode --> Motion(Motion\ndetection)
|
||||
Motion --> Object(Object\ndetection)
|
||||
Feed --> Recording(Recording\nand\nvisualization)
|
||||
Motion --> Recording
|
||||
Object --> Recording
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As the diagram shows, all feeds first need to be acquired. Depending on the data source, it may be as simple as using FFmpeg to connect to an RTSP source via TCP or something more involved like connecting to an Apple Homekit camera using go2rtc. A single camera can produce a main (i.e. high resolution) and a sub (i.e. lower resolution) video feed.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, the sub-feed will be decoded to produce full-frame images. As part of this process, the resolution may be downscaled and an image sampling frequency may be imposed (e.g. keep 5 frames per second).
|
||||
|
||||
These frames will then be compared over time to detect movement areas (a.k.a. motion boxes). These motion boxes are combined into motion regions and are analyzed by a machine learning model to detect known objects. Finally, the snapshot and recording retention config will decide what video clips and events should be saved.
|
||||
|
||||
## Detailed view of the video pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The following diagram adds a lot more detail than the simple view explained before. The goal is to show the detailed data paths between the processing steps.
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
%%{init: {"themeVariables": {"edgeLabelBackground": "transparent"}}}%%
|
||||
|
||||
flowchart TD
|
||||
RecStore[(Recording\nstore)]
|
||||
SnapStore[(Snapshot\nstore)]
|
||||
|
||||
subgraph Acquisition
|
||||
Cam["Camera"] -->|FFmpeg supported| Stream
|
||||
Cam -->|"Other streaming\nprotocols"| go2rtc
|
||||
go2rtc("go2rtc") --> Stream
|
||||
Stream[Capture main and\nsub streams] --> |detect stream|Decode(Decode and\ndownscale)
|
||||
end
|
||||
subgraph Motion
|
||||
Decode --> MotionM(Apply\nmotion masks)
|
||||
MotionM --> MotionD(Motion\ndetection)
|
||||
end
|
||||
subgraph Detection
|
||||
MotionD --> |motion regions| ObjectD(Object detection)
|
||||
Decode --> ObjectD
|
||||
ObjectD --> ObjectFilter(Apply object filters & zones)
|
||||
ObjectFilter --> ObjectZ(Track objects)
|
||||
end
|
||||
Decode --> |decoded frames|Birdseye
|
||||
MotionD --> |motion event|Birdseye
|
||||
ObjectZ --> |object event|Birdseye
|
||||
|
||||
MotionD --> |"video segments\n(retain motion)"|RecStore
|
||||
ObjectZ --> |detection clip|RecStore
|
||||
Stream -->|"video segments\n(retain all)"| RecStore
|
||||
ObjectZ --> |detection snapshot|SnapStore
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -3,6 +3,8 @@ id: configuring_go2rtc
|
||||
title: Configuring go2rtc
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuring go2rtc
|
||||
|
||||
Use of the bundled go2rtc is optional. You can still configure FFmpeg to connect directly to your cameras. However, adding go2rtc to your configuration is required for the following features:
|
||||
|
||||
- WebRTC or MSE for live viewing with higher resolutions and frame rates than the jsmpeg stream which is limited to the detect stream
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +13,7 @@ Use of the bundled go2rtc is optional. You can still configure FFmpeg to connect
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup a go2rtc stream
|
||||
|
||||
First, you will want to configure go2rtc to connect to your camera stream by adding the stream you want to use for live view in your Frigate config file. If you set the stream name under go2rtc to match the name of your camera, it will automatically be mapped and you will get additional live view options for the camera. Avoid changing any other parts of your config at this step. Note that go2rtc supports [many different stream types](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#module-streams), not just rtsp.
|
||||
First, you will want to configure go2rtc to connect to your camera stream by adding the stream you want to use for live view in your Frigate config file. If you set the stream name under go2rtc to match the name of your camera, it will automatically be mapped and you will get additional live view options for the camera. Avoid changing any other parts of your config at this step. Note that go2rtc supports [many different stream types](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#module-streams), not just rtsp.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +26,7 @@ The easiest live view to get working is MSE. After adding this to the config, re
|
||||
|
||||
### What if my video doesn't play?
|
||||
|
||||
If you are unable to see your video feed, first check the go2rtc logs in the Frigate UI under Logs in the sidebar. If go2rtc is having difficulty connecting to your camera, you should see some error messages in the log. If you do not see any errors, then the video codec of the stream may not be supported in your browser. If your camera stream is set to H265, try switching to H264. You can see more information about [video codec compatibility](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#codecs-madness) in the go2rtc documentation. If you are not able to switch your camera settings from H265 to H264 or your stream is a different format such as MJPEG, you can use go2rtc to re-encode the video using the [FFmpeg parameters](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#source-ffmpeg). It supports rotating and resizing video feeds and hardware acceleration. Keep in mind that transcoding video from one format to another is a resource intensive task and you may be better off using the built-in jsmpeg view. Here is an example of a config that will re-encode the stream to H264 without hardware acceleration:
|
||||
If you are unable to see your video feed, first check the go2rtc logs in the Frigate UI under Logs in the sidebar. If go2rtc is having difficulty connecting to your camera, you should see some error messages in the log. If you do not see any errors, then the video codec of the stream may not be supported in your browser. If your camera stream is set to H265, try switching to H264. You can see more information about [video codec compatibility](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#codecs-madness) in the go2rtc documentation. If you are not able to switch your camera settings from H265 to H264 or your stream is a different format such as MJPEG, you can use go2rtc to re-encode the video using the [FFmpeg parameters](https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#source-ffmpeg). It supports rotating and resizing video feeds and hardware acceleration. Keep in mind that transcoding video from one format to another is a resource intensive task and you may be better off using the built-in jsmpeg view. Here is an example of a config that will re-encode the stream to H264 without hardware acceleration:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
go2rtc:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,145 @@ id: getting_started
|
||||
title: Getting started
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This guide walks through the steps to build a configuration file for Frigate. It assumes that you already have an environment setup as described in [Installation](../frigate/installation.md). You should also configure your cameras according to the [camera setup guide](/frigate/camera_setup). Pay particular attention to the section on choosing a detect resolution.
|
||||
# Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting up hardware
|
||||
|
||||
This section guides you through setting up a server with Debian Bookworm and Docker. If you already have an environment with Linux and Docker installed, you can continue to [Installing Frigate](#installing-frigate) below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Debian 12 (Bookworm)
|
||||
|
||||
There are many guides on how to install Debian Server, so this will be an abbreviated guide. Connect a temporary monitor and keyboard to your device so you can install a minimal server without a desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prepare installation media
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download the small installation image from the [Debian website](https://www.debian.org/distrib/netinst)
|
||||
1. Flash the ISO to a USB device (popular tool is [balena Etcher](https://etcher.balena.io/))
|
||||
1. Boot your device from USB
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install and setup Debian for remote access
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ensure your device is connected to the network so updates and software options can be installed
|
||||
1. Choose the non-graphical install option if you don't have a mouse connected, but either install method works fine
|
||||
1. You will be prompted to set the root user password and create a user with a password
|
||||
1. Install the minimum software. Fewer dependencies result in less maintenance.
|
||||
1. Uncheck "Debian desktop environment" and "GNOME"
|
||||
1. Check "SSH server"
|
||||
1. Keep "standard system utilities" checked
|
||||
1. After reboot, login as root at the command prompt to add user to sudoers
|
||||
1. Install sudo
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
apt update && apt install -y sudo
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Add the user you created to the sudo group (change `blake` to your own user)
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
usermod -aG sudo blake
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Shutdown by running `poweroff`
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you can install the device in a permanent location. The remaining steps can be performed via SSH from another device. If you don't have an SSH client, you can install one of the options listed in the [Visual Studio Code documentation](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/troubleshooting#_installing-a-supported-ssh-client).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Finish setup via SSH
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect via SSH and login with your non-root user created during install
|
||||
1. Setup passwordless sudo so you don't have to type your password for each sudo command (change `blake` in the command below to your user)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo 'blake ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL' | sudo tee /etc/sudoers.d/user
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Logout and login again to activate passwordless sudo
|
||||
1. Setup automatic security updates for the OS (optional)
|
||||
1. Ensure everything is up to date by running
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Install unattended upgrades
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo apt install -y unattended-upgrades
|
||||
echo unattended-upgrades unattended-upgrades/enable_auto_updates boolean true | sudo debconf-set-selections
|
||||
sudo dpkg-reconfigure -f noninteractive unattended-upgrades
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have a minimal Debian server that requires very little maintenance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Docker
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Docker Engine (not Docker Desktop) using the [official docs](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/debian/)
|
||||
1. Specifically, follow the steps in the [Install using the apt repository](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/debian/#install-using-the-repository) section
|
||||
2. Add your user to the docker group as described in the [Linux postinstall steps](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing Frigate
|
||||
|
||||
This section shows how to create a minimal directory structure for a Docker installation on Debian. If you have installed Frigate as a Home Assistant addon or another way, you can continue to [Configuring Frigate](#configuring-frigate).
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup directories
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate requires a valid config file to start. The following directory structure is the bare minimum to get started. Once Frigate is running, you can use the built-in config editor which supports config validation.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── docker-compose.yml
|
||||
├── config/
|
||||
│ └── config.yml
|
||||
└── storage/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will create the above structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir storage config && touch docker-compose.yml config/config.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are setting up Frigate on a Linux device via SSH, you can use [nano](https://itsfoss.com/nano-editor-guide/) to edit the following files. If you prefer to edit remote files with a full editor instead of a terminal, I recommend using [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) with the [Remote SSH extension](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/ssh-tutorial).
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
This `docker-compose.yml` file is just a starter for amd64 devices. You will need to customize it for your setup as detailed in the [Installation docs](/frigate/installation#docker).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
`docker-compose.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3.9"
|
||||
services:
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
container_name: frigate
|
||||
restart: unless-stopped
|
||||
image: ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./config:/config
|
||||
- ./storage:/media/frigate
|
||||
- type: tmpfs # Optional: 1GB of memory, reduces SSD/SD Card wear
|
||||
target: /tmp/cache
|
||||
tmpfs:
|
||||
size: 1000000000
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "5000:5000"
|
||||
- "8554:8554" # RTSP feeds
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`config.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt:
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
dummy_camera: # <--- this will be changed to your actual camera later
|
||||
enabled: False
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://127.0.0.1:554/rtsp
|
||||
roles:
|
||||
- detect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you should be able to start Frigate by running `docker compose up -d` from within the folder containing `docker-compose.yml`. Frigate should now be accessible at `server_ip:5000` and you can finish the configuration using the built-in configuration editor.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring Frigate
|
||||
|
||||
This section assumes that you already have an environment setup as described in [Installation](../frigate/installation.md). You should also configure your cameras according to the [camera setup guide](/frigate/camera_setup). Pay particular attention to the section on choosing a detect resolution.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Add a detect stream
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,6 +153,7 @@ mqtt:
|
||||
|
||||
cameras:
|
||||
name_of_your_camera: # <------ Name the camera
|
||||
enabled: True
|
||||
ffmpeg:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
- path: rtsp://10.0.10.10:554/rtsp # <----- The stream you want to use for detection
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +175,21 @@ FFmpeg arguments for other types of cameras can be found [here](../configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have a working camera configuration, you want to setup hardware acceleration to minimize the CPU required to decode your video streams. See the [hardware acceleration](../configuration/hardware_acceleration.md) config reference for examples applicable to your hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example configuration with hardware acceleration configured for Intel processors with an integrated GPU using the [preset](../configuration/ffmpeg_presets.md):
|
||||
Here is an example configuration with hardware acceleration configured to work with most Intel processors with an integrated GPU using the [preset](../configuration/ffmpeg_presets.md):
|
||||
|
||||
`docker-compose.yml` (after modifying, you will need to run `docker compose up -d` to apply changes)
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3.9"
|
||||
services:
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
...
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/dri/renderD128 # for intel hwaccel, needs to be updated for your hardware
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`config.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt: ...
|
||||
@@ -53,6 +206,19 @@ cameras:
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Frigate will use a single CPU detector. If you have a USB Coral, you will need to add a detectors section to your config.
|
||||
|
||||
`docker-compose.yml` (after modifying, you will need to run `docker compose up -d` to apply changes)
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3.9"
|
||||
services:
|
||||
frigate:
|
||||
...
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb # passes the USB Coral, needs to be modified for other versions
|
||||
- /dev/apex_0:/dev/apex_0 # passes a PCIe Coral, follow driver instructions here https://coral.ai/docs/m2/get-started/#2a-on-linux
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
mqtt: ...
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +237,7 @@ cameras:
|
||||
|
||||
More details on available detectors can be found [here](../configuration/object_detectors.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Restart Frigate and you should start seeing detections for `person`. If you want to track other objects, they will need to be added according to the [configuration file reference](../configuration/index.md#full-configuration-reference).
|
||||
Restart Frigate and you should start seeing detections for `person`. If you want to track other objects, they will need to be added according to the [configuration file reference](../configuration/reference.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Setup motion masks
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -139,7 +305,7 @@ cameras:
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't have separate streams for detect and record, you would just add the record role to the list on the first input.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Frigate will retain video of all events for 10 days. The full set of options for recording can be found [here](../configuration/index.md#full-configuration-reference).
|
||||
By default, Frigate will retain video of all events for 10 days. The full set of options for recording can be found [here](../configuration/reference.md).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Snapshots
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,11 +325,17 @@ cameras:
|
||||
motion: ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Frigate will retain snapshots of all events for 10 days. The full set of options for snapshots can be found [here](../configuration/index.md#full-configuration-reference).
|
||||
By default, Frigate will retain snapshots of all events for 10 days. The full set of options for snapshots can be found [here](../configuration/reference.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 7: Follow up guides
|
||||
### Step 7: Complete config
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have a working install, you can use the following guides for additional features:
|
||||
At this point you have a complete config with basic functionality. You can see the [full config reference](../configuration/reference.md) for a complete list of configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Configuring go2rtc](configuring_go2rtc) - Additional live view options and RTSP relay
|
||||
### Follow up
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have a working install, you can use the following documentation for additional features:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Configuring go2rtc](configuring_go2rtc.md) - Additional live view options and RTSP relay
|
||||
2. [Home Assistant Integration](../integrations/home-assistant.md) - Integrate with Home Assistant
|
||||
3. [Masks](../configuration/masks.md)
|
||||
4. [Zones](../configuration/zones.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: ha_network_storage
|
||||
title: HA Network Storage
|
||||
title: Home Assistant network storage
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
As of HomeAsisstant Core 2023.6, Network Mounted Storage is supported for addons.
|
||||
As of Home Asisstant Core 2023.6, Network Mounted Storage is supported for addons.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Remote Storage For Frigate
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ As of HomeAsisstant Core 2023.6, Network Mounted Storage is supported for addons
|
||||
|
||||
1. Stop the Frigate addon
|
||||
2. Update your [config](configuration/index.md) so the DB is stored in the /config directory by adding:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
database:
|
||||
path: /config/frigate.db
|
||||
|
||||
71
docs/docs/guides/parked_cars.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: parked_cars
|
||||
title: Handling parked cars
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
This is an area targeted for improvement in future releases.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Many people use Frigate to detect cars entering their driveway, and they often run into an issue with repeated events of parked cars and/or long running events after the car parks. This can cause Frigate to store more video than desired.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
It is not recommended to use motion masks to try and eliminate parked cars in your driveway. Motion masks are designed to prevent motion from triggering object detection and will not prevent objects from being detected in the area if motion is detected outside of the motion mask.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Repeated events of parked cars
|
||||
|
||||
To only be notified of cars that enter your driveway from the street, you can create multiple zones that cover your driveway. For cars, you would only notify if `entered_zones` from the events MQTT topic has contains the entrance zone.
|
||||
|
||||
See [this example](../configuration/zones.md#restricting-zones-to-specific-objects) from the Zones documentation to see how to restrict zones to certain object types.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To limit snapshots and events, you can list the zone for the entrance of your driveway under `required_zones` in your configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
camera:
|
||||
record:
|
||||
events:
|
||||
required_zones:
|
||||
- zone_2
|
||||
zones:
|
||||
zone_1:
|
||||
coordinates: ... (parking area)
|
||||
zone_2:
|
||||
coordinates: ... (entrance to driveway)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will only save events if the car entered the entrance zone at any point.
|
||||
|
||||
## Long running events
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few recommended approaches to avoid excessive storage use due to parked cars. These can be used in combination.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Use `motion` or `active_objects` mode for event recordings
|
||||
|
||||
Leverages [recording settings](../configuration/record.md#what-do-the-different-retain-modes-mean) to avoid excess storage use.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Advantages of this approach
|
||||
|
||||
For users using `motion` mode for continuous recording, this successfully avoids extra video from being stored for cars parked in view because all motion video is already being saved.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Limitations of this approach
|
||||
|
||||
For users that only want to record motion during events, long running events will result in all motion being stored as long as the car is in view. You can mitigate this further by using the `active_objects` mode for event recordings, but that may result less video being retained than is desired.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Use an object mask to prevent detections in the parking zone
|
||||
|
||||
Leverages [object filter masks](../configuration/masks.md#object-filter-masks) to prevent detections of cars parked in the driveway.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Advantages of this approach
|
||||
|
||||
Using this approach, you will get two separate events for when a car enters the driveway, parks in the parking zone, and then later leaves the zone. Using an object mask will ensure that cars parked in the parking zone are not detected and confused with cars driving by on the street as well.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Limitations of this approach
|
||||
|
||||
This approach will only work for cars that park in the parking zone. Cars that park in other areas will still be tracked as long as they are in view. This will also prevent zone sensors from telling you if a car is parked in the parking zone from working.
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ This section points to your SSL files, the example below shows locations to a de
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup reverse proxy settings
|
||||
|
||||
Thhe settings below enabled connection upgrade, sets up logging (optional) and proxies everything from the `/` context to the docker host and port specified earlier in the configuration
|
||||
The settings below enabled connection upgrade, sets up logging (optional) and proxies everything from the `/` context to the docker host and port specified earlier in the configuration
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: stationary_objects
|
||||
title: Avoiding stationary objects
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Many people use Frigate to detect cars entering their driveway, and they often run into an issue with repeated notifications or events of a parked car being repeatedly detected over the course of multiple days (for example if the car is lost at night and detected again the following morning).
|
||||
|
||||
You can use zones to restrict events and notifications to objects that have entered specific areas.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
It is not recommended to use masks to try and eliminate parked cars in your driveway. Masks are designed to prevent motion from triggering object detection and/or to indicate areas that are guaranteed false positives.
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate is designed to track objects as they move and over-masking can prevent it from knowing that an object in the current frame is the same as the previous frame. You want Frigate to detect objects everywhere and configure your events and alerts to be based on the location of the object with zones.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
Once a vehicle crosses the entrance into the parking area, that event will stay `In Progress` until it is no longer seen in the frame. Frigate is designed to have an event last as long as an object is visible in the frame, an event being `In Progress` does not mean the event is being constantly recorded. You can define the recording behavior by adjusting the [recording retention settings](../configuration/record.md).
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
To only be notified of cars that enter your driveway from the street, you could create multiple zones that cover your driveway. For cars, you would only notify if `entered_zones` from the events MQTT topic has more than 1 zone.
|
||||
|
||||
See [this example](../configuration/zones.md#restricting-zones-to-specific-objects) from the Zones documentation to see how to restrict zones to certain object types.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To limit snapshots and events, you can list the zone for the entrance of your driveway under `required_zones` in your configuration file. Example below.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
camera:
|
||||
record:
|
||||
events:
|
||||
required_zones:
|
||||
- zone_2
|
||||
zones:
|
||||
zone_1:
|
||||
coordinates: ... (parking area)
|
||||
zone_2:
|
||||
coordinates: ... (entrance to driveway)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -263,6 +263,15 @@ Returns the snapshot image from the latest event for the given camera and label
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the snapshot image from the specific point in that cameras recordings.
|
||||
|
||||
### `GET /api/<camera_name>/grid.jpg`
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the latest camera image with the regions grid overlaid.
|
||||
|
||||
| param | Type | Description |
|
||||
| ------------ | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `color` | str | The color of the grid (red,green,blue,black,white). Defaults to "green". |
|
||||
| `font_scale` | float | Font scale. Can be used to increase font size on high resolution cameras. Defaults to 0.5. |
|
||||
|
||||
### `GET /clips/<camera>-<id>.jpg`
|
||||
|
||||
JPG snapshot for the given camera and event id.
|
||||
@@ -293,6 +302,14 @@ It is also possible to export this recording as a timelapse.
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `DELETE /api/export/<export_name>`
|
||||
|
||||
Delete an export from disk.
|
||||
|
||||
### `PATCH /api/export/<export_name_current>/<export_name_new>`
|
||||
|
||||
Renames an export.
|
||||
|
||||
### `GET /api/<camera_name>/recordings/summary`
|
||||
|
||||
Hourly summary of recordings data for a camera.
|
||||
@@ -361,3 +378,7 @@ Recording retention config still applies to manual events, if frigate is configu
|
||||
### `PUT /api/events/<event_id>/end`
|
||||
|
||||
End a specific manual event without a predetermined length.
|
||||
|
||||
### `POST /api/restart`
|
||||
|
||||
Restarts Frigate process.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ The Frigate integration seamlessly supports the use of multiple Frigate servers.
|
||||
In order for multiple Frigate instances to function correctly, the
|
||||
`topic_prefix` and `client_id` parameters must be set differently per server.
|
||||
See [MQTT
|
||||
configuration](mqtt.md)
|
||||
configuration](mqtt)
|
||||
for how to set these.
|
||||
|
||||
#### API URLs
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -221,6 +221,10 @@ Topic to turn the PTZ autotracker for a camera on and off. Expected values are `
|
||||
|
||||
Topic with current state of the PTZ autotracker for a camera. Published values are `ON` and `OFF`.
|
||||
|
||||
### `frigate/<camera_name>/ptz_autotracker/active`
|
||||
|
||||
Topic to determine if PTZ autotracker is actively tracking an object. Published values are `ON` and `OFF`.
|
||||
|
||||
### `frigate/<camera_name>/birdseye/set`
|
||||
|
||||
Topic to turn Birdseye for a camera on and off. Expected values are `ON` and `OFF`. Birdseye mode
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Once logged in, you can generate an API key for Frigate in Settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set your API key
|
||||
|
||||
In Frigate, you can set the `PLUS_API_KEY` environment variable to enable the `SEND TO FRIGATE+` buttons on the events page. You can set it in your Docker Compose file or in your Docker run command. Home Assistant Addon users can set it under Settings > Addons > Frigate NVR > Configuration > Options (be sure to toggle the "Show unused optional configuration options" switch).
|
||||
In Frigate, you can use an environment variable or a docker secret named `PLUS_API_KEY` to enable the `SEND TO FRIGATE+` buttons on the events page. Home Assistant Addon users can set it under Settings > Addons > Frigate NVR > Configuration > Options (be sure to toggle the "Show unused optional configuration options" switch).
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,11 +37,13 @@ Snapshots must be enabled to be able to submit examples to Frigate+
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Annotate and verify
|
||||
|
||||
You can view all of your submitted images at [https://plus.frigate.video](https://plus.frigate.video). Annotations can be added by clicking an image.
|
||||
You can view all of your submitted images at [https://plus.frigate.video](https://plus.frigate.video). Annotations can be added by clicking an image. For more detailed information about labeling, see the documentation on [improving your model](../plus/improving_model.md).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +58,7 @@ model:
|
||||
|
||||
Models are downloaded into the `/config/model_cache` folder and only downloaded if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
You can override the labelmap for Frigate+ models like this:
|
||||
If needed, you can override the labelmap for Frigate+ models. This is not recommended as renaming labels will break the Submit to Frigate+ feature if the labels are not available in Frigate+.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
model:
|
||||
|
||||
24
docs/docs/plus/faq.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: faq
|
||||
title: FAQ
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Are my models trained just on my image uploads? How are they built?
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ models are built by fine tuning a base model with the images you have annotated and verified. The base model is trained from scratch from a sampling of images across all Frigate+ user submissions and takes weeks of expensive GPU resources to train. If the models were built using your image uploads alone, you would need to provide tens of thousands of examples and it would take more than a week (and considerable cost) to train. Diversity helps the model generalize.
|
||||
|
||||
### Are my video feeds sent to the cloud for analysis when using Frigate+ models?
|
||||
|
||||
No. Frigate+ models are a drop in replacement for the default model. All processing is performed locally as always. The only images sent to Frigate+ are the ones you specifically submit via the `Send to Frigate+` button or upload directly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I label anything I want and train the model to recognize something custom for me?
|
||||
|
||||
Not currently. At the moment, the set of labels will be consistent for all users. The focus will be on expanding that set of labels before working on completely custom user labels.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can Frigate+ models be used offline?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Models and metadata are stored in the `model_cache` directory within the config folder. Frigate will only attempt to download a model if it does not exist in the cache. This means you can backup the directory and/or use it completely offline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I keep using my Frigate+ models even if I do not renew my subscription?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Subscriptions to Frigate+ provide access to the infrastructure used to train the models. Models trained with your subscription are yours to keep and use forever. However, do note that the terms and conditions prohibit you from sharing, reselling, or creating derivative products from the models.
|
||||
63
docs/docs/plus/first_model.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: first_model
|
||||
title: Requesting your first model
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Upload and annotate your images
|
||||
|
||||
Before requesting your first model, you will need to upload at least 10 images to Frigate+. But for the best results, you should provide at least 100 verified images per camera. Keep in mind that varying conditions should be included. You will want images from cloudy days, sunny days, dawn, dusk, and night. Refer to the [integration docs](../integrations/plus.md#generate-an-api-key) for instructions on how to easily submit images to Frigate+ directly from Frigate.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to submit **both** true positives and false positives. This will help the model differentiate between what is and isn't correct. You should aim for a target of 80% true positive submissions and 20% false positives across all of your images. If you are experiencing false positives in a specific area, submitting true positives for any object type near that area in similar lighting conditions will help teach the model what that area looks like when no objects are present.
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed recommendations, you can refer to the docs on [improving your model](./improving_model.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Submit a model request
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have an initial set of verified images, you can request a model on the Models page. Each model request requires 1 of the 12 trainings that you receive with your annual subscription. This model will support all [label types available](./index.md#available-label-types) even if you do not submit any examples for those labels. Model creation can take up to 36 hours.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Set your model id in the config
|
||||
|
||||
You will receive an email notification when your Frigate+ model is ready.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Models available in Frigate+ can be used with a special model path. No other information needs to be configured because it fetches the remaining config from Frigate+ automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
model:
|
||||
path: plus://<your_model_id>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 4: Adjust your object filters for higher scores
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ models generally have much higher scores than the default model provided in Frigate. You will likely need to increase your `threshold` and `min_score` values. Here is an example of how these values can be refined, but you should expect these to evolve as your model improves. For more information about how `threshold` and `min_score` are related, see the docs on [object filters](../configuration/object_filters.md#object-scores).
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
dog:
|
||||
min_score: .7
|
||||
threshold: .9
|
||||
cat:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .8
|
||||
face:
|
||||
min_score: .7
|
||||
package:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .9
|
||||
license_plate:
|
||||
min_score: .6
|
||||
amazon:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
ups:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
fedex:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
person:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .85
|
||||
car:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .85
|
||||
```
|
||||
33
docs/docs/plus/improving_model.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: improving_model
|
||||
title: Improving your model
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You may find that Frigate+ models result in more false positives initially, but by submitting true and false positives, the model will improve. Because a limited number of users submitted images to Frigate+ prior to this launch, you may need to submit several hundred images per camera to see good results. With all the new images now being submitted, future base models will improve as more and more users (including you) submit examples to Frigate+. Note that only verified images will be used when training your model. Submitting an image from Frigate as a true or false positive will not verify the image. You still must verify the image in Frigate+ in order for it to be used in training.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Submit both true positives and false positives**. This will help the model differentiate between what is and isn't correct. You should aim for a target of 80% true positive submissions and 20% false positives across all of your images. If you are experiencing false positives in a specific area, submitting true positives for any object type near that area in similar lighting conditions will help teach the model what that area looks like when no objects are present.
|
||||
- **Lower your thresholds a little in order to generate more false/true positives near the threshold value**. For example, if you have some false positives that are scoring at 68% and some true positives scoring at 72%, you can try lowering your threshold to 65% and submitting both true and false positives within that range. This will help the model learn and widen the gap between true and false positive scores.
|
||||
- **Submit diverse images**. For the best results, you should provide at least 100 verified images per camera. Keep in mind that varying conditions should be included. You will want images from cloudy days, sunny days, dawn, dusk, and night. As circumstances change, you may need to submit new examples to address new types of false positives. For example, the change from summer days to snowy winter days or other changes such as a new grill or patio furniture may require additional examples and training.
|
||||
|
||||
## Properly labeling images
|
||||
|
||||
For the best results, follow the following guidelines.
|
||||
|
||||
**Label every object in the image**: It is important that you label all objects in each image before verifying. If you don't label a car for example, the model will be taught that part of the image is _not_ a car and it will start to get confused.
|
||||
|
||||
**Make tight bounding boxes**: Tighter bounding boxes improve the recognition and ensure that accurate bounding boxes are predicted at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
**Label the full object even when occluded**: If you have a person standing behind a car, label the full person even though a portion of their body may be hidden behind the car. This helps predict accurate bounding boxes and improves zone accuracy and filters at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
**`amazon`, `ups`, and `fedex` should label the logo**: For a Fedex truck, label the truck as a `car` and make a different bounding box just for the Fedex logo. If there are multiple logos, label each of them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## False positive labels
|
||||
|
||||
False positives will be shown with a read box and the label will have a strike through.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Misidentified objects should have a correct label added. For example, if a person was mistakenly detected as a cat, you should submit it as a false positive in Frigate and add a label for the person. The boxes will overlap.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -1,87 +1,37 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: index
|
||||
title: Models Guide
|
||||
title: Models
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ offers models trained from scratch and specifically designed for the way Frigate NVR analyzes video footage. These models offer higher accuracy with less resources. By uploading your own labeled examples, your model is tuned for accuracy in your specific conditions. After tuning, performance is evaluated against a broad dataset and real world examples submitted by other Frigate+ users to prevent overfitting.
|
||||
<a href="https://plus.frigate.video" target="_blank" rel="nofollow">Frigate+</a> offers models trained on images submitted by Frigate+ users from their security cameras and is specifically designed for the way Frigate NVR analyzes video footage. These models offer higher accuracy with less resources. The images you upload are used to fine tune a baseline model trained from images uploaded by all Frigate+ users. This fine tuning process results in a model that is optimized for accuracy in your specific conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
With a subscription, and at each annual renewal, you will receive 12 model training credits that can be used to train tuned models. If you cancel your subscription, you will keep your existing credits and retain access to any trained models. Users with an active subscription can purchase additional training credits for $5 each.
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
Information on how to integrate Frigate+ with Frigate can be found in the [integrations docs](/integrations/plus).
|
||||
The baseline model isn't directly available after subscribing. This may change in the future, but for now you will need to submit a model request with the minimum number of images.
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Are my models trained just on my image uploads? How are they built?
|
||||
With a subscription, 12 model trainings per year are included. If you cancel your subscription, you will retain access to any trained models. An active subscription is required to submit model requests or purchase additional trainings.
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ models are built by fine tuning a base model with the images you have annotated and verified. The base model is trained from scratch from a sampling of images across all Frigate+ user submissions and takes weeks of expensive GPU resources to train. If the models were built using your image uploads alone, you would need to provide tens of thousands of examples and it would take more than a week (and considerable cost) to train. Diversity helps the model generalize.
|
||||
Information on how to integrate Frigate+ with Frigate can be found in the [integration docs](../integrations/plus.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What is a training credit and how do I use them?
|
||||
## Supported detector types
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, `1 training credit = 1 trained model`. When you have uploaded, annotated, and verified additional images and you are ready to train your model, you will submit a model request which will use one credit. The model that is trained will utilize all of the verified images in your account.
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
||||
### Are my video feeds sent to the cloud for analysis when using Frigate+ models?
|
||||
Frigate+ models are not supported for TensorRT or OpenVino yet.
|
||||
|
||||
No. Frigate+ models are a drop in replacement for the default model. All processing is performed locally as always. The only images sent to Frigate+ are the ones you specifically submit via the `Send to Frigate+` button or upload directly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I label anything I want and train the model to recognize something custom for me?
|
||||
|
||||
Not currently. At the moment, the set of labels will be consistent for all users. The focus will be on expanding that set of labels before working on completely custom user labels.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can Frigate+ models be used offline?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Models and metadata are stored in the `model_cache` directory within the config folder. Frigate will only attempt to download a model if it does not exist in the cache. This means you can backup the directory and/or use it completely offline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I keep using my Frigate+ models even if I do not renew my subscription?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Subscriptions to Frigate+ provide access to the infrastructure used to train the models. Models trained using the training credits that you purchased are yours to keep and use forever. However, do note that the terms and conditions prohibit you from sharing, reselling, or creating derivative products from the models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Important model information
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported Model Types
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, Frigate+ models only support CPU (`cpu`) and Coral (`edgetpu`) models. OpenVino is next in line to gain support.
|
||||
|
||||
The models are created using the same MobileDet architecture as the default model. Additional architectures will be added in future releases as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Higher Scores
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ models generally have much higher scores than the default model provided in Frigate. You will likely need to increase your `threshold` and `min_score` values. Here is an example of how these values can be refined, but you should expect these to evolve as your model improves:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
objects:
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
dog:
|
||||
min_score: .7
|
||||
threshold: .9
|
||||
cat:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .8
|
||||
face:
|
||||
min_score: .7
|
||||
package:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .9
|
||||
license_plate:
|
||||
min_score: .6
|
||||
amazon:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
ups:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
fedex:
|
||||
min_score: .75
|
||||
person:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .85
|
||||
car:
|
||||
min_score: .65
|
||||
threshold: .85
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Available label types
|
||||
## Available label types
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate+ models support a more relevant set of objects for security cameras. Currently, only the following objects are supported: `person`, `face`, `car`, `license_plate`, `amazon`, `ups`, `fedex`, `package`, `dog`, `cat`, `deer`. Other object types available in the default Frigate model are not available. Additional object types will be added in future releases.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Label attributes
|
||||
### Label attributes
|
||||
|
||||
Frigate has special handling for some labels when using Frigate+ models. `face`, `license_plate`, `amazon`, `ups`, and `fedex` are considered attribute labels which are not tracked like regular objects and do not generate events. In addition, the `threshold` filter will have no effect on these labels. You should adjust the `min_score` and other filter values as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -109,31 +59,3 @@ When using Frigate+ models, Frigate will choose the snapshot of a person object
|
||||
`amazon`, `ups`, and `fedex` labels are used to automatically assign a sub label to car objects.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Properly labeling images
|
||||
|
||||
For the best results, follow the following guidelines.
|
||||
|
||||
**Label every object in the image**: It is important that you label all objects in each image before verifying. If you don't label a car for example, the model will be taught that part of the image is _not_ a car and it will start to get confused.
|
||||
|
||||
**Make tight bounding boxes**: Tighter bounding boxes improve the recognition and ensure that accurate bounding boxes are predicted at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
**Label the full object even when occluded**: If you have a person standing behind a car, label the full person even though a portion of their body may be hidden behind the car. This helps predict accurate bounding boxes and improves zone accuracy and filters at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
**`amazon`, `ups`, and `fedex` should label the logo**: For a Fedex truck, label the truck as a `car` and make a different bounding box just for the Fedex logo. If there are multiple logos, label each of them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Improving your model
|
||||
|
||||
You may find that Frigate+ models result in more false positives initially, but by submitting true and false positives, the model will improve. This may be because your cameras don't look quite enough like the user submissions that were used to train the base model. Over time, this will improve as more and more users (including you) submit examples to Frigate+.
|
||||
|
||||
False positives can be reduced by submitting **both** true positives and false positives. This will help the model differentiate between what is and isn't correct.
|
||||
|
||||
You may find that it's helpful to lower your thresholds a little in order to generate more false/true positives near the threshold value. For example, if you have some false positives that are scoring at 68% and some true positives scoring at 72%, you can try lowering your threshold to 65% and submitting both true and false positives within that range. This will help the model learn and widen the gap between true and false positive scores.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that only verified images will be used when training your model. Submitting an image from Frigate as a true or false positive will not verify the image. You still must verify the image in Frigate+ in order for it to be used in training.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to request your first model, you will need to have annotated and verified at least 10 images. Each subsequent model request will require that 10 additional images are verified. However, this is the bare minimum. For the best results, you should provide at least 100 verified images per camera. Keep in mind that varying conditions should be included. You will want images from cloudy days, sunny days, dawn, dusk, and night.
|
||||
|
||||
As circumstances change, you may need to submit new examples to address new types of false positives. For example, the change from summer days to snowy winter days or other changes such as a new grill or patio furniture may require additional examples and training.
|
||||
|
||||
48
docs/docs/troubleshooting/edgetpu.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: edgetpu
|
||||
title: Troubleshooting EdgeTPU
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## USB Coral Not Detected
|
||||
|
||||
There are many possible causes for a USB coral not being detected and some are OS specific. It is important to understand how the USB coral works:
|
||||
|
||||
1. When the device is first plugged in and has not initialized it will appear as `1a6e:089a Global Unichip Corp.` when running `lsusb` or checking the hardware page in HA OS.
|
||||
2. Once initialized, the device will appear as `18d1:9302 Google Inc.` when running `lsusb` or checking the hardware page in HA OS.
|
||||
|
||||
If the coral does not initialize then Frigate can not interface with it. Some common reasons for the USB based Coral not initializing are:
|
||||
|
||||
### Not Enough Power
|
||||
|
||||
The USB coral can draw up to 900mA and this can be too much for some on-device USB ports, especially for small board computers like the RPi. If the coral is not initializing then some recommended steps are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Try a different port, some ports are capable of providing more power than others.
|
||||
2. Make sure the port is USB3, this is important for power and to ensure the coral runs at max speed.
|
||||
3. Try a different cable, some users have found the included cable to not work well.
|
||||
4. Use an externally powered USB hub.
|
||||
|
||||
### Incorrect Device Access
|
||||
|
||||
The USB coral has different IDs when it is uninitialized and initialized.
|
||||
|
||||
- When running Frigate in a VM, Proxmox lxc, etc. you must ensure both device IDs are mapped.
|
||||
- When running HA OS you may need to run the Full Access version of the Frigate addon with the `Protected Mode` switch disabled so that the coral can be accessed.
|
||||
|
||||
## USB Coral Detection Appears to be Stuck
|
||||
|
||||
The USB Coral can become stuck and need to be restarted, this can happen for a number of reasons depending on hardware and software setup. Some common reasons are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Some users have found the cable included with the coral to cause this problem and that switching to a different cable fixed it entirely.
|
||||
2. Running Frigate in a VM may cause communication with the device to be lost and need to be reset.
|
||||
|
||||
## PCIe Coral Not Detected
|
||||
|
||||
The most common reason for the PCIe coral not being detected is that the driver has not been installed. See [the coral docs(https://coral.ai/docs/m2/get-started/#2-install-the-pcie-driver-and-edge-tpu-runtime) for how to install the driver for the PCIe based coral.
|
||||
|
||||
## Only One PCIe Coral Is Detected With Coral Dual EdgeTPU
|
||||
|
||||
Coral Dual EdgeTPU is one card with two identical TPU cores. Each core has it's own PCIe interface and motherboard needs to have two PCIe busses on the m.2 slot to make them both work.
|
||||
|
||||
E-key slot implemented to full m.2 electomechanical specification has two PCIe busses. Most motherboard manufacturers implement only one PCIe bus in m.2 E-key connector (this is why only one TPU is working). Some SBCs can have only USB bus on m.2 connector, ie none of TPUs will work.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case it is recommended to use a Dual EdgeTPU Adapter [like the one from MagicBlueSmoke](https://github.com/magic-blue-smoke/Dual-Edge-TPU-Adapter)
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ id: recordings
|
||||
title: Troubleshooting Recordings
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `WARNING : Unable to keep up with recording segments in cache for {camera}. Keeping the 5 most recent segments out of 6 and discarding the rest...`
|
||||
### WARNING : Unable to keep up with recording segments in cache for camera. Keeping the 5 most recent segments out of 6 and discarding the rest...
|
||||
|
||||
This error can be caused by a number of different issues. The first step in troubleshooting is to enable debug logging for recording, this will enable logging showing how long it takes for recordings to be moved from RAM cache to the disk.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,18 +21,18 @@ DEBUG : Copied /media/frigate/recordings/{segment_path} in 0.2 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to let this run until the errors begin to happen, to confirm that there is not a slow down in the disk at the time of the error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Copy Times > 1 second
|
||||
#### Copy Times > 1 second
|
||||
|
||||
If the storage is too slow to keep up with the recordings then the maintainer will fall behind and purge the oldest recordings to ensure the cache does not fill up causing a crash. In this case it is important to diagnose why the copy times are slow.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Check Storage Type
|
||||
##### Check Storage Type
|
||||
|
||||
Mounting a network share is a popular option for storing Recordings, but this can lead to reduced copy times and cause problems. Some users have found that using `NFS` instead of `SMB` considerably decreased the copy times and fixed the issue. It is also important to ensure that the network connection between the device running Frigate and the network share is stable and fast.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Check mount options
|
||||
##### Check mount options
|
||||
|
||||
Some users found that mounting a drive via `fstab` with the `sync` option caused dramatically reduce performance and led to this issue. Using `async` instead greatly reduced copy times.
|
||||
|
||||
### Copy Times < 1 second
|
||||
#### Copy Times < 1 second
|
||||
|
||||
If the storage is working quickly then this error may be caused by CPU load on the machine being too high for Frigate to have the resources to keep up. Try temporarily shutting down other services to see if the issue improves.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,70 +1,77 @@
|
||||
const path = require('path');
|
||||
const path = require("path");
|
||||
|
||||
module.exports = {
|
||||
title: 'Frigate',
|
||||
tagline: 'NVR With Realtime Object Detection for IP Cameras',
|
||||
url: 'https://docs.frigate.video',
|
||||
baseUrl: '/',
|
||||
onBrokenLinks: 'throw',
|
||||
onBrokenMarkdownLinks: 'warn',
|
||||
favicon: 'img/favicon.ico',
|
||||
organizationName: 'blakeblackshear',
|
||||
projectName: 'frigate',
|
||||
title: "Frigate",
|
||||
tagline: "NVR With Realtime Object Detection for IP Cameras",
|
||||
url: "https://docs.frigate.video",
|
||||
baseUrl: "/",
|
||||
onBrokenLinks: "throw",
|
||||
onBrokenMarkdownLinks: "warn",
|
||||
favicon: "img/favicon.ico",
|
||||
organizationName: "blakeblackshear",
|
||||
projectName: "frigate",
|
||||
themes: ["@docusaurus/theme-mermaid"],
|
||||
markdown: {
|
||||
mermaid: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
themeConfig: {
|
||||
algolia: {
|
||||
appId: 'WIURGBNBPY',
|
||||
apiKey: 'd02cc0a6a61178b25da550212925226b',
|
||||
indexName: 'frigate',
|
||||
appId: "WIURGBNBPY",
|
||||
apiKey: "d02cc0a6a61178b25da550212925226b",
|
||||
indexName: "frigate",
|
||||
},
|
||||
docs: {
|
||||
sidebar: {
|
||||
hideable: true,
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
prism: {
|
||||
additionalLanguages: ["bash", "json"],
|
||||
},
|
||||
navbar: {
|
||||
title: 'Frigate',
|
||||
title: "Frigate",
|
||||
logo: {
|
||||
alt: 'Frigate',
|
||||
src: 'img/logo.svg',
|
||||
srcDark: 'img/logo-dark.svg',
|
||||
alt: "Frigate",
|
||||
src: "img/logo.svg",
|
||||
srcDark: "img/logo-dark.svg",
|
||||
},
|
||||
items: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
to: '/',
|
||||
activeBasePath: 'docs',
|
||||
label: 'Docs',
|
||||
position: 'left',
|
||||
to: "/",
|
||||
activeBasePath: "docs",
|
||||
label: "Docs",
|
||||
position: "left",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: 'https://frigate.video',
|
||||
label: 'Website',
|
||||
position: 'right',
|
||||
href: "https://frigate.video",
|
||||
label: "Website",
|
||||
position: "right",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: 'http://demo.frigate.video',
|
||||
label: 'Demo',
|
||||
position: 'right',
|
||||
href: "http://demo.frigate.video",
|
||||
label: "Demo",
|
||||
position: "right",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: 'https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate',
|
||||
label: 'GitHub',
|
||||
position: 'right',
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate",
|
||||
label: "GitHub",
|
||||
position: "right",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
footer: {
|
||||
style: 'dark',
|
||||
style: "dark",
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: 'Community',
|
||||
title: "Community",
|
||||
items: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: 'GitHub',
|
||||
href: 'https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate',
|
||||
label: "GitHub",
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: 'Discussions',
|
||||
href: 'https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/discussions',
|
||||
label: "Discussions",
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/discussions",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -72,21 +79,22 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
copyright: `Copyright © ${new Date().getFullYear()} Blake Blackshear`,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
plugins: [path.resolve(__dirname, 'plugins', 'raw-loader')],
|
||||
plugins: [path.resolve(__dirname, "plugins", "raw-loader")],
|
||||
presets: [
|
||||
[
|
||||
'@docusaurus/preset-classic',
|
||||
"@docusaurus/preset-classic",
|
||||
{
|
||||
docs: {
|
||||
routeBasePath: '/',
|
||||
sidebarPath: require.resolve('./sidebars.js'),
|
||||
routeBasePath: "/",
|
||||
sidebarPath: require.resolve("./sidebars.js"),
|
||||
// Please change this to your repo.
|
||||
editUrl: 'https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/edit/master/docs/',
|
||||
sidebarCollapsible: false
|
||||
editUrl:
|
||||
"https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/edit/master/docs/",
|
||||
sidebarCollapsible: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
theme: {
|
||||
customCss: require.resolve('./src/css/custom.css'),
|
||||
customCss: require.resolve("./src/css/custom.css"),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
19954
docs/package-lock.json
generated
@@ -14,14 +14,15 @@
|
||||
"write-heading-ids": "docusaurus write-heading-ids"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@docusaurus/core": "^2.4.1",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/preset-classic": "^2.4.1",
|
||||
"@mdx-js/react": "^1.6.22",
|
||||
"clsx": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"prism-react-renderer": "^1.3.5",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/core": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/preset-classic": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/theme-mermaid": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"@mdx-js/react": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"clsx": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"prism-react-renderer": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"raw-loader": "^4.0.2",
|
||||
"react": "^17.0.2",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^17.0.2"
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
@@ -36,10 +37,11 @@
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"devDependencies": {
|
||||
"@docusaurus/module-type-aliases": "^2.4.0",
|
||||
"@types/react": "^17.0.0"
|
||||
"@docusaurus/module-type-aliases": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/types": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"@types/react": "^18.2.29"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"engines": {
|
||||
"node": ">=16.14"
|
||||
"node": ">=18.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,23 +5,25 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
"frigate/hardware",
|
||||
"frigate/installation",
|
||||
"frigate/camera_setup",
|
||||
"frigate/video_pipeline",
|
||||
"frigate/glossary",
|
||||
],
|
||||
Guides: [
|
||||
"guides/getting_started",
|
||||
"guides/configuring_go2rtc",
|
||||
"guides/false_positives",
|
||||
"guides/ha_notifications",
|
||||
"guides/ha_network_storage",
|
||||
"guides/stationary_objects",
|
||||
"guides/parked_cars",
|
||||
"guides/reverse_proxy",
|
||||
],
|
||||
Configuration: {
|
||||
"Configuration Files": [
|
||||
"configuration/index",
|
||||
"configuration/reference",
|
||||
{
|
||||
type: "link",
|
||||
label: "Go2RTC Configuration Reference",
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.1#configuration",
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/AlexxIT/go2rtc/tree/v1.8.4#configuration",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
Detectors: [
|
||||
@@ -32,6 +34,7 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
"configuration/cameras",
|
||||
"configuration/record",
|
||||
"configuration/snapshots",
|
||||
"configuration/motion_detection",
|
||||
"configuration/birdseye",
|
||||
"configuration/live",
|
||||
"configuration/restream",
|
||||
@@ -39,10 +42,11 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
"configuration/camera_specific",
|
||||
],
|
||||
Objects: [
|
||||
"configuration/object_filters",
|
||||
"configuration/masks",
|
||||
"configuration/zones",
|
||||
"configuration/objects",
|
||||
"configuration/stationary_objects",
|
||||
"configuration/zones",
|
||||
],
|
||||
"Extra Configuration": [
|
||||
"configuration/hardware_acceleration",
|
||||
@@ -57,8 +61,17 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
"integrations/mqtt",
|
||||
"integrations/third_party_extensions",
|
||||
],
|
||||
"Frigate+": ["plus/index"],
|
||||
Troubleshooting: ["troubleshooting/faqs", "troubleshooting/recordings"],
|
||||
"Frigate+": [
|
||||
"plus/index",
|
||||
"plus/first_model",
|
||||
"plus/improving_model",
|
||||
"plus/faq",
|
||||
],
|
||||
Troubleshooting: [
|
||||
"troubleshooting/faqs",
|
||||
"troubleshooting/recordings",
|
||||
"troubleshooting/edgetpu",
|
||||
],
|
||||
Development: [
|
||||
"development/contributing",
|
||||
"development/contributing-boards",
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
docs/static/img/bottom-center-mask.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 58 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/bottom-center.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 115 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/false-positive-overlap.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 22 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/false-positive.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 45 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/model-ready-email.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 33 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/plus-models.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 71 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/send-to-plus.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 57 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/plus/submit-to-plus.jpg
vendored
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 63 KiB |
BIN
docs/static/img/send-to-plus.png
vendored
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB |
@@ -191,7 +191,8 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
"i",
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.enabled,
|
||||
),
|
||||
"ptz_stopped": mp.Event(),
|
||||
"ptz_tracking_active": mp.Event(),
|
||||
"ptz_motor_stopped": mp.Event(),
|
||||
"ptz_reset": mp.Event(),
|
||||
"ptz_start_time": mp.Value("d", 0.0), # type: ignore[typeddict-item]
|
||||
# issue https://github.com/python/typeshed/issues/8799
|
||||
@@ -212,7 +213,7 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
# issue https://github.com/python/typeshed/issues/8799
|
||||
# from mypy 0.981 onwards
|
||||
}
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].set()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].set()
|
||||
self.feature_metrics[camera_name] = {
|
||||
"audio_enabled": mp.Value( # type: ignore[typeddict-item]
|
||||
# issue https://github.com/python/typeshed/issues/8799
|
||||
@@ -270,6 +271,7 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
|
||||
def init_database(self) -> None:
|
||||
def vacuum_db(db: SqliteExtDatabase) -> None:
|
||||
logger.info("Running database vacuum")
|
||||
db.execute_sql("VACUUM;")
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@@ -278,6 +280,17 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
except PermissionError:
|
||||
logger.error("Unable to write to /config to save DB state")
|
||||
|
||||
def cleanup_timeline_db(db: SqliteExtDatabase) -> None:
|
||||
db.execute_sql(
|
||||
"DELETE FROM timeline WHERE source_id NOT IN (SELECT id FROM event);"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with open(f"{CONFIG_DIR}/.timeline", "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(str(datetime.datetime.now().timestamp()))
|
||||
except PermissionError:
|
||||
logger.error("Unable to write to /config to save DB state")
|
||||
|
||||
# Migrate DB location
|
||||
old_db_path = DEFAULT_DB_PATH
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile(self.config.database.path) and os.path.isfile(
|
||||
@@ -293,6 +306,11 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
router = Router(migrate_db)
|
||||
router.run()
|
||||
|
||||
# this is a temporary check to clean up user DB from beta
|
||||
# will be removed before final release
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(f"{CONFIG_DIR}/.timeline"):
|
||||
cleanup_timeline_db(migrate_db)
|
||||
|
||||
# check if vacuum needs to be run
|
||||
if os.path.exists(f"{CONFIG_DIR}/.vacuum"):
|
||||
with open(f"{CONFIG_DIR}/.vacuum") as f:
|
||||
@@ -444,6 +462,7 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
self.config,
|
||||
self.onvif_controller,
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics,
|
||||
self.dispatcher,
|
||||
self.stop_event,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.ptz_autotracker_thread.start()
|
||||
@@ -485,7 +504,9 @@ class FrigateApp:
|
||||
# create or update region grids for each camera
|
||||
for camera in self.config.cameras.values():
|
||||
self.region_grids[camera.name] = get_camera_regions_grid(
|
||||
camera.name, camera.detect
|
||||
camera.name,
|
||||
camera.detect,
|
||||
max(self.config.model.width, self.config.model.height),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def start_camera_processors(self) -> None:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +96,11 @@ class Dispatcher:
|
||||
elif topic == REQUEST_REGION_GRID:
|
||||
camera = payload
|
||||
self.camera_metrics[camera]["region_grid_queue"].put(
|
||||
get_camera_regions_grid(camera, self.config.cameras[camera].detect)
|
||||
get_camera_regions_grid(
|
||||
camera,
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera].detect,
|
||||
max(self.config.model.width, self.config.model.height),
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.publish(topic, payload, retain=False)
|
||||
@@ -181,6 +185,13 @@ class Dispatcher:
|
||||
ptz_autotracker_settings = self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking
|
||||
|
||||
if payload == "ON":
|
||||
if not self.config.cameras[
|
||||
camera_name
|
||||
].onvif.autotracking.enabled_in_config:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"Autotracking must be enabled in the config to be turned on via MQTT."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Turning on ptz autotracker for {camera_name}")
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = True
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ class MqttClient(Communicator): # type: ignore[misc]
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.publish(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}/ptz_autotracker/state",
|
||||
"ON" if camera.onvif.autotracking.enabled else "OFF",
|
||||
"ON" if camera.onvif.autotracking.enabled_in_config else "OFF",
|
||||
retain=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.publish(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
"""Websocket communicator."""
|
||||
|
||||
import errno
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +13,7 @@ from ws4py.server.wsgirefserver import (
|
||||
WSGIServer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ws4py.server.wsgiutils import WebSocketWSGIApplication
|
||||
from ws4py.websocket import WebSocket
|
||||
from ws4py.websocket import WebSocket as WebSocket_
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.comms.dispatcher import Communicator
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig
|
||||
@@ -20,11 +21,24 @@ from frigate.config import FrigateConfig
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class WebSocket(WebSocket_):
|
||||
def unhandled_error(self, error):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Handles the unfriendly socket closures on the server side
|
||||
without showing a confusing error message
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if hasattr(error, "errno") and error.errno == errno.ECONNRESET:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logging.getLogger("ws4py").exception("Failed to receive data")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class WebSocketClient(Communicator): # type: ignore[misc]
|
||||
"""Frigate wrapper for ws client."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: FrigateConfig) -> None:
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.websocket_server = None
|
||||
|
||||
def subscribe(self, receiver: Callable) -> None:
|
||||
self._dispatcher = receiver
|
||||
@@ -85,6 +99,10 @@ class WebSocketClient(Communicator): # type: ignore[misc]
|
||||
logger.debug(f"payload for {topic} wasn't text. Skipping...")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if self.websocket_server is None:
|
||||
logger.debug("Skipping message, websocket not connected yet")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.websocket_server.manager.broadcast(ws_message)
|
||||
except ConnectionResetError:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from enum import Enum
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +17,9 @@ from frigate.const import (
|
||||
ALL_ATTRIBUTE_LABELS,
|
||||
AUDIO_MIN_CONFIDENCE,
|
||||
CACHE_DIR,
|
||||
CACHE_SEGMENT_FORMAT,
|
||||
DEFAULT_DB_PATH,
|
||||
MAX_PRE_CAPTURE,
|
||||
REGEX_CAMERA_NAME,
|
||||
YAML_EXT,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -47,6 +50,13 @@ DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT = "%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
# DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT = "%d.%m.%Y %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
|
||||
FRIGATE_ENV_VARS = {k: v for k, v in os.environ.items() if k.startswith("FRIGATE_")}
|
||||
# read docker secret files as env vars too
|
||||
if os.path.isdir("/run/secrets"):
|
||||
for secret_file in os.listdir("/run/secrets"):
|
||||
if secret_file.startswith("FRIGATE_"):
|
||||
FRIGATE_ENV_VARS[secret_file] = Path(
|
||||
os.path.join("/run/secrets", secret_file)
|
||||
).read_text()
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_TRACKED_OBJECTS = ["person"]
|
||||
DEFAULT_LISTEN_AUDIO = ["bark", "fire_alarm", "scream", "speech", "yell"]
|
||||
@@ -171,10 +181,13 @@ class PtzAutotrackConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
timeout: int = Field(
|
||||
default=10, title="Seconds to delay before returning to preset."
|
||||
)
|
||||
movement_weights: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]] = Field(
|
||||
movement_weights: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = Field(
|
||||
default=[],
|
||||
title="Internal value used for PTZ movements based on the speed of your camera's motor.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
enabled_in_config: Optional[bool] = Field(
|
||||
title="Keep track of original state of autotracking."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@validator("movement_weights", pre=True)
|
||||
def validate_weights(cls, v):
|
||||
@@ -220,7 +233,9 @@ class RetainConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EventsConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
pre_capture: int = Field(default=5, title="Seconds to retain before event starts.")
|
||||
pre_capture: int = Field(
|
||||
default=5, title="Seconds to retain before event starts.", le=MAX_PRE_CAPTURE
|
||||
)
|
||||
post_capture: int = Field(default=5, title="Seconds to retain after event ends.")
|
||||
required_zones: List[str] = Field(
|
||||
default_factory=list,
|
||||
@@ -247,8 +262,8 @@ class RecordExportConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
class RecordConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
enabled: bool = Field(default=False, title="Enable record on all cameras.")
|
||||
sync_on_startup: bool = Field(
|
||||
default=False, title="Sync recordings with disk on startup."
|
||||
sync_recordings: bool = Field(
|
||||
default=False, title="Sync recordings with disk on startup and once a day."
|
||||
)
|
||||
expire_interval: int = Field(
|
||||
default=60,
|
||||
@@ -352,6 +367,9 @@ class DetectConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
default=5, title="Number of frames per second to process through detection."
|
||||
)
|
||||
enabled: bool = Field(default=True, title="Detection Enabled.")
|
||||
min_initialized: Optional[int] = Field(
|
||||
title="Minimum number of consecutive hits for an object to be initialized by the tracker."
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_disappeared: Optional[int] = Field(
|
||||
title="Maximum number of frames the object can dissapear before detection ends."
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -510,6 +528,13 @@ class BirdseyeModeEnum(str, Enum):
|
||||
return list(cls)[index]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BirdseyeLayoutConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
scaling_factor: float = Field(
|
||||
default=2.0, title="Birdseye Scaling Factor", ge=1.0, le=5.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_cameras: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, title="Max cameras")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BirdseyeConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
enabled: bool = Field(default=True, title="Enable birdseye view.")
|
||||
restream: bool = Field(default=False, title="Restream birdseye via RTSP.")
|
||||
@@ -521,9 +546,15 @@ class BirdseyeConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
ge=1,
|
||||
le=31,
|
||||
)
|
||||
inactivity_threshold: int = Field(
|
||||
default=30, title="Birdseye Inactivity Threshold", gt=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
mode: BirdseyeModeEnum = Field(
|
||||
default=BirdseyeModeEnum.objects, title="Tracking mode."
|
||||
)
|
||||
layout: BirdseyeLayoutConfig = Field(
|
||||
default_factory=BirdseyeLayoutConfig, title="Birdseye Layout Config"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# uses BaseModel because some global attributes are not available at the camera level
|
||||
@@ -728,6 +759,9 @@ class CameraConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
default=60,
|
||||
title="How long to wait for the image with the highest confidence score.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
webui_url: Optional[str] = Field(
|
||||
title="URL to visit the camera directly from system page",
|
||||
)
|
||||
zones: Dict[str, ZoneConfig] = Field(
|
||||
default_factory=dict, title="Zone configuration."
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -851,7 +885,7 @@ class CameraConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg_output_args = (
|
||||
record_args
|
||||
+ [f"{os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, self.name)}-%Y%m%d%H%M%S.mp4"]
|
||||
+ [f"{os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, self.name)}@{CACHE_SEGMENT_FORMAT}.mp4"]
|
||||
+ ffmpeg_output_args
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1143,6 +1177,11 @@ class FrigateConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
else DEFAULT_DETECT_DIMENSIONS["height"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Default min_initialized configuration
|
||||
min_initialized = camera_config.detect.fps / 2
|
||||
if camera_config.detect.min_initialized is None:
|
||||
camera_config.detect.min_initialized = min_initialized
|
||||
|
||||
# Default max_disappeared configuration
|
||||
max_disappeared = camera_config.detect.fps * 5
|
||||
if camera_config.detect.max_disappeared is None:
|
||||
@@ -1171,6 +1210,9 @@ class FrigateConfig(FrigateBaseModel):
|
||||
# set config pre-value
|
||||
camera_config.record.enabled_in_config = camera_config.record.enabled
|
||||
camera_config.audio.enabled_in_config = camera_config.audio.enabled
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled_in_config = (
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add default filters
|
||||
object_keys = camera_config.objects.track
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,6 +26,10 @@ LABEL_CONSOLIDATION_MAP = {
|
||||
"face": 0.5,
|
||||
}
|
||||
LABEL_CONSOLIDATION_DEFAULT = 0.9
|
||||
LABEL_NMS_MAP = {
|
||||
"car": 0.6,
|
||||
}
|
||||
LABEL_NMS_DEFAULT = 0.4
|
||||
|
||||
# Audio Consts
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,7 +54,10 @@ DRIVER_INTEL_iHD = "iHD"
|
||||
|
||||
# Record Values
|
||||
|
||||
CACHE_SEGMENT_FORMAT = "%Y%m%d%H%M%S%z"
|
||||
MAX_PRE_CAPTURE = 60
|
||||
MAX_SEGMENT_DURATION = 600
|
||||
MAX_SEGMENTS_IN_CACHE = 6
|
||||
MAX_PLAYLIST_SECONDS = 7200 # support 2 hour segments for a single playlist to account for cameras with inconsistent segment times
|
||||
|
||||
# Internal Comms Topics
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +67,7 @@ REQUEST_REGION_GRID = "request_region_grid"
|
||||
|
||||
# Autotracking
|
||||
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO = 0.5
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO = 0.6
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MOTION_MIN_DISTANCE = 20
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MOTION_MAX_POINTS = 500
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MAX_MOVE_METRICS = 500
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -49,12 +49,18 @@ class DeepStack(DetectionApi):
|
||||
image.save(output, format="JPEG")
|
||||
image_bytes = output.getvalue()
|
||||
data = {"api_key": self.api_key}
|
||||
response = requests.post(
|
||||
self.api_url,
|
||||
data=data,
|
||||
files={"image": image_bytes},
|
||||
timeout=self.api_timeout,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = requests.post(
|
||||
self.api_url,
|
||||
data=data,
|
||||
files={"image": image_bytes},
|
||||
timeout=self.api_timeout,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
|
||||
logger.error("Error calling deepstack API")
|
||||
return np.zeros((20, 6), np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
response_json = response.json()
|
||||
detections = np.zeros((20, 6), np.float32)
|
||||
if response_json.get("predictions") is None:
|
||||
|
||||
205
frigate/detectors/plugins/rknn.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
import urllib.request
|
||||
from typing import Literal
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from hide_warnings import hide_warnings
|
||||
except: # noqa: E722
|
||||
|
||||
def hide_warnings(func):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import Field
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.detectors.detection_api import DetectionApi
|
||||
from frigate.detectors.detector_config import BaseDetectorConfig
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
DETECTOR_KEY = "rknn"
|
||||
|
||||
supported_socs = ["rk3562", "rk3566", "rk3568", "rk3588"]
|
||||
|
||||
yolov8_suffix = {
|
||||
"default-yolov8n": "n",
|
||||
"default-yolov8s": "s",
|
||||
"default-yolov8m": "m",
|
||||
"default-yolov8l": "l",
|
||||
"default-yolov8x": "x",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class RknnDetectorConfig(BaseDetectorConfig):
|
||||
type: Literal[DETECTOR_KEY]
|
||||
core_mask: int = Field(default=0, ge=0, le=7, title="Core mask for NPU.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Rknn(DetectionApi):
|
||||
type_key = DETECTOR_KEY
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: RknnDetectorConfig):
|
||||
# create symlink for Home Assistant add on
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile("/proc/device-tree/compatible"):
|
||||
if os.path.isfile("/device-tree/compatible"):
|
||||
os.symlink("/device-tree/compatible", "/proc/device-tree/compatible")
|
||||
|
||||
# find out SoC
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with open("/proc/device-tree/compatible") as file:
|
||||
soc = file.read().split(",")[-1].strip("\x00")
|
||||
except FileNotFoundError:
|
||||
logger.error("Make sure to run docker in privileged mode.")
|
||||
raise Exception("Make sure to run docker in privileged mode.")
|
||||
|
||||
if soc not in supported_socs:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"Your SoC is not supported. Your SoC is: {}. Currently these SoCs are supported: {}.".format(
|
||||
soc, supported_socs
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
"Your SoC is not supported. Your SoC is: {}. Currently these SoCs are supported: {}.".format(
|
||||
soc, supported_socs
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile("/usr/lib/librknnrt.so"):
|
||||
if "rk356" in soc:
|
||||
os.rename("/usr/lib/librknnrt_rk356x.so", "/usr/lib/librknnrt.so")
|
||||
elif "rk3588" in soc:
|
||||
os.rename("/usr/lib/librknnrt_rk3588.so", "/usr/lib/librknnrt.so")
|
||||
|
||||
self.model_path = config.model.path or "default-yolov8n"
|
||||
self.core_mask = config.core_mask
|
||||
self.height = config.model.height
|
||||
self.width = config.model.width
|
||||
|
||||
if self.model_path in yolov8_suffix:
|
||||
if self.model_path == "default-yolov8n":
|
||||
self.model_path = "/models/rknn/yolov8n-320x320-{soc}.rknn".format(
|
||||
soc=soc
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_suffix = yolov8_suffix[self.model_path]
|
||||
self.model_path = (
|
||||
"/config/model_cache/rknn/yolov8{suffix}-320x320-{soc}.rknn".format(
|
||||
suffix=model_suffix, soc=soc
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
os.makedirs("/config/model_cache/rknn", exist_ok=True)
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile(self.model_path):
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
"Downloading yolov8{suffix} model.".format(suffix=model_suffix)
|
||||
)
|
||||
urllib.request.urlretrieve(
|
||||
"https://github.com/MarcA711/rknn-models/releases/download/v1.5.2-{soc}/yolov8{suffix}-320x320-{soc}.rknn".format(
|
||||
soc=soc, suffix=model_suffix
|
||||
),
|
||||
self.model_path,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if (config.model.width != 320) or (config.model.height != 320):
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"Make sure to set the model width and heigth to 320 in your config.yml."
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
"Make sure to set the model width and heigth to 320 in your config.yml."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if config.model.input_pixel_format != "bgr":
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
'Make sure to set the model input_pixel_format to "bgr" in your config.yml.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
'Make sure to set the model input_pixel_format to "bgr" in your config.yml.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if config.model.input_tensor != "nhwc":
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
'Make sure to set the model input_tensor to "nhwc" in your config.yml.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
'Make sure to set the model input_tensor to "nhwc" in your config.yml.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
|
||||
|
||||
self.rknn = RKNNLite(verbose=False)
|
||||
if self.rknn.load_rknn(self.model_path) != 0:
|
||||
logger.error("Error initializing rknn model.")
|
||||
if self.rknn.init_runtime(core_mask=self.core_mask) != 0:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"Error initializing rknn runtime. Do you run docker in privileged mode?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
self.rknn.release()
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, results):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Processes yolov8 output.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
results: array with shape: (1, 84, n, 1) where n depends on yolov8 model size (for 320x320 model n=2100)
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
detections: array with shape (20, 6) with 20 rows of (class, confidence, y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
results = np.transpose(results[0, :, :, 0]) # array shape (2100, 84)
|
||||
scores = np.max(
|
||||
results[:, 4:], axis=1
|
||||
) # array shape (2100,); max confidence of each row
|
||||
|
||||
# remove lines with score scores < 0.4
|
||||
filtered_arg = np.argwhere(scores > 0.4)
|
||||
results = results[filtered_arg[:, 0]]
|
||||
scores = scores[filtered_arg[:, 0]]
|
||||
|
||||
num_detections = len(scores)
|
||||
|
||||
if num_detections == 0:
|
||||
return np.zeros((20, 6), np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
if num_detections > 20:
|
||||
top_arg = np.argpartition(scores, -20)[-20:]
|
||||
results = results[top_arg]
|
||||
scores = scores[top_arg]
|
||||
num_detections = 20
|
||||
|
||||
classes = np.argmax(results[:, 4:], axis=1)
|
||||
|
||||
boxes = np.transpose(
|
||||
np.vstack(
|
||||
(
|
||||
(results[:, 1] - 0.5 * results[:, 3]) / self.height,
|
||||
(results[:, 0] - 0.5 * results[:, 2]) / self.width,
|
||||
(results[:, 1] + 0.5 * results[:, 3]) / self.height,
|
||||
(results[:, 0] + 0.5 * results[:, 2]) / self.width,
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
detections = np.zeros((20, 6), np.float32)
|
||||
detections[:num_detections, 0] = classes
|
||||
detections[:num_detections, 1] = scores
|
||||
detections[:num_detections, 2:] = boxes
|
||||
|
||||
return detections
|
||||
|
||||
@hide_warnings
|
||||
def inference(self, tensor_input):
|
||||
return self.rknn.inference(inputs=tensor_input)
|
||||
|
||||
def detect_raw(self, tensor_input):
|
||||
output = self.inference(
|
||||
[
|
||||
tensor_input,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self.postprocess(output[0])
|
||||
@@ -303,6 +303,7 @@ class TensorRtDetector(DetectionApi):
|
||||
ordered[:, 3] = np.clip(ordered[:, 3] + ordered[:, 1], 0, 1)
|
||||
# put result into the correct order and limit to top 20
|
||||
detections = ordered[:, [5, 4, 1, 0, 3, 2]][:20]
|
||||
|
||||
# pad to 20x6 shape
|
||||
append_cnt = 20 - len(detections)
|
||||
if append_cnt > 0:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -43,9 +43,9 @@ def get_ffmpeg_command(ffmpeg: FfmpegConfig) -> list[str]:
|
||||
ffmpeg_input: CameraInput = [i for i in ffmpeg.inputs if "audio" in i.roles][0]
|
||||
input_args = get_ffmpeg_arg_list(ffmpeg.global_args) + (
|
||||
parse_preset_input(ffmpeg_input.input_args, 1)
|
||||
or ffmpeg_input.input_args
|
||||
or get_ffmpeg_arg_list(ffmpeg_input.input_args)
|
||||
or parse_preset_input(ffmpeg.input_args, 1)
|
||||
or ffmpeg.input_args
|
||||
or get_ffmpeg_arg_list(ffmpeg.input_args)
|
||||
)
|
||||
return (
|
||||
["ffmpeg", "-vn"]
|
||||
@@ -240,7 +240,10 @@ class AudioEventMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
rms = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.absolute(np.square(audio_as_float))))
|
||||
|
||||
# Transform RMS to dBFS (decibels relative to full scale)
|
||||
dBFS = 20 * np.log10(np.abs(rms) / AUDIO_MAX_BIT_RANGE)
|
||||
if rms > 0:
|
||||
dBFS = 20 * np.log10(np.abs(rms) / AUDIO_MAX_BIT_RANGE)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dBFS = 0
|
||||
|
||||
self.inter_process_communicator.queue.put(
|
||||
(f"{self.config.name}/audio/dBFS", float(dBFS))
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -106,10 +106,10 @@ class ExternalEventProcessor:
|
||||
# write jpg snapshot with optional annotations
|
||||
if draw.get("boxes") and isinstance(draw.get("boxes"), list):
|
||||
for box in draw.get("boxes"):
|
||||
x = box["box"][0] * camera_config.detect.width
|
||||
y = box["box"][1] * camera_config.detect.height
|
||||
width = box["box"][2] * camera_config.detect.width
|
||||
height = box["box"][3] * camera_config.detect.height
|
||||
x = int(box["box"][0] * camera_config.detect.width)
|
||||
y = int(box["box"][1] * camera_config.detect.height)
|
||||
width = int(box["box"][2] * camera_config.detect.width)
|
||||
height = int(box["box"][3] * camera_config.detect.height)
|
||||
|
||||
draw_box_with_label(
|
||||
img_frame,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,8 +55,8 @@ _user_agent_args = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_DECODE = {
|
||||
"preset-rpi-32-h264": "-c:v:1 h264_v4l2m2m",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h264": "-c:v:1 h264_v4l2m2m",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h265": "-c:v:1 hevc_v4l2m2m",
|
||||
"preset-vaapi": f"-hwaccel_flags allow_profile_mismatch -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_device {_gpu_selector.get_selected_gpu()} -hwaccel_output_format vaapi",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h264": f"-hwaccel qsv -qsv_device {_gpu_selector.get_selected_gpu()} -hwaccel_output_format qsv -c:v h264_qsv",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h265": f"-load_plugin hevc_hw -hwaccel qsv -qsv_device {_gpu_selector.get_selected_gpu()} -hwaccel_output_format qsv -c:v hevc_qsv",
|
||||
@@ -65,24 +65,28 @@ PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_DECODE = {
|
||||
"preset-nvidia-mjpeg": "-hwaccel cuda -hwaccel_output_format cuda",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h264": "-c:v h264_nvmpi -resize {1}x{2}",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h265": "-c:v hevc_nvmpi -resize {1}x{2}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h264": "-c:v h264_rkmpp_decoder",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h265": "-c:v hevc_rkmpp_decoder",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_SCALE = {
|
||||
"preset-rpi-32-h264": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h264": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
"preset-vaapi": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale_vaapi=w={1}:h={2},hwdownload,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h265": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
"preset-vaapi": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale_vaapi=w={1}:h={2}:format=nv12,hwdownload,format=nv12,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h264": "-r {0} -vf vpp_qsv=framerate={0}:w={1}:h={2}:format=nv12,hwdownload,format=nv12,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h265": "-r {0} -vf vpp_qsv=framerate={0}:w={1}:h={2}:format=nv12,hwdownload,format=nv12,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-nvidia-h264": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale_cuda=w={1}:h={2}:format=nv12,hwdownload,format=nv12,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-nvidia-h265": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale_cuda=w={1}:h={2}:format=nv12,hwdownload,format=nv12,format=yuv420p",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h264": "-r {0}", # scaled in decoder
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h265": "-r {0}", # scaled in decoder
|
||||
"preset-rk-h264": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h265": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
"default": "-r {0} -vf fps={0},scale={1}:{2}",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_ENCODE_BIRDSEYE = {
|
||||
"preset-rpi-32-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_v4l2m2m {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_v4l2m2m {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_v4l2m2m {1}",
|
||||
"preset-vaapi": "ffmpeg -hide_banner -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_output_format vaapi -hwaccel_device {2} {0} -c:v h264_vaapi -g 50 -bf 0 -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -sei:v 0 -an -vf format=vaapi|nv12,hwupload {1}",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_qsv -g 50 -bf 0 -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -async_depth:v 1 {1}",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_qsv -g 50 -bf 0 -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -async_depth:v 1 {1}",
|
||||
@@ -90,12 +94,14 @@ PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_ENCODE_BIRDSEYE = {
|
||||
"preset-nvidia-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_nvenc -g 50 -profile:v high -level:v auto -preset:v p2 -tune:v ll {1}",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_nvmpi -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_nvmpi -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_rkmpp_encoder -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_rkmpp_encoder -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"default": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v libx264 -g 50 -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -preset:v superfast -tune:v zerolatency {1}",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_ENCODE_TIMELAPSE = {
|
||||
"preset-rpi-32-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_v4l2m2m {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_v4l2m2m {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_v4l2m2m -pix_fmt yuv420p {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rpi-64-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_v4l2m2m -pix_fmt yuv420p {1}",
|
||||
"preset-vaapi": "ffmpeg -hide_banner -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_output_format vaapi -hwaccel_device {2} {0} -c:v h264_vaapi {1}",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_qsv -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -async_depth:v 1 {1}",
|
||||
"preset-intel-qsv-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_qsv -profile:v high -level:v 4.1 -async_depth:v 1 {1}",
|
||||
@@ -103,6 +109,8 @@ PRESETS_HW_ACCEL_ENCODE_TIMELAPSE = {
|
||||
"preset-nvidia-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner -hwaccel cuda -hwaccel_output_format cuda -extra_hw_frames 8 {0} -c:v hevc_nvenc {1}",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_nvmpi -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-jetson-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_nvmpi -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h264": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v h264_rkmpp_encoder -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"preset-rk-h265": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v hevc_rkmpp_encoder -profile high {1}",
|
||||
"default": "ffmpeg -hide_banner {0} -c:v libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency {1}",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
293
frigate/http.py
@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@ import glob
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import subprocess as sp
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
@@ -15,6 +16,7 @@ from urllib.parse import unquote
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pytz
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from flask import (
|
||||
Blueprint,
|
||||
Flask,
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +43,7 @@ from frigate.const import (
|
||||
RECORD_DIR,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from frigate.events.external import ExternalEventProcessor
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings, Timeline
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings, Regions, Timeline
|
||||
from frigate.object_processing import TrackedObject
|
||||
from frigate.plus import PlusApi
|
||||
from frigate.ptz.onvif import OnvifController
|
||||
@@ -115,7 +117,7 @@ def is_healthy():
|
||||
@bp.route("/events/summary")
|
||||
def events_summary():
|
||||
tz_name = request.args.get("timezone", default="utc", type=str)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier, seconds_offset = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
has_clip = request.args.get("has_clip", type=int)
|
||||
has_snapshot = request.args.get("has_snapshot", type=int)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -149,12 +151,7 @@ def events_summary():
|
||||
Event.camera,
|
||||
Event.label,
|
||||
Event.sub_label,
|
||||
fn.strftime(
|
||||
"%Y-%m-%d",
|
||||
fn.datetime(
|
||||
Event.start_time, "unixepoch", hour_modifier, minute_modifier
|
||||
),
|
||||
),
|
||||
(Event.start_time + seconds_offset).cast("int") / (3600 * 24),
|
||||
Event.zones,
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -278,6 +275,13 @@ def send_to_plus(id):
|
||||
box,
|
||||
event.label,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
message = "Error uploading annotation, unsupported label provided."
|
||||
logger.error(message)
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": message}),
|
||||
400,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as ex:
|
||||
logger.exception(ex)
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
@@ -349,6 +353,13 @@ def false_positive(id):
|
||||
event.model_type,
|
||||
event.detector_type,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
message = "Error uploading false positive, unsupported label provided."
|
||||
logger.error(message)
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": message}),
|
||||
400,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as ex:
|
||||
logger.exception(ex)
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
@@ -726,6 +737,126 @@ def label_snapshot(camera_name, label):
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/<camera_name>/grid.jpg")
|
||||
def grid_snapshot(camera_name):
|
||||
request.args.get("type", default="region")
|
||||
|
||||
if camera_name in current_app.frigate_config.cameras:
|
||||
detect = current_app.frigate_config.cameras[camera_name].detect
|
||||
frame = current_app.detected_frames_processor.get_current_frame(camera_name, {})
|
||||
retry_interval = float(
|
||||
current_app.frigate_config.cameras.get(camera_name).ffmpeg.retry_interval
|
||||
or 10
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if frame is None or datetime.now().timestamp() > (
|
||||
current_app.detected_frames_processor.get_current_frame_time(camera_name)
|
||||
+ retry_interval
|
||||
):
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": "Unable to get valid frame"}),
|
||||
500,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
grid = (
|
||||
Regions.select(Regions.grid)
|
||||
.where(Regions.camera == camera_name)
|
||||
.get()
|
||||
.grid
|
||||
)
|
||||
except DoesNotExist:
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": "Unable to get region grid"}),
|
||||
500,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
color_arg = request.args.get("color", default="", type=str).lower()
|
||||
draw_font_scale = request.args.get("font_scale", default=0.5, type=float)
|
||||
|
||||
if color_arg == "red":
|
||||
draw_color = (0, 0, 255)
|
||||
elif color_arg == "blue":
|
||||
draw_color = (255, 0, 0)
|
||||
elif color_arg == "black":
|
||||
draw_color = (0, 0, 0)
|
||||
elif color_arg == "white":
|
||||
draw_color = (255, 255, 255)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
draw_color = (0, 255, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
grid_size = len(grid)
|
||||
grid_coef = 1.0 / grid_size
|
||||
width = detect.width
|
||||
height = detect.height
|
||||
for x in range(grid_size):
|
||||
for y in range(grid_size):
|
||||
cell = grid[x][y]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(cell["sizes"]) == 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
std_dev = round(cell["std_dev"] * width, 2)
|
||||
mean = round(cell["mean"] * width, 2)
|
||||
cv2.rectangle(
|
||||
frame,
|
||||
(int(x * grid_coef * width), int(y * grid_coef * height)),
|
||||
(
|
||||
int((x + 1) * grid_coef * width),
|
||||
int((y + 1) * grid_coef * height),
|
||||
),
|
||||
draw_color,
|
||||
2,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cv2.putText(
|
||||
frame,
|
||||
f"#: {len(cell['sizes'])}",
|
||||
(
|
||||
int(x * grid_coef * width + 10),
|
||||
int((y * grid_coef + 0.02) * height),
|
||||
),
|
||||
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
|
||||
fontScale=draw_font_scale,
|
||||
color=draw_color,
|
||||
thickness=2,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cv2.putText(
|
||||
frame,
|
||||
f"std: {std_dev}",
|
||||
(
|
||||
int(x * grid_coef * width + 10),
|
||||
int((y * grid_coef + 0.05) * height),
|
||||
),
|
||||
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
|
||||
fontScale=draw_font_scale,
|
||||
color=draw_color,
|
||||
thickness=2,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cv2.putText(
|
||||
frame,
|
||||
f"avg: {mean}",
|
||||
(
|
||||
int(x * grid_coef * width + 10),
|
||||
int((y * grid_coef + 0.08) * height),
|
||||
),
|
||||
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
|
||||
fontScale=draw_font_scale,
|
||||
color=draw_color,
|
||||
thickness=2,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
ret, jpg = cv2.imencode(".jpg", frame, [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), 70])
|
||||
response = make_response(jpg.tobytes())
|
||||
response.headers["Content-Type"] = "image/jpeg"
|
||||
response.headers["Cache-Control"] = "no-store"
|
||||
return response
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": "Camera not found"}),
|
||||
404,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/events/<id>/clip.mp4")
|
||||
def event_clip(id):
|
||||
download = request.args.get("download", type=bool)
|
||||
@@ -760,7 +891,7 @@ def event_clip(id):
|
||||
response.headers["Content-Length"] = os.path.getsize(clip_path)
|
||||
response.headers[
|
||||
"X-Accel-Redirect"
|
||||
] = f"/clips/{file_name}" # nginx: http://wiki.nginx.org/NginxXSendfile
|
||||
] = f"/clips/{file_name}" # nginx: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_ignore_headers
|
||||
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -889,7 +1020,7 @@ def events():
|
||||
if time_range != DEFAULT_TIME_RANGE:
|
||||
# get timezone arg to ensure browser times are used
|
||||
tz_name = request.args.get("timezone", default="utc", type=str)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier, _ = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
|
||||
times = time_range.split(",")
|
||||
time_after = times[0]
|
||||
@@ -946,7 +1077,7 @@ def events():
|
||||
if is_submitted is not None:
|
||||
if is_submitted == 0:
|
||||
clauses.append((Event.plus_id.is_null()))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
elif is_submitted > 0:
|
||||
clauses.append((Event.plus_id != ""))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(clauses) == 0:
|
||||
@@ -1038,6 +1169,9 @@ def end_event(event_id):
|
||||
def config():
|
||||
config = current_app.frigate_config.dict()
|
||||
|
||||
# remove the mqtt password
|
||||
config["mqtt"].pop("password", None)
|
||||
|
||||
for camera_name, camera in current_app.frigate_config.cameras.items():
|
||||
camera_dict = config["cameras"][camera_name]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1226,6 +1360,22 @@ def config_schema():
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/go2rtc/streams")
|
||||
def go2rtc_streams():
|
||||
r = requests.get("http://127.0.0.1:1984/api/streams")
|
||||
if not r.ok:
|
||||
logger.error("Failed to fetch streams from go2rtc")
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": "Error fetching stream data"}),
|
||||
500,
|
||||
)
|
||||
stream_data = r.json()
|
||||
for data in stream_data.values():
|
||||
for producer in data.get("producers", []):
|
||||
producer["url"] = clean_camera_user_pass(producer.get("url", ""))
|
||||
return jsonify(stream_data)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/version")
|
||||
def version():
|
||||
return VERSION
|
||||
@@ -1388,6 +1538,8 @@ def get_snapshot_from_recording(camera_name: str, frame_time: str):
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
.where(Recordings.camera == camera_name)
|
||||
.order_by(Recordings.start_time.desc())
|
||||
.limit(1)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@@ -1461,7 +1613,7 @@ def get_recordings_storage_usage():
|
||||
@bp.route("/<camera_name>/recordings/summary")
|
||||
def recordings_summary(camera_name):
|
||||
tz_name = request.args.get("timezone", default="utc", type=str)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
hour_modifier, minute_modifier, seconds_offset = get_tz_modifiers(tz_name)
|
||||
recording_groups = (
|
||||
Recordings.select(
|
||||
fn.strftime(
|
||||
@@ -1475,22 +1627,8 @@ def recordings_summary(camera_name):
|
||||
fn.SUM(Recordings.objects).alias("objects"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
.where(Recordings.camera == camera_name)
|
||||
.group_by(
|
||||
fn.strftime(
|
||||
"%Y-%m-%d %H",
|
||||
fn.datetime(
|
||||
Recordings.start_time, "unixepoch", hour_modifier, minute_modifier
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
.order_by(
|
||||
fn.strftime(
|
||||
"%Y-%m-%d H",
|
||||
fn.datetime(
|
||||
Recordings.start_time, "unixepoch", hour_modifier, minute_modifier
|
||||
),
|
||||
).desc()
|
||||
)
|
||||
.group_by((Recordings.start_time + seconds_offset).cast("int") / 3600)
|
||||
.order_by(Recordings.start_time.desc())
|
||||
.namedtuples()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1505,14 +1643,7 @@ def recordings_summary(camera_name):
|
||||
fn.COUNT(Event.id).alias("count"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
.where(Event.camera == camera_name, Event.has_clip)
|
||||
.group_by(
|
||||
fn.strftime(
|
||||
"%Y-%m-%d %H",
|
||||
fn.datetime(
|
||||
Event.start_time, "unixepoch", hour_modifier, minute_modifier
|
||||
),
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
.group_by((Event.start_time + seconds_offset).cast("int") / 3600)
|
||||
.namedtuples()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1656,7 +1787,7 @@ def recording_clip(camera_name, start_ts, end_ts):
|
||||
response.headers["Content-Length"] = os.path.getsize(path)
|
||||
response.headers[
|
||||
"X-Accel-Redirect"
|
||||
] = f"/cache/{file_name}" # nginx: http://wiki.nginx.org/NginxXSendfile
|
||||
] = f"/cache/{file_name}" # nginx: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_ignore_headers
|
||||
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1858,9 +1989,68 @@ def export_recording(camera_name: str, start_time, end_time):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def export_filename_check_extension(filename: str):
|
||||
if filename.endswith(".mp4"):
|
||||
return filename
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return filename + ".mp4"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def export_filename_is_valid(filename: str):
|
||||
if re.search(r"[^:_A-Za-z0-9]", filename) or filename.startswith("in_progress."):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/export/<file_name_current>/<file_name_new>", methods=["PATCH"])
|
||||
def export_rename(file_name_current, file_name_new: str):
|
||||
safe_file_name_current = secure_filename(
|
||||
export_filename_check_extension(file_name_current)
|
||||
)
|
||||
file_current = os.path.join(EXPORT_DIR, safe_file_name_current)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(file_current):
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": f"{file_name_current} not found."}),
|
||||
404,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not export_filename_is_valid(file_name_new):
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": False,
|
||||
"message": f"{file_name_new} contains illegal characters.",
|
||||
}
|
||||
),
|
||||
400,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
safe_file_name_new = secure_filename(export_filename_check_extension(file_name_new))
|
||||
file_new = os.path.join(EXPORT_DIR, safe_file_name_new)
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.exists(file_new):
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": f"{file_name_new} already exists."}),
|
||||
400,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
os.rename(file_current, file_new)
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": True,
|
||||
"message": "Successfully renamed file.",
|
||||
}
|
||||
),
|
||||
200,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/export/<file_name>", methods=["DELETE"])
|
||||
def export_delete(file_name: str):
|
||||
safe_file_name = secure_filename(file_name)
|
||||
safe_file_name = secure_filename(export_filename_check_extension(file_name))
|
||||
file = os.path.join(EXPORT_DIR, safe_file_name)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(file):
|
||||
@@ -1995,3 +2185,30 @@ def logs(service: str):
|
||||
jsonify({"success": False, "message": "Could not find log file"}),
|
||||
500,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@bp.route("/restart", methods=["POST"])
|
||||
def restart():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
restart_frigate()
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
logging.error(f"Error restarting Frigate: {e}")
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": False,
|
||||
"message": "Unable to restart Frigate.",
|
||||
}
|
||||
),
|
||||
500,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return make_response(
|
||||
jsonify(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": True,
|
||||
"message": "Restarting (this can take up to one minute)...",
|
||||
}
|
||||
),
|
||||
200,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,9 +128,6 @@ class TrackedObject:
|
||||
self.frame = None
|
||||
self.previous = self.to_dict()
|
||||
|
||||
# start the score history
|
||||
self.score_history = [self.obj_data["score"]]
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_false_positive(self):
|
||||
# once a true positive, always a true positive
|
||||
if not self.false_positive:
|
||||
@@ -198,7 +195,7 @@ class TrackedObject:
|
||||
self.zone_presence[name] = zone_score + 1
|
||||
|
||||
# an object is only considered present in a zone if it has a zone inertia of 3+
|
||||
if zone_score >= zone.inertia:
|
||||
if self.zone_presence[name] >= zone.inertia:
|
||||
current_zones.append(name)
|
||||
|
||||
if name not in self.entered_zones:
|
||||
@@ -248,10 +245,8 @@ class TrackedObject:
|
||||
if self.obj_data["frame_time"] - self.previous["frame_time"] > 60:
|
||||
significant_change = True
|
||||
|
||||
# update autotrack at half fps
|
||||
if self.obj_data["frame_time"] - self.previous["frame_time"] > (
|
||||
1 / (self.camera_config.detect.fps / 2)
|
||||
):
|
||||
# update autotrack at most 3 objects per second
|
||||
if self.obj_data["frame_time"] - self.previous["frame_time"] >= (1 / 3):
|
||||
autotracker_update = True
|
||||
|
||||
self.obj_data.update(obj_data)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,8 +20,8 @@ from ws4py.server.wsgirefserver import (
|
||||
WSGIServer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ws4py.server.wsgiutils import WebSocketWSGIApplication
|
||||
from ws4py.websocket import WebSocket
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.comms.ws import WebSocket
|
||||
from frigate.config import BirdseyeModeEnum, FrigateConfig
|
||||
from frigate.const import BASE_DIR, BIRDSEYE_PIPE
|
||||
from frigate.types import CameraMetricsTypes
|
||||
@@ -41,10 +41,13 @@ def get_standard_aspect_ratio(width: int, height: int) -> tuple[int, int]:
|
||||
(16, 9),
|
||||
(9, 16),
|
||||
(20, 10),
|
||||
(16, 3), # max wide camera
|
||||
(16, 6), # reolink duo 2
|
||||
(32, 9), # panoramic cameras
|
||||
(12, 9),
|
||||
(9, 12),
|
||||
(22, 15), # Amcrest, NTSC DVT
|
||||
(1, 1), # fisheye
|
||||
] # aspects are scaled to have common relative size
|
||||
known_aspects_ratios = list(
|
||||
map(lambda aspect: aspect[0] / aspect[1], known_aspects)
|
||||
@@ -63,8 +66,8 @@ def get_canvas_shape(width: int, height: int) -> tuple[int, int]:
|
||||
a_w, a_h = get_standard_aspect_ratio(width, height)
|
||||
|
||||
if round(a_w / a_h, 2) != round(width / height, 2):
|
||||
canvas_width = width
|
||||
canvas_height = int((canvas_width / a_w) * a_h)
|
||||
canvas_width = int(width // 4 * 4)
|
||||
canvas_height = int((canvas_width / a_w * a_h) // 4 * 4)
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"The birdseye resolution is a non-standard aspect ratio, forcing birdseye resolution to {canvas_width} x {canvas_height}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -73,7 +76,13 @@ def get_canvas_shape(width: int, height: int) -> tuple[int, int]:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Canvas:
|
||||
def __init__(self, canvas_width: int, canvas_height: int) -> None:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
canvas_width: int,
|
||||
canvas_height: int,
|
||||
scaling_factor: int,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
self.scaling_factor = scaling_factor
|
||||
gcd = math.gcd(canvas_width, canvas_height)
|
||||
self.aspect = get_standard_aspect_ratio(
|
||||
(canvas_width / gcd), (canvas_height / gcd)
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +96,7 @@ class Canvas:
|
||||
return (self.aspect[0] * coefficient, self.aspect[1] * coefficient)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_coefficient(self, camera_count: int) -> int:
|
||||
return self.coefficient_cache.get(camera_count, 2)
|
||||
return self.coefficient_cache.get(camera_count, self.scaling_factor)
|
||||
|
||||
def set_coefficient(self, camera_count: int, coefficient: int) -> None:
|
||||
self.coefficient_cache[camera_count] = coefficient
|
||||
@@ -108,9 +117,12 @@ class Canvas:
|
||||
return camera_aspect
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FFMpegConverter:
|
||||
class FFMpegConverter(threading.Thread):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
camera: str,
|
||||
input_queue: queue.Queue,
|
||||
stop_event: mp.Event,
|
||||
in_width: int,
|
||||
in_height: int,
|
||||
out_width: int,
|
||||
@@ -118,6 +130,11 @@ class FFMpegConverter:
|
||||
quality: int,
|
||||
birdseye_rtsp: bool = False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
|
||||
self.name = f"{camera}_output_converter"
|
||||
self.camera = camera
|
||||
self.input_queue = input_queue
|
||||
self.stop_event = stop_event
|
||||
self.bd_pipe = None
|
||||
|
||||
if birdseye_rtsp:
|
||||
@@ -167,7 +184,7 @@ class FFMpegConverter:
|
||||
os.close(stdin)
|
||||
self.reading_birdseye = False
|
||||
|
||||
def write(self, b) -> None:
|
||||
def __write(self, b) -> None:
|
||||
self.process.stdin.write(b)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.bd_pipe:
|
||||
@@ -203,9 +220,25 @@ class FFMpegConverter:
|
||||
self.process.kill()
|
||||
self.process.communicate()
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self) -> None:
|
||||
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
frame = self.input_queue.get(True, timeout=1)
|
||||
self.__write(frame)
|
||||
except queue.Empty:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
self.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BroadcastThread(threading.Thread):
|
||||
def __init__(self, camera, converter, websocket_server, stop_event):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
camera: str,
|
||||
converter: FFMpegConverter,
|
||||
websocket_server,
|
||||
stop_event: mp.Event,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super(BroadcastThread, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.camera = camera
|
||||
self.converter = converter
|
||||
@@ -251,9 +284,13 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
self.frame_shape = (height, width)
|
||||
self.yuv_shape = (height * 3 // 2, width)
|
||||
self.frame = np.ndarray(self.yuv_shape, dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
self.canvas = Canvas(width, height)
|
||||
self.canvas = Canvas(width, height, config.birdseye.layout.scaling_factor)
|
||||
self.stop_event = stop_event
|
||||
self.camera_metrics = camera_metrics
|
||||
self.inactivity_threshold = config.birdseye.inactivity_threshold
|
||||
|
||||
if config.birdseye.layout.max_cameras:
|
||||
self.last_refresh_time = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# initialize the frame as black and with the Frigate logo
|
||||
self.blank_frame = np.zeros(self.yuv_shape, np.uint8)
|
||||
@@ -359,16 +396,39 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
def update_frame(self):
|
||||
"""Update to a new frame for birdseye."""
|
||||
|
||||
# determine how many cameras are tracking objects within the last 30 seconds
|
||||
active_cameras = set(
|
||||
# determine how many cameras are tracking objects within the last inactivity_threshold seconds
|
||||
active_cameras: set[str] = set(
|
||||
[
|
||||
cam
|
||||
for cam, cam_data in self.cameras.items()
|
||||
if cam_data["last_active_frame"] > 0
|
||||
and cam_data["current_frame"] - cam_data["last_active_frame"] < 30
|
||||
and cam_data["current_frame"] - cam_data["last_active_frame"]
|
||||
< self.inactivity_threshold
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
max_cameras = self.config.birdseye.layout.max_cameras
|
||||
max_camera_refresh = False
|
||||
if max_cameras:
|
||||
now = datetime.datetime.now().timestamp()
|
||||
|
||||
if len(active_cameras) == max_cameras and now - self.last_refresh_time < 10:
|
||||
# don't refresh cameras too often
|
||||
active_cameras = self.active_cameras
|
||||
else:
|
||||
limited_active_cameras = sorted(
|
||||
active_cameras,
|
||||
key=lambda active_camera: (
|
||||
self.cameras[active_camera]["current_frame"]
|
||||
- self.cameras[active_camera]["last_active_frame"]
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
active_cameras = limited_active_cameras[
|
||||
: self.config.birdseye.layout.max_cameras
|
||||
]
|
||||
max_camera_refresh = True
|
||||
self.last_refresh_time = now
|
||||
|
||||
# if there are no active cameras
|
||||
if len(active_cameras) == 0:
|
||||
# if the layout is already cleared
|
||||
@@ -382,7 +442,15 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
# check if we need to reset the layout because there is a different number of cameras
|
||||
reset_layout = len(self.active_cameras) - len(active_cameras) != 0
|
||||
if len(self.active_cameras) - len(active_cameras) == 0:
|
||||
if len(self.active_cameras) == 1 and self.active_cameras != active_cameras:
|
||||
reset_layout = True
|
||||
elif max_camera_refresh:
|
||||
reset_layout = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset_layout = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset_layout = True
|
||||
|
||||
# reset the layout if it needs to be different
|
||||
if reset_layout:
|
||||
@@ -406,17 +474,23 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
camera = active_cameras_to_add[0]
|
||||
camera_dims = self.cameras[camera]["dimensions"].copy()
|
||||
scaled_width = int(self.canvas.height * camera_dims[0] / camera_dims[1])
|
||||
coefficient = (
|
||||
1
|
||||
if scaled_width <= self.canvas.width
|
||||
else self.canvas.width / scaled_width
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# center camera view in canvas and ensure that it fits
|
||||
if scaled_width < self.canvas.width:
|
||||
coefficient = 1
|
||||
x_offset = int((self.canvas.width - scaled_width) / 2)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
coefficient = self.canvas.width / scaled_width
|
||||
x_offset = int(
|
||||
(self.canvas.width - (scaled_width * coefficient)) / 2
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.camera_layout = [
|
||||
[
|
||||
(
|
||||
camera,
|
||||
(
|
||||
0,
|
||||
x_offset,
|
||||
0,
|
||||
int(scaled_width * coefficient),
|
||||
int(self.canvas.height * coefficient),
|
||||
@@ -460,10 +534,14 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_layout(self, cameras_to_add: list[str], coefficient) -> tuple[any]:
|
||||
def calculate_layout(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
cameras_to_add: list[str],
|
||||
coefficient: float,
|
||||
) -> tuple[any]:
|
||||
"""Calculate the optimal layout for 2+ cameras."""
|
||||
|
||||
def map_layout(row_height: int):
|
||||
def map_layout(camera_layout: list[list[any]], row_height: int):
|
||||
"""Map the calculated layout."""
|
||||
candidate_layout = []
|
||||
starting_x = 0
|
||||
@@ -492,7 +570,7 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
x + scaled_width > self.canvas.width
|
||||
or y + scaled_height > self.canvas.height
|
||||
):
|
||||
return 0, 0, None
|
||||
return x + scaled_width, y + scaled_height, None
|
||||
|
||||
final_row.append((cameras[0], (x, y, scaled_width, scaled_height)))
|
||||
x += scaled_width
|
||||
@@ -564,10 +642,24 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
row_height = int(self.canvas.height / coefficient)
|
||||
total_width, total_height, standard_candidate_layout = map_layout(row_height)
|
||||
total_width, total_height, standard_candidate_layout = map_layout(
|
||||
camera_layout, row_height
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not standard_candidate_layout:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
# if standard layout didn't work
|
||||
# try reducing row_height by the % overflow
|
||||
scale_down_percent = max(
|
||||
total_width / self.canvas.width,
|
||||
total_height / self.canvas.height,
|
||||
)
|
||||
row_height = int(row_height / scale_down_percent)
|
||||
total_width, total_height, standard_candidate_layout = map_layout(
|
||||
camera_layout, row_height
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not standard_candidate_layout:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# layout can't be optimized more
|
||||
if total_width / self.canvas.width >= 0.99:
|
||||
@@ -578,7 +670,7 @@ class BirdsEyeFrameManager:
|
||||
1 / (total_height / self.canvas.height),
|
||||
)
|
||||
row_height = int(row_height * scale_up_percent)
|
||||
_, _, scaled_layout = map_layout(row_height)
|
||||
_, _, scaled_layout = map_layout(camera_layout, row_height)
|
||||
|
||||
if scaled_layout:
|
||||
return scaled_layout
|
||||
@@ -664,15 +756,20 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
websocket_server.initialize_websockets_manager()
|
||||
websocket_thread = threading.Thread(target=websocket_server.serve_forever)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs: dict[str, queue.Queue] = {}
|
||||
converters = {}
|
||||
broadcasters = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for camera, cam_config in config.cameras.items():
|
||||
inputs[camera] = queue.Queue(maxsize=cam_config.detect.fps)
|
||||
width = int(
|
||||
cam_config.live.height
|
||||
* (cam_config.frame_shape[1] / cam_config.frame_shape[0])
|
||||
)
|
||||
converters[camera] = FFMpegConverter(
|
||||
camera,
|
||||
inputs[camera],
|
||||
stop_event,
|
||||
cam_config.frame_shape[1],
|
||||
cam_config.frame_shape[0],
|
||||
width,
|
||||
@@ -684,7 +781,11 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if config.birdseye.enabled:
|
||||
inputs["birdseye"] = queue.Queue(maxsize=10)
|
||||
converters["birdseye"] = FFMpegConverter(
|
||||
"birdseye",
|
||||
inputs["birdseye"],
|
||||
stop_event,
|
||||
config.birdseye.width,
|
||||
config.birdseye.height,
|
||||
config.birdseye.width,
|
||||
@@ -701,6 +802,9 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
|
||||
websocket_thread.start()
|
||||
|
||||
for t in converters.values():
|
||||
t.start()
|
||||
|
||||
for t in broadcasters.values():
|
||||
t.start()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -735,7 +839,11 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
ws.environ["PATH_INFO"].endswith(camera) for ws in websocket_server.manager
|
||||
):
|
||||
# write to the converter for the camera if clients are listening to the specific camera
|
||||
converters[camera].write(frame.tobytes())
|
||||
try:
|
||||
inputs[camera].put_nowait(frame.tobytes())
|
||||
except queue.Full:
|
||||
# drop frames if queue is full
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
if config.birdseye.enabled and (
|
||||
config.birdseye.restream
|
||||
@@ -756,7 +864,11 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
if config.birdseye.restream:
|
||||
birdseye_buffer[:] = frame_bytes
|
||||
|
||||
converters["birdseye"].write(frame_bytes)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
inputs["birdseye"].put_nowait(frame_bytes)
|
||||
except queue.Full:
|
||||
# drop frames if queue is full
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
if camera in previous_frames:
|
||||
frame_manager.delete(f"{camera}{previous_frames[camera]}")
|
||||
@@ -776,10 +888,9 @@ def output_frames(
|
||||
frame = frame_manager.get(frame_id, config.cameras[camera].frame_shape_yuv)
|
||||
frame_manager.delete(frame_id)
|
||||
|
||||
for c in converters.values():
|
||||
c.exit()
|
||||
for b in broadcasters.values():
|
||||
b.join()
|
||||
|
||||
websocket_server.manager.close_all()
|
||||
websocket_server.manager.stop()
|
||||
websocket_server.manager.join()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import Any, List
|
||||
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
@@ -36,6 +37,10 @@ class PlusApi:
|
||||
self.key = None
|
||||
if PLUS_ENV_VAR in os.environ:
|
||||
self.key = os.environ.get(PLUS_ENV_VAR)
|
||||
elif os.path.isdir("/run/secrets") and PLUS_ENV_VAR in os.listdir(
|
||||
"/run/secrets"
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.key = Path(os.path.join("/run/secrets", PLUS_ENV_VAR)).read_text()
|
||||
# check for the addon options file
|
||||
elif os.path.isfile("/data/options.json"):
|
||||
with open("/data/options.json") as f:
|
||||
@@ -166,6 +171,17 @@ class PlusApi:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not r.ok:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
error_response = r.json()
|
||||
errors = error_response.get("errors", [])
|
||||
for error in errors:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
error.get("param") == "label"
|
||||
and error.get("type") == "invalid_enum_value"
|
||||
):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported label value provided: {label}")
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
raise Exception(r.text)
|
||||
|
||||
def add_annotation(
|
||||
@@ -188,6 +204,17 @@ class PlusApi:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not r.ok:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
error_response = r.json()
|
||||
errors = error_response.get("errors", [])
|
||||
for error in errors:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
error.get("param") == "label"
|
||||
and error.get("type") == "invalid_enum_value"
|
||||
):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported label value provided: {label}")
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
raise Exception(r.text)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_model_download_url(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ from norfair.camera_motion import (
|
||||
TranslationTransformationGetter,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.comms.dispatcher import Dispatcher
|
||||
from frigate.config import CameraConfig, FrigateConfig, ZoomingModeEnum
|
||||
from frigate.const import (
|
||||
AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO,
|
||||
@@ -144,11 +145,14 @@ class PtzAutoTrackerThread(threading.Thread):
|
||||
config: FrigateConfig,
|
||||
onvif: OnvifController,
|
||||
ptz_metrics: dict[str, PTZMetricsTypes],
|
||||
dispatcher: Dispatcher,
|
||||
stop_event: MpEvent,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
|
||||
self.name = "ptz_autotracker"
|
||||
self.ptz_autotracker = PtzAutoTracker(config, onvif, ptz_metrics)
|
||||
self.ptz_autotracker = PtzAutoTracker(
|
||||
config, onvif, ptz_metrics, dispatcher, stop_event
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.stop_event = stop_event
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -175,10 +179,14 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
config: FrigateConfig,
|
||||
onvif: OnvifController,
|
||||
ptz_metrics: PTZMetricsTypes,
|
||||
dispatcher: Dispatcher,
|
||||
stop_event: MpEvent,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.onvif = onvif
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics = ptz_metrics
|
||||
self.dispatcher = dispatcher
|
||||
self.stop_event = stop_event
|
||||
self.tracked_object: dict[str, object] = {}
|
||||
self.tracked_object_history: dict[str, object] = {}
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics: dict[str, object] = {}
|
||||
@@ -200,7 +208,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
self.autotracker_init[camera] = False
|
||||
if camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled
|
||||
and camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled_in_config
|
||||
):
|
||||
self._autotracker_setup(camera_config, camera)
|
||||
|
||||
def _autotracker_setup(self, camera_config, camera):
|
||||
@@ -215,8 +226,8 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
maxlen=round(camera_config.detect.fps * 1.5)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera] = {
|
||||
"max_target_box": 1
|
||||
- (AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO ** self.zoom_factor[camera])
|
||||
"max_target_box": AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO
|
||||
** (1 / self.zoom_factor[camera])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
self.calibrating[camera] = False
|
||||
@@ -227,32 +238,40 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.move_queues[camera] = queue.Queue()
|
||||
self.move_queue_locks[camera] = threading.Lock()
|
||||
|
||||
# handle onvif constructor failing due to no connection
|
||||
if camera not in self.onvif.cams:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking for {camera}: onvif connection failed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if not self.onvif.cams[camera]["init"]:
|
||||
if not self.onvif._init_onvif(camera):
|
||||
logger.warning(f"Unable to initialize onvif for {camera}")
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking for {camera}: Unable to initialize onvif"
|
||||
)
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if "pt-r-fov" not in self.onvif.cams[camera]["features"]:
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking for {camera}: FOV relative movement not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
movestatus_supported = self.onvif.get_service_capabilities(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
if movestatus_supported is None or movestatus_supported.lower() != "true":
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking for {camera}: ONVIF MoveStatus not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.enabled = False
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_autotracker_enabled"].value = False
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if self.onvif.cams[camera]["init"]:
|
||||
@@ -268,6 +287,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
|
||||
if camera_config.onvif.autotracking.movement_weights:
|
||||
if len(camera_config.onvif.autotracking.movement_weights) == 5:
|
||||
camera_config.onvif.autotracking.movement_weights = [
|
||||
float(val)
|
||||
for val in camera_config.onvif.autotracking.movement_weights
|
||||
]
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera][
|
||||
"ptz_min_zoom"
|
||||
].value = camera_config.onvif.autotracking.movement_weights[0]
|
||||
@@ -290,6 +313,8 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
if camera_config.onvif.autotracking.calibrate_on_startup:
|
||||
self._calibrate_camera(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_tracking_active"].clear()
|
||||
self.dispatcher.publish(f"{camera}/ptz_autotracker/active", "OFF", retain=False)
|
||||
self.autotracker_init[camera] = True
|
||||
|
||||
def _write_config(self, camera):
|
||||
@@ -334,7 +359,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
zoom_out_values.append(self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_zoom_level"].value)
|
||||
@@ -345,7 +370,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
zoom_in_values.append(self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_zoom_level"].value)
|
||||
@@ -363,7 +388,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
zoom_out_values.append(
|
||||
@@ -379,7 +404,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
zoom_in_values.append(
|
||||
@@ -402,10 +427,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera].onvif.autotracking.return_preset.lower(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_reset"].set()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
|
||||
# Wait until the camera finishes moving
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
for step in range(num_steps):
|
||||
@@ -416,7 +441,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.onvif._move_relative(camera, pan, tilt, 0, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Wait until the camera finishes moving
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
stop_time = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -434,10 +459,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera].onvif.autotracking.return_preset.lower(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_reset"].set()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
|
||||
# Wait until the camera finishes moving
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
@@ -521,7 +546,11 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
camera_height = camera_config.frame_shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Extract areas and calculate weighted average
|
||||
areas = [obj["area"] for obj in self.tracked_object_history[camera]]
|
||||
# grab the largest dimension of the bounding box and create a square from that
|
||||
areas = [
|
||||
max(obj["box"][2] - obj["box"][0], obj["box"][3] - obj["box"][1]) ** 2
|
||||
for obj in self.tracked_object_history[camera]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
filtered_areas = (
|
||||
remove_outliers(areas)
|
||||
@@ -567,8 +596,11 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
camera_config.frame_shape[1]
|
||||
camera_config.frame_shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
move_data = self.move_queues[camera].get()
|
||||
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
move_data = self.move_queues[camera].get(True, 0.1)
|
||||
except queue.Empty:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
with self.move_queue_locks[camera]:
|
||||
frame_time, pan, tilt, zoom = move_data
|
||||
@@ -598,7 +630,9 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.onvif._move_relative(camera, pan, tilt, 0, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Wait until the camera finishes moving
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera][
|
||||
"ptz_motor_stopped"
|
||||
].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
@@ -608,7 +642,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
self.onvif._zoom_absolute(camera, zoom, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Wait until the camera finishes moving
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
while not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.config.cameras[camera].onvif.autotracking.movement_weights:
|
||||
@@ -686,19 +720,20 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
camera_height = camera_config.frame_shape[0]
|
||||
camera_fps = camera_config.detect.fps
|
||||
|
||||
# estimate_velocity is a numpy array of bbox top,left and bottom,right velocities
|
||||
velocities = obj.obj_data["estimate_velocity"]
|
||||
logger.debug(f"{camera}: Velocities from norfair: {velocities}")
|
||||
|
||||
# if we are close enough to zero, return right away
|
||||
if np.all(np.round(velocities) == 0):
|
||||
return True, np.zeros((2, 2))
|
||||
return True, np.zeros((4,))
|
||||
|
||||
# Thresholds
|
||||
x_mags_thresh = camera_width / camera_fps / 2
|
||||
y_mags_thresh = camera_height / camera_fps / 2
|
||||
dir_thresh = 0.93
|
||||
delta_thresh = 12
|
||||
var_thresh = 5
|
||||
delta_thresh = 20
|
||||
var_thresh = 10
|
||||
|
||||
# Check magnitude
|
||||
x_mags = np.abs(velocities[:, 0])
|
||||
@@ -722,7 +757,6 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(velocities[0]) * np.linalg.norm(velocities[1])
|
||||
)
|
||||
dir_thresh = 0.6 if np.all(delta < delta_thresh / 2) else dir_thresh
|
||||
print(f"cosine sim: {cosine_sim}")
|
||||
invalid_dirs = cosine_sim < dir_thresh
|
||||
|
||||
# Combine
|
||||
@@ -752,10 +786,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
# invalid velocity
|
||||
return False, np.zeros((2, 2))
|
||||
return False, np.zeros((4,))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.debug(f"{camera}: Valid velocity ")
|
||||
return True, np.mean(velocities, axis=0)
|
||||
return True, velocities.flatten()
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_distance_threshold(self, camera, obj):
|
||||
# Returns true if Euclidean distance from object to center of frame is
|
||||
@@ -836,7 +870,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
# ensure object is not moving quickly
|
||||
below_velocity_threshold = np.all(
|
||||
np.abs(average_velocity)
|
||||
< np.array([velocity_threshold_x, velocity_threshold_y])
|
||||
< np.tile([velocity_threshold_x, velocity_threshold_y], 2)
|
||||
) or np.all(average_velocity == 0)
|
||||
|
||||
below_area_threshold = (
|
||||
@@ -847,21 +881,11 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
# introduce some hysteresis to prevent a yo-yo zooming effect
|
||||
zoom_out_hysteresis = (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
> (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["original_target_box"]
|
||||
* AUTOTRACKING_ZOOM_OUT_HYSTERESIS
|
||||
)
|
||||
or self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
> self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]
|
||||
* AUTOTRACKING_ZOOM_OUT_HYSTERESIS
|
||||
)
|
||||
zoom_in_hysteresis = (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
< (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["original_target_box"]
|
||||
* AUTOTRACKING_ZOOM_IN_HYSTERESIS
|
||||
)
|
||||
or self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
< self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]
|
||||
* AUTOTRACKING_ZOOM_IN_HYSTERESIS
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -938,7 +962,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
camera_height = camera_config.frame_shape[0]
|
||||
camera_fps = camera_config.detect.fps
|
||||
|
||||
average_velocity = np.zeros((2, 2))
|
||||
average_velocity = np.zeros((4,))
|
||||
predicted_box = obj.obj_data["box"]
|
||||
|
||||
centroid_x = obj.obj_data["centroid"][0]
|
||||
@@ -966,7 +990,6 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
# this box could exceed the frame boundaries if velocity is high
|
||||
# but we'll handle that in _enqueue_move() as two separate moves
|
||||
current_box = np.array(obj.obj_data["box"])
|
||||
average_velocity = np.tile(average_velocity, 2)
|
||||
predicted_box = (
|
||||
current_box
|
||||
+ camera_fps * predicted_movement_time * average_velocity
|
||||
@@ -1010,7 +1033,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
zoom = 0
|
||||
result = None
|
||||
current_zoom_level = self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_zoom_level"].value
|
||||
target_box = obj.obj_data["area"] / (camera_width * camera_height)
|
||||
target_box = max(
|
||||
obj.obj_data["box"][2] - obj.obj_data["box"][0],
|
||||
obj.obj_data["box"][3] - obj.obj_data["box"][1],
|
||||
) ** 2 / (camera_width * camera_height)
|
||||
|
||||
# absolute zooming separately from pan/tilt
|
||||
if camera_config.onvif.autotracking.zooming == ZoomingModeEnum.absolute:
|
||||
@@ -1055,30 +1081,20 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
)
|
||||
) is not None:
|
||||
# zoom value
|
||||
limit = (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["original_target_box"]
|
||||
if self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
< self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]
|
||||
else self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]
|
||||
ratio = (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]
|
||||
/ self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
zoom = (
|
||||
2
|
||||
* (
|
||||
limit
|
||||
/ (
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["target_box"]
|
||||
+ limit
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
zoom = (ratio - 1) / (ratio + 1)
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f'{camera}: limit: {self.tracked_object_metrics[camera]["max_target_box"]}, ratio: {ratio} zoom calculation: {zoom}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.debug(f"{camera}: Zoom calculation: {zoom}")
|
||||
if not result:
|
||||
# zoom out with special condition if zooming out because of velocity, edges, etc.
|
||||
zoom = -(1 - zoom) if zoom > 0 else -(zoom + 1)
|
||||
zoom = -(1 - zoom) if zoom > 0 else -(zoom * 2 + 1)
|
||||
if result:
|
||||
# zoom in
|
||||
zoom = 1 - zoom if zoom > 0 else (zoom + 1)
|
||||
zoom = 1 - zoom if zoom > 0 else (zoom * 2 + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(f"{camera}: Zooming: {result} Zoom amount: {zoom}")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1117,6 +1133,10 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera}: New object: {obj.obj_data['id']} {obj.obj_data['box']} {obj.obj_data['frame_time']}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_tracking_active"].set()
|
||||
self.dispatcher.publish(
|
||||
f"{camera}/ptz_autotracker/active", "ON", retain=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.tracked_object[camera] = obj
|
||||
|
||||
self.tracked_object_history[camera].append(copy.deepcopy(obj.obj_data))
|
||||
@@ -1199,8 +1219,8 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.tracked_object[camera] = None
|
||||
self.tracked_object_metrics[camera] = {
|
||||
"max_target_box": 1
|
||||
- (AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO ** self.zoom_factor[camera])
|
||||
"max_target_box": AUTOTRACKING_MAX_AREA_RATIO
|
||||
** (1 / self.zoom_factor[camera])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def camera_maintenance(self, camera):
|
||||
@@ -1219,7 +1239,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
if not self.autotracker_init[camera]:
|
||||
self._autotracker_setup(self.config.cameras[camera], camera)
|
||||
# regularly update camera status
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
# return to preset if tracking is over
|
||||
@@ -1242,7 +1262,7 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
while not self.move_queues[camera].empty():
|
||||
self.move_queues[camera].get()
|
||||
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].wait()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].wait()
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera}: Time is {self.ptz_metrics[camera]['ptz_frame_time'].value}, returning to preset: {autotracker_config.return_preset}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -1252,7 +1272,11 @@ class PtzAutoTracker:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# update stored zoom level from preset
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.onvif.get_camera_status(camera)
|
||||
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_tracking_active"].clear()
|
||||
self.dispatcher.publish(
|
||||
f"{camera}/ptz_autotracker/active", "OFF", retain=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera]["ptz_reset"].set()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ from enum import Enum
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy
|
||||
from onvif import ONVIFCamera, ONVIFError
|
||||
from zeep.exceptions import Fault, TransportError
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig, ZoomingModeEnum
|
||||
from frigate.types import PTZMetricsTypes
|
||||
@@ -66,19 +67,56 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
|
||||
# create init services
|
||||
media = onvif.create_media_service()
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Onvif media xaddr for {camera_name}: {media.xaddr}")
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
profile = media.GetProfiles()[0]
|
||||
except ONVIFError as e:
|
||||
logger.error(f"Unable to connect to camera: {camera_name}: {e}")
|
||||
# this will fire an exception if camera is not a ptz
|
||||
capabilities = onvif.get_definition("ptz")
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Onvif capabilities for {camera_name}: {capabilities}")
|
||||
except (ONVIFError, Fault, TransportError) as e:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
f"Unable to get Onvif capabilities for camera: {camera_name}: {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
profiles = media.GetProfiles()
|
||||
except (ONVIFError, Fault, TransportError) as e:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
f"Unable to get Onvif media profiles for camera: {camera_name}: {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
profile = None
|
||||
for key, onvif_profile in enumerate(profiles):
|
||||
if (
|
||||
onvif_profile.VideoEncoderConfiguration
|
||||
and onvif_profile.VideoEncoderConfiguration.Encoding == "H264"
|
||||
):
|
||||
profile = onvif_profile
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Selected Onvif profile for {camera_name}: {profile}")
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if profile is None:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
f"No appropriate Onvif profiles found for camera: {camera_name}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# get the PTZ config for the profile
|
||||
try:
|
||||
configs = profile.PTZConfiguration
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Onvif ptz config for media profile in {camera_name}: {configs}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
f"Invalid Onvif PTZ configuration for camera: {camera_name}: {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
ptz = onvif.create_ptz_service()
|
||||
|
||||
request = ptz.create_type("GetConfigurations")
|
||||
configs = ptz.GetConfigurations(request)[0]
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Onvif configs for {camera_name}: {configs}")
|
||||
|
||||
request = ptz.create_type("GetConfigurationOptions")
|
||||
request.ConfigurationToken = profile.PTZConfiguration.token
|
||||
ptz_config = ptz.GetConfigurationOptions(request)
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +151,10 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
|
||||
# autoracking relative panning/tilting needs a relative zoom value set to 0
|
||||
# if camera supports relative movement
|
||||
if self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
!= ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
):
|
||||
zoom_space_id = next(
|
||||
(
|
||||
i
|
||||
@@ -133,6 +174,7 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
# setup relative moving request for autotracking
|
||||
move_request = ptz.create_type("RelativeMove")
|
||||
move_request.ProfileToken = profile.token
|
||||
logger.debug(f"{camera_name}: Relative move request: {move_request}")
|
||||
if move_request.Translation is None and fov_space_id is not None:
|
||||
move_request.Translation = status.Position
|
||||
move_request.Translation.PanTilt.space = ptz_config["Spaces"][
|
||||
@@ -143,26 +185,27 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
== ZoomingModeEnum.relative
|
||||
!= ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
):
|
||||
if zoom_space_id is not None:
|
||||
move_request.Translation.Zoom.space = ptz_config["Spaces"][
|
||||
"RelativeZoomTranslationSpace"
|
||||
][0]["URI"]
|
||||
][zoom_space_id]["URI"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
move_request.Translation.Zoom = []
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
== ZoomingModeEnum.relative
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.config.cameras[
|
||||
camera_name
|
||||
].onvif.autotracking.zooming = ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking zooming for {camera_name}: Relative zoom not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.config.cameras[
|
||||
camera_name
|
||||
].onvif.autotracking.zooming = ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking zooming for {camera_name}: Relative zoom not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if move_request.Speed is None:
|
||||
move_request.Speed = status.Position if status else None
|
||||
move_request.Speed = configs.DefaultPTZSpeed if configs else None
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}: Relative move request after setup: {move_request}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["relative_move_request"] = move_request
|
||||
|
||||
# setup absolute moving request for autotracking zooming
|
||||
@@ -183,19 +226,18 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
] = preset["token"]
|
||||
|
||||
# get list of supported features
|
||||
ptz_config = ptz.GetConfigurationOptions(request)
|
||||
supported_features = []
|
||||
|
||||
if ptz_config.Spaces and ptz_config.Spaces.ContinuousPanTiltVelocitySpace:
|
||||
if configs.DefaultContinuousPanTiltVelocitySpace:
|
||||
supported_features.append("pt")
|
||||
|
||||
if ptz_config.Spaces and ptz_config.Spaces.ContinuousZoomVelocitySpace:
|
||||
if configs.DefaultContinuousZoomVelocitySpace:
|
||||
supported_features.append("zoom")
|
||||
|
||||
if ptz_config.Spaces and ptz_config.Spaces.RelativePanTiltTranslationSpace:
|
||||
if configs.DefaultRelativePanTiltTranslationSpace:
|
||||
supported_features.append("pt-r")
|
||||
|
||||
if ptz_config.Spaces and ptz_config.Spaces.RelativeZoomTranslationSpace:
|
||||
if configs.DefaultRelativeZoomTranslationSpace:
|
||||
supported_features.append("zoom-r")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# get camera's zoom limits from onvif config
|
||||
@@ -207,12 +249,14 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
== ZoomingModeEnum.relative
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming = False
|
||||
self.config.cameras[
|
||||
camera_name
|
||||
].onvif.autotracking.zooming = ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking zooming for {camera_name}: Relative zoom not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if ptz_config.Spaces and ptz_config.Spaces.AbsoluteZoomPositionSpace:
|
||||
if configs.DefaultAbsoluteZoomPositionSpace:
|
||||
supported_features.append("zoom-a")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# get camera's zoom limits from onvif config
|
||||
@@ -222,13 +266,18 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["zoom_limits"] = configs.ZoomLimits
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
if self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming:
|
||||
self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming = False
|
||||
self.config.cameras[
|
||||
camera_name
|
||||
].onvif.autotracking.zooming = ZoomingModeEnum.disabled
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Disabling autotracking zooming for {camera_name}: Absolute zoom not supported"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# set relative pan/tilt space for autotracker
|
||||
if fov_space_id is not None:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
fov_space_id is not None
|
||||
and configs.DefaultRelativePanTiltTranslationSpace is not None
|
||||
):
|
||||
supported_features.append("pt-r-fov")
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name][
|
||||
"relative_fov_range"
|
||||
@@ -299,7 +348,7 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = True
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}: PTZ start time: {self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]['ptz_frame_time'].value}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -339,7 +388,11 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
move_request.Translation.PanTilt.x = pan
|
||||
move_request.Translation.PanTilt.y = tilt
|
||||
|
||||
if "zoom-r" in self.cams[camera_name]["features"]:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
"zoom-r" in self.cams[camera_name]["features"]
|
||||
and self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
== ZoomingModeEnum.relative
|
||||
):
|
||||
move_request.Speed = {
|
||||
"PanTilt": {
|
||||
"x": speed,
|
||||
@@ -355,7 +408,11 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
move_request.Translation.PanTilt.x = 0
|
||||
move_request.Translation.PanTilt.y = 0
|
||||
|
||||
if "zoom-r" in self.cams[camera_name]["features"]:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
"zoom-r" in self.cams[camera_name]["features"]
|
||||
and self.config.cameras[camera_name].onvif.autotracking.zooming
|
||||
== ZoomingModeEnum.relative
|
||||
):
|
||||
move_request.Translation.Zoom.x = 0
|
||||
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = False
|
||||
@@ -366,7 +423,7 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = True
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_start_time"].value = 0
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stop_time"].value = 0
|
||||
move_request = self.cams[camera_name]["move_request"]
|
||||
@@ -413,7 +470,7 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = True
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}: PTZ start time: {self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]['ptz_frame_time'].value}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -543,8 +600,8 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
zoom_status is None or zoom_status.lower() == "idle"
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = False
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].set()
|
||||
if not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].set()
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}: PTZ stop time: {self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]['ptz_frame_time'].value}"
|
||||
@@ -555,8 +612,8 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
]["ptz_frame_time"].value
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.cams[camera_name]["active"] = True
|
||||
if self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
if self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set():
|
||||
self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].clear()
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"{camera_name}: PTZ start time: {self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]['ptz_frame_time'].value}"
|
||||
@@ -586,7 +643,7 @@ class OnvifController:
|
||||
|
||||
# some hikvision cams won't update MoveStatus, so warn if it hasn't changed
|
||||
if (
|
||||
not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_stopped"].is_set()
|
||||
not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_motor_stopped"].is_set()
|
||||
and not self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_reset"].is_set()
|
||||
and self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_start_time"].value != 0
|
||||
and self.ptz_metrics[camera_name]["ptz_frame_time"].value
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,17 +3,15 @@
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
import itertools
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
from multiprocessing.synchronize import Event as MpEvent
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
from peewee import DatabaseError, chunked
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig, RetainModeEnum
|
||||
from frigate.const import CACHE_DIR, RECORD_DIR
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings, RecordingsToDelete
|
||||
from frigate.record.util import remove_empty_directories
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings
|
||||
from frigate.record.util import remove_empty_directories, sync_recordings
|
||||
from frigate.util.builtin import clear_and_unlink, get_tomorrow_at_time
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,11 +31,7 @@ class RecordingCleanup(threading.Thread):
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Checking tmp clip {p}.")
|
||||
if p.stat().st_mtime < (datetime.datetime.now().timestamp() - 60 * 1):
|
||||
logger.debug("Deleting tmp clip.")
|
||||
|
||||
# empty contents of file before unlinking https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate/issues/4769
|
||||
with open(p, "w"):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
p.unlink(missing_ok=True)
|
||||
clear_and_unlink(p)
|
||||
|
||||
def expire_recordings(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Delete recordings based on retention config."""
|
||||
@@ -180,76 +174,28 @@ class RecordingCleanup(threading.Thread):
|
||||
logger.debug("End all cameras.")
|
||||
logger.debug("End expire recordings.")
|
||||
|
||||
def sync_recordings(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Check the db for stale recordings entries that don't exist in the filesystem."""
|
||||
logger.debug("Start sync recordings.")
|
||||
|
||||
# get all recordings in the db
|
||||
recordings = Recordings.select(Recordings.id, Recordings.path)
|
||||
|
||||
# get all recordings files on disk and put them in a set
|
||||
files_on_disk = {
|
||||
os.path.join(root, file)
|
||||
for root, _, files in os.walk(RECORD_DIR)
|
||||
for file in files
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Use pagination to process records in chunks
|
||||
page_size = 1000
|
||||
num_pages = (recordings.count() + page_size - 1) // page_size
|
||||
recordings_to_delete = set()
|
||||
|
||||
for page in range(num_pages):
|
||||
for recording in recordings.paginate(page, page_size):
|
||||
if recording.path not in files_on_disk:
|
||||
recordings_to_delete.add(recording.id)
|
||||
|
||||
# convert back to list of dictionaries for insertion
|
||||
recordings_to_delete = [
|
||||
{"id": recording_id} for recording_id in recordings_to_delete
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(recordings_to_delete) / max(1, recordings.count()) > 0.5:
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Deleting {(len(recordings_to_delete) / recordings.count()):2f}% of recordings could be due to configuration error. Aborting..."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Deleting {len(recordings_to_delete)} recordings with missing files"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# create a temporary table for deletion
|
||||
RecordingsToDelete.create_table(temporary=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# insert ids to the temporary table
|
||||
max_inserts = 1000
|
||||
for batch in chunked(recordings_to_delete, max_inserts):
|
||||
RecordingsToDelete.insert_many(batch).execute()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# delete records in the main table that exist in the temporary table
|
||||
query = Recordings.delete().where(
|
||||
Recordings.id.in_(RecordingsToDelete.select(RecordingsToDelete.id))
|
||||
)
|
||||
query.execute()
|
||||
except DatabaseError as e:
|
||||
logger.error(f"Database error during delete: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug("End sync recordings.")
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self) -> None:
|
||||
# on startup sync recordings with disk if enabled
|
||||
if self.config.record.sync_on_startup:
|
||||
self.sync_recordings()
|
||||
if self.config.record.sync_recordings:
|
||||
sync_recordings(limited=False)
|
||||
next_sync = get_tomorrow_at_time(3)
|
||||
|
||||
# Expire tmp clips every minute, recordings and clean directories every hour.
|
||||
for counter in itertools.cycle(range(self.config.record.expire_interval)):
|
||||
if self.stop_event.wait(60):
|
||||
logger.info("Exiting recording cleanup...")
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
self.clean_tmp_clips()
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config.record.sync_recordings
|
||||
and datetime.datetime.now().astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
|
||||
> next_sync
|
||||
):
|
||||
sync_recordings(limited=True)
|
||||
next_sync = get_tomorrow_at_time(3)
|
||||
|
||||
if counter == 0:
|
||||
self.expire_recordings()
|
||||
remove_empty_directories(RECORD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import subprocess as sp
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
from enum import Enum
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig
|
||||
from frigate.const import EXPORT_DIR, MAX_PLAYLIST_SECONDS
|
||||
@@ -121,6 +122,7 @@ class RecordingExporter(threading.Thread):
|
||||
f"Failed to export recording for command {' '.join(ffmpeg_cmd)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.error(p.stderr)
|
||||
Path(file_name).unlink(missing_ok=True)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Updating finalized export {file_name}")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,8 +20,10 @@ import psutil
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig, RetainModeEnum
|
||||
from frigate.const import (
|
||||
CACHE_DIR,
|
||||
CACHE_SEGMENT_FORMAT,
|
||||
INSERT_MANY_RECORDINGS,
|
||||
MAX_SEGMENT_DURATION,
|
||||
MAX_SEGMENTS_IN_CACHE,
|
||||
RECORD_DIR,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings
|
||||
@@ -31,6 +33,8 @@ from frigate.util.services import get_video_properties
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
QUEUE_READ_TIMEOUT = 0.00001 # seconds
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SegmentInfo:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
@@ -74,15 +78,13 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
self.end_time_cache: dict[str, Tuple[datetime.datetime, float]] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
async def move_files(self) -> None:
|
||||
cache_files = sorted(
|
||||
[
|
||||
d
|
||||
for d in os.listdir(CACHE_DIR)
|
||||
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, d))
|
||||
and d.endswith(".mp4")
|
||||
and not d.startswith("clip_")
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_files = [
|
||||
d
|
||||
for d in os.listdir(CACHE_DIR)
|
||||
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, d))
|
||||
and d.endswith(".mp4")
|
||||
and not d.startswith("clip_")
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
files_in_use = []
|
||||
for process in psutil.process_iter():
|
||||
@@ -106,8 +108,12 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
|
||||
cache_path = os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, cache)
|
||||
basename = os.path.splitext(cache)[0]
|
||||
camera, date = basename.rsplit("-", maxsplit=1)
|
||||
start_time = datetime.datetime.strptime(date, "%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
|
||||
camera, date = basename.rsplit("@", maxsplit=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# important that start_time is utc because recordings are stored and compared in utc
|
||||
start_time = datetime.datetime.strptime(
|
||||
date, CACHE_SEGMENT_FORMAT
|
||||
).astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
|
||||
|
||||
grouped_recordings[camera].append(
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -116,9 +122,14 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# delete all cached files past the most recent 5
|
||||
keep_count = 5
|
||||
# delete all cached files past the most recent MAX_SEGMENTS_IN_CACHE
|
||||
keep_count = MAX_SEGMENTS_IN_CACHE
|
||||
for camera in grouped_recordings.keys():
|
||||
# sort based on start time
|
||||
grouped_recordings[camera] = sorted(
|
||||
grouped_recordings[camera], key=lambda s: s["start_time"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
segment_count = len(grouped_recordings[camera])
|
||||
if segment_count > keep_count:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
@@ -163,8 +174,6 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
Event.has_clip,
|
||||
)
|
||||
.order_by(Event.start_time)
|
||||
.namedtuples()
|
||||
.iterator()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tasks.extend(
|
||||
@@ -217,12 +226,8 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
|
||||
# if cached file's start_time is earlier than the retain days for the camera
|
||||
if start_time <= (
|
||||
(
|
||||
datetime.datetime.now()
|
||||
- datetime.timedelta(
|
||||
days=self.config.cameras[camera].record.retain.days
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
datetime.datetime.now().astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
|
||||
- datetime.timedelta(days=self.config.cameras[camera].record.retain.days)
|
||||
):
|
||||
# if the cached segment overlaps with the events:
|
||||
overlaps = False
|
||||
@@ -260,8 +265,10 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
most_recently_processed_frame_time = (
|
||||
camera_info[-1][0] if len(camera_info) > 0 else 0
|
||||
)
|
||||
retain_cutoff = most_recently_processed_frame_time - pre_capture
|
||||
if end_time.timestamp() < retain_cutoff:
|
||||
retain_cutoff = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(
|
||||
most_recently_processed_frame_time - pre_capture
|
||||
).astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
|
||||
if end_time < retain_cutoff:
|
||||
Path(cache_path).unlink(missing_ok=True)
|
||||
self.end_time_cache.pop(cache_path, None)
|
||||
# else retain days includes this segment
|
||||
@@ -273,7 +280,12 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# ensure delayed segment info does not lead to lost segments
|
||||
if most_recently_processed_frame_time >= end_time.timestamp():
|
||||
if (
|
||||
datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(
|
||||
most_recently_processed_frame_time
|
||||
).astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
|
||||
>= end_time
|
||||
):
|
||||
record_mode = self.config.cameras[camera].record.retain.mode
|
||||
return await self.move_segment(
|
||||
camera, start_time, end_time, duration, cache_path, record_mode
|
||||
@@ -339,18 +351,18 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
self.end_time_cache.pop(cache_path, None)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# directory will be in utc due to start_time being in utc
|
||||
directory = os.path.join(
|
||||
RECORD_DIR,
|
||||
start_time.astimezone(tz=datetime.timezone.utc).strftime("%Y-%m-%d/%H"),
|
||||
start_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d/%H"),
|
||||
camera,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(directory):
|
||||
os.makedirs(directory)
|
||||
|
||||
file_name = (
|
||||
f"{start_time.replace(tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc).strftime('%M.%S.mp4')}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# file will be in utc due to start_time being in utc
|
||||
file_name = f"{start_time.strftime('%M.%S.mp4')}"
|
||||
file_path = os.path.join(directory, file_name)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@@ -437,7 +449,9 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
current_tracked_objects,
|
||||
motion_boxes,
|
||||
regions,
|
||||
) = self.object_recordings_info_queue.get(True, timeout=0.01)
|
||||
) = self.object_recordings_info_queue.get(
|
||||
True, timeout=QUEUE_READ_TIMEOUT
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if frame_time < run_start - stale_frame_count_threshold:
|
||||
stale_frame_count += 1
|
||||
@@ -473,7 +487,9 @@ class RecordingMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
frame_time,
|
||||
dBFS,
|
||||
audio_detections,
|
||||
) = self.audio_recordings_info_queue.get(True, timeout=0.01)
|
||||
) = self.audio_recordings_info_queue.get(
|
||||
True, timeout=QUEUE_READ_TIMEOUT
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if frame_time < run_start - stale_frame_count_threshold:
|
||||
stale_frame_count += 1
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,16 @@
|
||||
"""Recordings Utilities."""
|
||||
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
from peewee import DatabaseError, chunked
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.const import RECORD_DIR
|
||||
from frigate.models import Recordings, RecordingsToDelete
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def remove_empty_directories(directory: str) -> None:
|
||||
# list all directories recursively and sort them by path,
|
||||
@@ -17,3 +26,122 @@ def remove_empty_directories(directory: str) -> None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if len(os.listdir(path)) == 0:
|
||||
os.rmdir(path)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sync_recordings(limited: bool) -> None:
|
||||
"""Check the db for stale recordings entries that don't exist in the filesystem."""
|
||||
|
||||
def delete_db_entries_without_file(check_timestamp: float) -> bool:
|
||||
"""Delete db entries where file was deleted outside of frigate."""
|
||||
|
||||
if limited:
|
||||
recordings = Recordings.select(Recordings.id, Recordings.path).where(
|
||||
Recordings.start_time >= check_timestamp
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# get all recordings in the db
|
||||
recordings = Recordings.select(Recordings.id, Recordings.path)
|
||||
|
||||
# Use pagination to process records in chunks
|
||||
page_size = 1000
|
||||
num_pages = (recordings.count() + page_size - 1) // page_size
|
||||
recordings_to_delete = set()
|
||||
|
||||
for page in range(num_pages):
|
||||
for recording in recordings.paginate(page, page_size):
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(recording.path):
|
||||
recordings_to_delete.add(recording.id)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(recordings_to_delete) == 0:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Deleting {len(recordings_to_delete)} recording DB entries with missing files"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# convert back to list of dictionaries for insertion
|
||||
recordings_to_delete = [
|
||||
{"id": recording_id} for recording_id in recordings_to_delete
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if float(len(recordings_to_delete)) / max(1, recordings.count()) > 0.5:
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Deleting {(float(len(recordings_to_delete)) / recordings.count()):2f}% of recordings DB entries, could be due to configuration error. Aborting..."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# create a temporary table for deletion
|
||||
RecordingsToDelete.create_table(temporary=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# insert ids to the temporary table
|
||||
max_inserts = 1000
|
||||
for batch in chunked(recordings_to_delete, max_inserts):
|
||||
RecordingsToDelete.insert_many(batch).execute()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# delete records in the main table that exist in the temporary table
|
||||
query = Recordings.delete().where(
|
||||
Recordings.id.in_(RecordingsToDelete.select(RecordingsToDelete.id))
|
||||
)
|
||||
query.execute()
|
||||
except DatabaseError as e:
|
||||
logger.error(f"Database error during recordings db cleanup: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def delete_files_without_db_entry(files_on_disk: list[str]):
|
||||
"""Delete files where file is not inside frigate db."""
|
||||
files_to_delete = []
|
||||
|
||||
for file in files_on_disk:
|
||||
if not Recordings.select().where(Recordings.path == file).exists():
|
||||
files_to_delete.append(file)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(files_to_delete) == 0:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Deleting {len(files_to_delete)} recordings files with missing DB entries"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if float(len(files_to_delete)) / max(1, len(files_on_disk)) > 0.5:
|
||||
logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Deleting {(float(len(files_to_delete)) / len(files_on_disk)):2f}% of recordings DB entries, could be due to configuration error. Aborting..."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
for file in files_to_delete:
|
||||
os.unlink(file)
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug("Start sync recordings.")
|
||||
|
||||
# start checking on the hour 36 hours ago
|
||||
check_point = datetime.datetime.now().replace(
|
||||
minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0
|
||||
).astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc) - datetime.timedelta(hours=36)
|
||||
db_success = delete_db_entries_without_file(check_point.timestamp())
|
||||
|
||||
# only try to cleanup files if db cleanup was successful
|
||||
if db_success:
|
||||
if limited:
|
||||
# get recording files from last 36 hours
|
||||
hour_check = f"{RECORD_DIR}/{check_point.strftime('%Y-%m-%d/%H')}"
|
||||
files_on_disk = {
|
||||
os.path.join(root, file)
|
||||
for root, _, files in os.walk(RECORD_DIR)
|
||||
for file in files
|
||||
if root > hour_check
|
||||
}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# get all recordings files on disk and put them in a set
|
||||
files_on_disk = {
|
||||
os.path.join(root, file)
|
||||
for root, _, files in os.walk(RECORD_DIR)
|
||||
for file in files
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
delete_files_without_db_entry(files_on_disk)
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug("End sync recordings.")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,6 +10,7 @@ from peewee import fn
|
||||
from frigate.config import FrigateConfig
|
||||
from frigate.const import RECORD_DIR
|
||||
from frigate.models import Event, Recordings
|
||||
from frigate.util.builtin import clear_and_unlink
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
bandwidth_equation = Recordings.segment_size / (
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +36,7 @@ class StorageMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
if self.camera_storage_stats.get(camera, {}).get("needs_refresh", True):
|
||||
self.camera_storage_stats[camera] = {
|
||||
"needs_refresh": (
|
||||
Recordings.select(fn.COUNT(Recordings.id))
|
||||
Recordings.select(fn.COUNT("*"))
|
||||
.where(Recordings.camera == camera, Recordings.segment_size > 0)
|
||||
.scalar()
|
||||
< 50
|
||||
@@ -159,9 +160,13 @@ class StorageMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
|
||||
# Delete recordings not retained indefinitely
|
||||
if not keep:
|
||||
deleted_segments_size += recording.segment_size
|
||||
Path(recording.path).unlink(missing_ok=True)
|
||||
deleted_recordings.add(recording.id)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
clear_and_unlink(Path(recording.path), missing_ok=False)
|
||||
deleted_recordings.add(recording.id)
|
||||
deleted_segments_size += recording.segment_size
|
||||
except FileNotFoundError:
|
||||
# this file was not found so we must assume no space was cleaned up
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# check if need to delete retained segments
|
||||
if deleted_segments_size < hourly_bandwidth:
|
||||
@@ -183,9 +188,15 @@ class StorageMaintainer(threading.Thread):
|
||||
if deleted_segments_size > hourly_bandwidth:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
deleted_segments_size += recording.segment_size
|
||||
Path(recording.path).unlink(missing_ok=True)
|
||||
deleted_recordings.add(recording.id)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
clear_and_unlink(Path(recording.path), missing_ok=False)
|
||||
deleted_segments_size += recording.segment_size
|
||||
deleted_recordings.add(recording.id)
|
||||
except FileNotFoundError:
|
||||
# this file was not found so we must assume no space was cleaned up
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Cleaned up {deleted_segments_size} MB of recordings")
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug(f"Expiring {len(deleted_recordings)} recordings")
|
||||
# delete up to 100,000 at a time
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1651,11 +1651,11 @@ class TestConfig(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
runtime_config = frigate_config.runtime_config()
|
||||
assert runtime_config.cameras["back"].onvif.autotracking.movement_weights == [
|
||||
0,
|
||||
1,
|
||||
1.23,
|
||||
2.34,
|
||||
0.50,
|
||||
"0.0",
|
||||
"1.0",
|
||||
"1.23",
|
||||
"2.34",
|
||||
"0.5",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
def test_fails_invalid_movement_weights(self):
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from unittest.mock import MagicMock
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,6 +27,7 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.db = SqliteQueueDatabase(TEST_DB)
|
||||
models = [Event, Recordings]
|
||||
self.db.bind(models)
|
||||
self.test_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
|
||||
|
||||
self.minimal_config = {
|
||||
"mqtt": {"host": "mqtt"},
|
||||
@@ -94,6 +96,7 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
rec_bd_id = "1234568.backdoor"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_fd_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_fd_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
camera="front_door",
|
||||
@@ -102,6 +105,7 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_bd_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_bd_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
time_keep + 20,
|
||||
camera="back_door",
|
||||
@@ -123,6 +127,7 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
rec_fd_id = "1234567.frontdoor"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_fd_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_fd_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
camera="front_door",
|
||||
@@ -141,13 +146,33 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
id = "123456.keep"
|
||||
time_keep = datetime.datetime.now().timestamp()
|
||||
_insert_mock_event(id, time_keep, time_keep + 30, True)
|
||||
_insert_mock_event(
|
||||
id,
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 30,
|
||||
True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
rec_k_id = "1234567.keep"
|
||||
rec_k2_id = "1234568.keep"
|
||||
rec_k3_id = "1234569.keep"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k_id, time_keep, time_keep + 10)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k2_id, time_keep + 10, time_keep + 20)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k3_id, time_keep + 20, time_keep + 30)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k2_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k2_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
time_keep + 20,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k3_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k3_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep + 20,
|
||||
time_keep + 30,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
id2 = "7890.delete"
|
||||
time_delete = datetime.datetime.now().timestamp() - 360
|
||||
@@ -155,9 +180,24 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
rec_d_id = "78901.delete"
|
||||
rec_d2_id = "78902.delete"
|
||||
rec_d3_id = "78903.delete"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_d_id, time_delete, time_delete + 10)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_d2_id, time_delete + 10, time_delete + 20)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_d3_id, time_delete + 20, time_delete + 30)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_d_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_d_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_delete,
|
||||
time_delete + 10,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_d2_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_d2_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_delete + 10,
|
||||
time_delete + 20,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_d3_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_d3_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_delete + 20,
|
||||
time_delete + 30,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
storage.calculate_camera_bandwidth()
|
||||
storage.reduce_storage_consumption()
|
||||
@@ -176,18 +216,42 @@ class TestHttp(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
id = "123456.keep"
|
||||
time_keep = datetime.datetime.now().timestamp()
|
||||
_insert_mock_event(id, time_keep, time_keep + 30, True)
|
||||
_insert_mock_event(
|
||||
id,
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 30,
|
||||
True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
rec_k_id = "1234567.keep"
|
||||
rec_k2_id = "1234568.keep"
|
||||
rec_k3_id = "1234569.keep"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k_id, time_keep, time_keep + 10)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k2_id, time_keep + 10, time_keep + 20)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(rec_k3_id, time_keep + 20, time_keep + 30)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep,
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k2_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k2_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep + 10,
|
||||
time_keep + 20,
|
||||
)
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
rec_k3_id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{rec_k3_id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_keep + 20,
|
||||
time_keep + 30,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
time_delete = datetime.datetime.now().timestamp() - 7200
|
||||
for i in range(0, 59):
|
||||
id = f"{123456 + i}.delete"
|
||||
_insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
f"{123456 + i}.delete", time_delete, time_delete + 600
|
||||
id,
|
||||
os.path.join(self.test_dir, f"{id}.tmp"),
|
||||
time_delete,
|
||||
time_delete + 600,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
storage.calculate_camera_bandwidth()
|
||||
@@ -219,13 +283,23 @@ def _insert_mock_event(id: str, start: int, end: int, retain: bool) -> Event:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _insert_mock_recording(
|
||||
id: str, start: int, end: int, camera="front_door", seg_size=8, seg_dur=10
|
||||
id: str,
|
||||
file: str,
|
||||
start: int,
|
||||
end: int,
|
||||
camera="front_door",
|
||||
seg_size=8,
|
||||
seg_dur=10,
|
||||
) -> Event:
|
||||
"""Inserts a basic recording model with a given id."""
|
||||
# we must open the file so storage maintainer will delete it
|
||||
with open(file, "w"):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
return Recordings.insert(
|
||||
id=id,
|
||||
camera=camera,
|
||||
path=f"/recordings/{id}",
|
||||
path=file,
|
||||
start_time=start,
|
||||
end_time=end,
|
||||
duration=seg_dur,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ import numpy as np
|
||||
from norfair.drawing.color import Palette
|
||||
from norfair.drawing.drawer import Drawer
|
||||
|
||||
from frigate.util.image import intersection
|
||||
from frigate.util.image import intersection, transliterate_to_latin
|
||||
from frigate.util.object import (
|
||||
get_cluster_boundary,
|
||||
get_cluster_candidates,
|
||||
@@ -82,6 +82,11 @@ class TestRegion(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(cluster_candidates) == 2
|
||||
|
||||
def test_transliterate_to_latin(self):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(transliterate_to_latin("frégate"), "fregate")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(transliterate_to_latin("utilité"), "utilite")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(transliterate_to_latin("imágé"), "image")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cluster_boundary(self):
|
||||
boxes = [(100, 100, 200, 200), (215, 215, 325, 325)]
|
||||
boundary_boxes = [
|
||||
@@ -282,6 +287,15 @@ class TestObjectBoundingBoxes(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
consolidated_detections = reduce_detections(frame_shape, detections)
|
||||
assert len(consolidated_detections) == len(detections)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_vert_stacked_cars_not_reduced(self):
|
||||
detections = [
|
||||
("car", 0.8, (954, 312, 1247, 475), 498512, 1.48, (800, 200, 1400, 600)),
|
||||
("car", 0.85, (970, 380, 1273, 610), 698752, 1.56, (800, 200, 1400, 700)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
frame_shape = (720, 1280)
|
||||
consolidated_detections = reduce_detections(frame_shape, detections)
|
||||
assert len(consolidated_detections) == len(detections)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestRegionGrid(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self) -> None:
|
||||
|
||||