mirror of
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
synced 2025-10-07 01:22:59 +08:00
[Doc] Update English version of some documents (#1084)
* Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README_CN.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README_CN.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update and rename README_en.md to README_CN.md * Update WebDemo.md * Update and rename WebDemo_en.md to WebDemo_CN.md * Update and rename DEVELOPMENT_cn.md to DEVELOPMENT_CN.md * Update DEVELOPMENT_CN.md * Update DEVELOPMENT.md * Update RNN.md * Update and rename RNN_EN.md to RNN_CN.md * Update README.md * Update and rename README_en.md to README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update and rename README_en.md to README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README_cn.md * Rename README_cn.md to README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README_cn.md * Rename README_cn.md to README_CN.md * Update export.md * Update and rename export_EN.md to export_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Create README_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update kunlunxin.md * Update classification_result.md * Update classification_result_EN.md * Rename classification_result_EN.md to classification_result_CN.md * Update detection_result.md * Update and rename detection_result_EN.md to detection_result_CN.md * Update face_alignment_result.md * Update and rename face_alignment_result_EN.md to face_alignment_result_CN.md * Update face_detection_result.md * Update and rename face_detection_result_EN.md to face_detection_result_CN.md * Update face_recognition_result.md * Update and rename face_recognition_result_EN.md to face_recognition_result_CN.md * Update headpose_result.md * Update and rename headpose_result_EN.md to headpose_result_CN.md * Update keypointdetection_result.md * Update and rename keypointdetection_result_EN.md to keypointdetection_result_CN.md * Update matting_result.md * Update and rename matting_result_EN.md to matting_result_CN.md * Update mot_result.md * Update and rename mot_result_EN.md to mot_result_CN.md * Update ocr_result.md * Update and rename ocr_result_EN.md to ocr_result_CN.md * Update segmentation_result.md * Update and rename segmentation_result_EN.md to segmentation_result_CN.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update quantize.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README.md * Update README.md
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](classification_result_EN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](classification_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# ClassifyResult 图像分类结果
|
# Image Classification Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ClassifyResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像的分类结果和置信度。
|
The ClassifyResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the classification result and confidence level of the image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::ClassifyResult`
|
`fastdeploy::vision::ClassifyResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -16,14 +16,14 @@ struct ClassifyResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**: 成员变量,表示单张图片的分类结果,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类结果
|
- **label_ids**: Member variable which indicates the classification results of a single image. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification results.
|
||||||
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片在相应分类结果上的置信度,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类置信度
|
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of a single image on the corresponding classification result. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification confidence level.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.ClassifyResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.ClassifyResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片的分类结果,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类结果
|
- **label_ids**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the classification results of a single image. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification results.
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片在相应分类结果上的置信度,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类置信度
|
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of a single image on the corresponding classification result. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification confidence level.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
29
docs/api/vision_results/classification_result_CN.md
Normal file
29
docs/api/vision_results/classification_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](classification_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# ClassifyResult 图像分类结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ClassifyResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像的分类结果和置信度。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::ClassifyResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct ClassifyResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int32_t> label_ids;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **label_ids**: 成员变量,表示单张图片的分类结果,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类结果
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片在相应分类结果上的置信度,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类置信度
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.ClassifyResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **label_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片的分类结果,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类结果
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片在相应分类结果上的置信度,其个数根据在使用分类模型时传入的topk决定,例如可以返回top 5的分类置信度
|
||||||
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](classification_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Image Classification Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The ClassifyResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the classification result and confidence level of the image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::ClassifyResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct ClassifyResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int32_t> label_ids;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> scores;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**: Member variable which indicates the classification results of a single image. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification results.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of a single image on the corresponding classification result. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification confidence level.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.ClassifyResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the classification results of a single image. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification results.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of a single image on the corresponding classification result. Its number is determined by the topk passed in when using the classification model, e.g. it can return the top 5 classification confidence level.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](detection_result_EN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](detection_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# DetectionResult 目标检测结果
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
DetectionResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像检测出来的目标框、目标类别和目标置信度。
|
# Target Detection Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
The DetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the target frame, target class and target confidence level detected in the image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::DetectionResult
|
fastdeploy::vision::DetectionResult
|
||||||
@@ -21,13 +22,13 @@ struct DetectionResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **label_ids**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **label_ids**: Member variable which indicates all target categories detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **masks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有实例mask,其元素个数及shape大小与`boxes`一致
|
- **masks**: Member variable which indicates all detected instance masks of a single image, where the number of elements and the shape size are the same as `boxes`.
|
||||||
- **contain_masks**: 成员变量,表示检测结果中是否包含实例mask,实例分割模型的结果此项一般为true.
|
- **contain_masks**: Member variable which indicates whether the detected result contains instance masks, which is generally true for the instance segmentation model.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::Mask
|
fastdeploy::vision::Mask
|
||||||
@@ -41,25 +42,25 @@ struct Mask {
|
|||||||
std::string Str();
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
- **data**: 成员变量,表示检测到的一个mask
|
- **data**: Member variable which indicates a detected mask.
|
||||||
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示mask的shape,如 (h,w)
|
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the mask, e.g. (h,w).
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.DetectionResult
|
fastdeploy.vision.DetectionResult
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image.
|
||||||
- **label_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标类别
|
- **label_ids**(list of int): Member variable which indicates all target categories detected in a single image.
|
||||||
- **masks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有实例mask,其元素个数及shape大小与`boxes`一致
|
- **masks**: Member variable which indicates all detected instance masks of a single image, where the number of elements and the shape size are the same as `boxes`.
|
||||||
- **contain_masks**: 成员变量,表示检测结果中是否包含实例mask,实例分割模型的结果此项一般为True.
|
- **contain_masks**: Member variable which indicates whether the detected result contains instance masks, which is generally true for the instance segmentation model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.Mask
|
fastdeploy.vision.Mask
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
- **data**: 成员变量,表示检测到的一个mask
|
- **data**: Member variable which indicates a detected mask.
|
||||||
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示mask的shape,如 (h,w)
|
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the mask, e.g. (h,w).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
65
docs/api/vision_results/detection_result_CN.md
Normal file
65
docs/api/vision_results/detection_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](detection_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# DetectionResult 目标检测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
DetectionResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像检测出来的目标框、目标类别和目标置信度。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy::vision::DetectionResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct DetectionResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 4>> boxes;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int32_t> label_ids;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<Mask> masks;
|
||||||
|
bool contain_masks = false;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **label_ids**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **masks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有实例mask,其元素个数及shape大小与`boxes`一致
|
||||||
|
- **contain_masks**: 成员变量,表示检测结果中是否包含实例mask,实例分割模型的结果此项一般为true.
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy::vision::Mask
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct Mask {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int32_t> data;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int64_t> shape; // (H,W) ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
- **data**: 成员变量,表示检测到的一个mask
|
||||||
|
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示mask的shape,如 (h,w)
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```python
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy.vision.DetectionResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
||||||
|
- **label_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标类别
|
||||||
|
- **masks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有实例mask,其元素个数及shape大小与`boxes`一致
|
||||||
|
- **contain_masks**: 成员变量,表示检测结果中是否包含实例mask,实例分割模型的结果此项一般为True.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```python
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy.vision.Mask
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
- **data**: 成员变量,表示检测到的一个mask
|
||||||
|
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示mask的shape,如 (h,w)
|
||||||
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](detection_result.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Target Detection Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The DetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the target frame, target class and target confidence level detected in the image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::DetectionResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct DetectionResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<float, 4>> boxes;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> scores;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int32_t> label_ids;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<Mask> masks;
|
|
||||||
bool contain_masks = false;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**: Member variable which indicates all target categories detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **masks**: Member variable which indicates all detected instance masks of a single image, where the number of elements and the shape size are the same as `boxes`.
|
|
||||||
- **contain_masks**: Member variable which indicates whether the detected result contains instance masks, which is generally true for the instance segmentation model.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::Mask
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct Mask {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int32_t> data;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int64_t> shape; // (H,W) ...
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
- **data**: Member variable which indicates a detected mask.
|
|
||||||
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the mask, e.g. (h,w).
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.DetectionResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image.
|
|
||||||
- **label_ids**(list of int): Member variable which indicates all target categories detected in a single image.
|
|
||||||
- **masks**: Member variable which indicates all detected instance masks of a single image, where the number of elements and the shape size are the same as `boxes`.
|
|
||||||
- **contain_masks**: Member variable which indicates whether the detected result contains instance masks, which is generally true for the instance segmentation model.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.Mask
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
- **data**: Member variable which indicates a detected mask.
|
|
||||||
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the mask, e.g. (h,w).
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](face_alignment_result_EN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](face_alignment_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# FaceAlignmentResult 人脸对齐(人脸关键点检测)结果
|
# Face Alignment Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FaceAlignmentResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸landmarks。
|
The FaceAlignmentResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate face landmarks.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceAlignmentResult`
|
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceAlignmentResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -15,12 +15,12 @@ struct FaceAlignmentResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**: 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片检测出来的所有关键点
|
- **landmarks**: Member variable which indicates all the key points detected in a single face image.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceAlignmentResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceAlignmentResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片检测出来的所有关键点
|
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates all the key points detected in a single face image.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
35
docs/api/vision_results/face_alignment_result_CN.md
Normal file
35
docs/api/vision_results/face_alignment_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](face_detection_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# FaceDetectionResult 人脸检测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FaceDetectionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸检测出来的目标框、人脸landmarks,目标置信度和每张人脸的landmark数量。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 4>> boxes;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> landmarks;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
int landmarks_per_face;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks_per_face**: 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks_per_face**(int): 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
||||||
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](face_alignment_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Face Alignment Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The FaceAlignmentResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate face landmarks.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceAlignmentResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct FaceAlignmentResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> landmarks;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**: Member variable which indicates all the key points detected in a single face image.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceAlignmentResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates all the key points detected in a single face image.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](face_detection_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](face_detection_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# FaceDetectionResult 人脸检测结果
|
# Face Detection Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FaceDetectionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸检测出来的目标框、人脸landmarks,目标置信度和每张人脸的landmark数量。
|
The FaceDetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the target frames, face landmarks, target confidence and the number of landmark per face.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult`
|
``fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult``
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
||||||
@@ -18,18 +18,18 @@ struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **landmarks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **landmarks**: Member variable which indicates the keypoints of all faces detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **landmarks_per_face**: 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
- **landmarks_per_face**: Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints in each face box.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceDetectionResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image.
|
||||||
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点
|
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the keypoints of all faces detected in a single image.
|
||||||
- **landmarks_per_face**(int): 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
- **landmarks_per_face**(int): Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints in each face box.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
35
docs/api/vision_results/face_detection_result_CN.md
Normal file
35
docs/api/vision_results/face_detection_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](face_detection_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# FaceDetectionResult 人脸检测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FaceDetectionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸检测出来的目标框、人脸landmarks,目标置信度和每张人脸的landmark数量。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 4>> boxes;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> landmarks;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
int landmarks_per_face;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks_per_face**: 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有人脸的关键点
|
||||||
|
- **landmarks_per_face**(int): 成员变量,表示每个人脸框中的关键点的数量。
|
||||||
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](face_detection_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Face Detection Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The FaceDetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the target frames, face landmarks, target confidence and the number of landmark per face.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult``
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct FaceDetectionResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<float, 4>> boxes;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> landmarks;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> scores;
|
|
||||||
int landmarks_per_face;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**: Member variable which indicates the keypoints of all faces detected in a single image, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks_per_face**: Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints in each face box.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceDetectionResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single image.
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the keypoints of all faces detected in a single image.
|
|
||||||
- **landmarks_per_face**(int): Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints in each face box.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](face_recognition_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](face_recognition_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# FaceRecognitionResult 人脸识别结果
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FaceRecognitionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸识别模型对图像特征的embedding。
|
# Face Recognition Result
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
|
||||||
|
The FaceRecognitionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the image features embedding in the face recognition model.
|
||||||
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceRecognitionResult`
|
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceRecognitionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -14,12 +15,12 @@ struct FaceRecognitionResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **embedding**: 成员变量,表示人脸识别模型最终的提取的特征embedding,可以用来计算人脸之间的特征相似度。
|
- **embedding**: Member variable which indicates the final extracted feature embedding of the face recognition model, and can be used to calculate the facial feature similarity.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceRecognitionResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceRecognitionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **embedding**(list of float): 成员变量,表示人脸识别模型最终提取的特征embedding,可以用来计算人脸之间的特征相似度。
|
- **embedding**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the final extracted feature embedding of the face recognition model, and can be used to calculate the facial feature similarity.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
25
docs/api/vision_results/face_recognition_result_CN.md
Normal file
25
docs/api/vision_results/face_recognition_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](face_recognition_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# FaceRecognitionResult 人脸识别结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FaceRecognitionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明人脸识别模型对图像特征的embedding。
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceRecognitionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct FaceRecognitionResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> embedding;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **embedding**: 成员变量,表示人脸识别模型最终的提取的特征embedding,可以用来计算人脸之间的特征相似度。
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceRecognitionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **embedding**(list of float): 成员变量,表示人脸识别模型最终提取的特征embedding,可以用来计算人脸之间的特征相似度。
|
||||||
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](face_recognition_result.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Face Recognition Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The FaceRecognitionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the image features embedding in the face recognition model.
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::FaceRecognitionResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct FaceRecognitionResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> embedding;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **embedding**: Member variable which indicates the final extracted feature embedding of the face recognition model, and can be used to calculate the facial feature similarity.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.FaceRecognitionResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **embedding**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the final extracted feature embedding of the face recognition model, and can be used to calculate the facial feature similarity.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](headpose_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](headpose_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# HeadPoseResult 头部姿态结果
|
# Head Pose Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
HeadPoseResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明头部姿态结果。
|
The HeadPoseResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the head pose result.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::HeadPoseResult`
|
``fastdeploy::vision::HeadPoseResult`''
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
struct HeadPoseResult {
|
struct HeadPoseResult {
|
||||||
@@ -15,12 +15,12 @@ struct HeadPoseResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **euler_angles**: 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片预测的欧拉角,存放的顺序是(yaw, pitch, roll), yaw 代表水平转角,pitch 代表垂直角,roll 代表翻滚角,值域都为 [-90,+90]度
|
- **euler_angles**: Member variable which indicates the Euler angles predicted for a single face image, stored in the order (yaw, pitch, roll), with yaw representing the horizontal turn angle, pitch representing the vertical angle, and roll representing the roll angle, all with a value range of [-90,+90].
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.HeadPoseResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.HeadPoseResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **euler_angles**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片预测的欧拉角,存放的顺序是(yaw, pitch, roll), yaw 代表水平转角,pitch 代表垂直角,roll 代表翻滚角,值域都为 [-90,+90]度
|
- **euler_angles**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the Euler angles predicted for a single face image, stored in the order (yaw, pitch, roll), with yaw representing the horizontal turn angle, pitch representing the vertical angle, and roll representing the roll angle, all with a value range of [-90,+90].
|
||||||
|
|||||||
26
docs/api/vision_results/headpose_result_CN.md
Normal file
26
docs/api/vision_results/headpose_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](headpose_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# HeadPoseResult 头部姿态结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
HeadPoseResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明头部姿态结果。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::HeadPoseResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct HeadPoseResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> euler_angles;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **euler_angles**: 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片预测的欧拉角,存放的顺序是(yaw, pitch, roll), yaw 代表水平转角,pitch 代表垂直角,roll 代表翻滚角,值域都为 [-90,+90]度
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.HeadPoseResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **euler_angles**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单张人脸图片预测的欧拉角,存放的顺序是(yaw, pitch, roll), yaw 代表水平转角,pitch 代表垂直角,roll 代表翻滚角,值域都为 [-90,+90]度
|
||||||
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](headpose_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Head Pose Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The HeadPoseResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the head pose result.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``fastdeploy::vision::HeadPoseResult`''
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct HeadPoseResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> euler_angles;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **euler_angles**: Member variable which indicates the Euler angles predicted for a single face image, stored in the order (yaw, pitch, roll), with yaw representing the horizontal turn angle, pitch representing the vertical angle, and roll representing the roll angle, all with a value range of [-90,+90].
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.HeadPoseResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **euler_angles**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the Euler angles predicted for a single face image, stored in the order (yaw, pitch, roll), with yaw representing the horizontal turn angle, pitch representing the vertical angle, and roll representing the roll angle, all with a value range of [-90,+90].
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](keypointdetection_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](keypointdetection_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# KeyPointDetectionResult 目标检测结果
|
# Keypoint Detection Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KeyPointDetectionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像中目标行为的各个关键点坐标和置信度。
|
The KeyPointDetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the coordinates and confidence level of each keypoint of the target's behavior in the image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
``fastdeploy::vision::KeyPointDetectionResult``
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
struct KeyPointDetectionResult {
|
struct KeyPointDetectionResult {
|
||||||
@@ -17,28 +17,28 @@ struct KeyPointDetectionResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **keypoints**: 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标。
|
- **keypoints**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of the identified target behavior keypoint.
|
||||||
`keypoints.size()= N * J`
|
` keypoints.size() = N * J`:
|
||||||
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
- `N`: the number of targets in the image
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
- `J`: num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
||||||
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标的置信度。
|
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the keypoint coordinates of the identified target behavior.
|
||||||
`scores.size()= N * J`
|
`scores.size() = N * J`:
|
||||||
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
- `N`: the number of targets in the picture
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
- `J`:num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
||||||
- **num_joints**: 成员变量,一个目标的关键点数量
|
- **num_joints**: Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints of a target.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **keypoints**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标。
|
- **keypoints**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of the identified target behavior keypoint.
|
||||||
`keypoints.size()= N * J`
|
` keypoints.size() = N * J`:
|
||||||
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
- `N`: the number of targets in the image
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints(关键点数量)
|
- `J`: num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标的置信度。
|
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the keypoint coordinates of the identified target behavior.
|
||||||
`scores.size()= N * J`
|
`scores.size() = N * J`:
|
||||||
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
- `N`: the number of targets in the picture
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
- `J`:num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
||||||
- **num_joints**(int): 成员变量,一个目标的关键点数量
|
- **num_joints**(int): Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints of a target.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
44
docs/api/vision_results/keypointdetection_result_CN.md
Normal file
44
docs/api/vision_results/keypointdetection_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](keypointdetection_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# KeyPointDetectionResult 目标检测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
KeyPointDetectionResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像中目标行为的各个关键点坐标和置信度。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct KeyPointDetectionResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> keypoints;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
int num_joints = -1;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **keypoints**: 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标。
|
||||||
|
`keypoints.size()= N * J`
|
||||||
|
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
||||||
|
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标的置信度。
|
||||||
|
`scores.size()= N * J`
|
||||||
|
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
||||||
|
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
||||||
|
- **num_joints**: 成员变量,一个目标的关键点数量
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **keypoints**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标。
|
||||||
|
`keypoints.size()= N * J`
|
||||||
|
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
||||||
|
- `J`:num_joints(关键点数量)
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示识别到的目标行为的关键点坐标的置信度。
|
||||||
|
`scores.size()= N * J`
|
||||||
|
- `N`:图片中的目标数量
|
||||||
|
- `J`:num_joints(一个目标的关键点数量)
|
||||||
|
- **num_joints**(int): 成员变量,一个目标的关键点数量
|
||||||
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](keypointdetection_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Keypoint Detection Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The KeyPointDetectionResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the coordinates and confidence level of each keypoint of the target's behavior in the image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``fastdeploy::vision::KeyPointDetectionResult``
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct KeyPointDetectionResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<float, 2>> keypoints;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> scores;
|
|
||||||
int num_joints = -1;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **keypoints**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of the identified target behavior keypoint.
|
|
||||||
` keypoints.size() = N * J`:
|
|
||||||
- `N`: the number of targets in the image
|
|
||||||
- `J`: num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
|
||||||
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the keypoint coordinates of the identified target behavior.
|
|
||||||
`scores.size() = N * J`:
|
|
||||||
- `N`: the number of targets in the picture
|
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
|
||||||
- **num_joints**: Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints of a target.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.KeyPointDetectionResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **keypoints**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of the identified target behavior keypoint.
|
|
||||||
` keypoints.size() = N * J`:
|
|
||||||
- `N`: the number of targets in the image
|
|
||||||
- `J`: num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the keypoint coordinates of the identified target behavior.
|
|
||||||
`scores.size() = N * J`:
|
|
||||||
- `N`: the number of targets in the picture
|
|
||||||
- `J`:num_joints (the number of keypoints of a target)
|
|
||||||
- **num_joints**(int): Member variable which indicates the number of keypoints of a target.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,11 +1,12 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](matting_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](matting_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# MattingResult 抠图结果
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
MattingResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明模型预测的alpha透明度的值,预测的前景等。
|
# Matting Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
The MattingResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the predicted value of alpha transparency predicted and the predicted foreground, etc.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::MattingResult`
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
``fastdeploy::vision::MattingResult`''
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
struct MattingResult {
|
struct MattingResult {
|
||||||
@@ -18,19 +19,19 @@ struct MattingResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **alpha**: 是一维向量,为预测的alpha透明度的值,值域为[0.,1.],长度为hxw,h,w为输入图像的高和宽
|
- **alpha**: It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted value of alpha transparency. The value range is [0.,1.], and the length is hxw, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image seperately.
|
||||||
- **foreground**: 是一维向量,为预测的前景,值域为[0.,255.],长度为hxwxc,h,w为输入图像的高和宽,c一般为3,foreground不是一定有的,只有模型本身预测了前景,这个属性才会有效
|
- **foreground**: It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted foreground. The value range is [0.,255.], and the length is hxwxc, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image, and c is generally 3. This vector is valid only when the model itself predicts the foreground.
|
||||||
- **contain_foreground**: 表示预测的结果是否包含前景
|
- **contain_foreground**: Used to indicate whether the result contains foreground.
|
||||||
- **shape**: 表示输出结果的shape,当contain_foreground为false,shape只包含(h,w),当contain_foreground为true,shape包含(h,w,c), c一般为3
|
- **shape**: Used to indicate the shape of the output. When contain_foreground is false, the shape only contains (h,w), while when contain_foreground is true, the shape contains (h,w,c), in which c is generally 3.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.MattingResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.MattingResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **alpha**(list of float): 是一维向量,为预测的alpha透明度的值,值域为[0.,1.],长度为hxw,h,w为输入图像的高和宽
|
- **alpha**(list of float): It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted value of alpha transparency. The value range is [0.,1.], and the length is hxw, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image seperately.
|
||||||
- **foreground**(list of float): 是一维向量,为预测的前景,值域为[0.,255.],长度为hxwxc,h,w为输入图像的高和宽,c一般为3,foreground不是一定有的,只有模型本身预测了前景,这个属性才会有效
|
- **foreground**(list of float): It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted foreground. The value range is [0.,255.], and the length is hxwxc, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image, and c is generally 3. This vector is valid only when the model itself predicts the foreground.
|
||||||
- **contain_foreground**(bool): 表示预测的结果是否包含前景
|
- **contain_foreground**(bool): Used to indicate whether the result contains foreground.
|
||||||
- **shape**(list of int): 表示输出结果的shape,当contain_foreground为false,shape只包含(h,w),当contain_foreground为true,shape包含(h,w,c), c一般为3
|
- **shape**(list of int): Used to indicate the shape of the output. When contain_foreground is false, the shape only contains (h,w), while when contain_foreground is true, the shape contains (h,w,c), in which c is generally 3.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
36
docs/api/vision_results/matting_result_CN.md
Normal file
36
docs/api/vision_results/matting_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](matting_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# MattingResult 抠图结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
MattingResult 代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明模型预测的alpha透明度的值,预测的前景等。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::MattingResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct MattingResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> alpha;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> foreground;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int64_t> shape;
|
||||||
|
bool contain_foreground = false;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **alpha**: 是一维向量,为预测的alpha透明度的值,值域为[0.,1.],长度为hxw,h,w为输入图像的高和宽
|
||||||
|
- **foreground**: 是一维向量,为预测的前景,值域为[0.,255.],长度为hxwxc,h,w为输入图像的高和宽,c一般为3,foreground不是一定有的,只有模型本身预测了前景,这个属性才会有效
|
||||||
|
- **contain_foreground**: 表示预测的结果是否包含前景
|
||||||
|
- **shape**: 表示输出结果的shape,当contain_foreground为false,shape只包含(h,w),当contain_foreground为true,shape包含(h,w,c), c一般为3
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.MattingResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **alpha**(list of float): 是一维向量,为预测的alpha透明度的值,值域为[0.,1.],长度为hxw,h,w为输入图像的高和宽
|
||||||
|
- **foreground**(list of float): 是一维向量,为预测的前景,值域为[0.,255.],长度为hxwxc,h,w为输入图像的高和宽,c一般为3,foreground不是一定有的,只有模型本身预测了前景,这个属性才会有效
|
||||||
|
- **contain_foreground**(bool): 表示预测的结果是否包含前景
|
||||||
|
- **shape**(list of int): 表示输出结果的shape,当contain_foreground为false,shape只包含(h,w),当contain_foreground为true,shape包含(h,w,c), c一般为3
|
||||||
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](matting_result.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Matting Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The MattingResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the predicted value of alpha transparency predicted and the predicted foreground, etc.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``fastdeploy::vision::MattingResult`''
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct MattingResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> alpha;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> foreground;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int64_t> shape;
|
|
||||||
bool contain_foreground = false;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **alpha**: It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted value of alpha transparency. The value range is [0.,1.], and the length is hxw, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image seperately.
|
|
||||||
- **foreground**: It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted foreground. The value range is [0.,255.], and the length is hxwxc, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image, and c is generally 3. This vector is valid only when the model itself predicts the foreground.
|
|
||||||
- **contain_foreground**: Used to indicate whether the result contains foreground.
|
|
||||||
- **shape**: Used to indicate the shape of the output. When contain_foreground is false, the shape only contains (h,w), while when contain_foreground is true, the shape contains (h,w,c), in which c is generally 3.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.MattingResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **alpha**(list of float): It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted value of alpha transparency. The value range is [0.,1.], and the length is hxw, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image seperately.
|
|
||||||
- **foreground**(list of float): It is a one-dimensional vector, indicating the predicted foreground. The value range is [0.,255.], and the length is hxwxc, in which h,w represent the height and the width of the input image, and c is generally 3. This vector is valid only when the model itself predicts the foreground.
|
|
||||||
- **contain_foreground**(bool): Used to indicate whether the result contains foreground.
|
|
||||||
- **shape**(list of int): Used to indicate the shape of the output. When contain_foreground is false, the shape only contains (h,w), while when contain_foreground is true, the shape contains (h,w,c), in which c is generally 3.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](mot_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](mot_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# MOTResult 多目标跟踪结果
|
# Multi-target Tracking Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
MOTResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明多目标跟踪中的检测出来的目标框、目标跟踪id、目标类别和目标置信度。
|
The MOTResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the detected target frame, target tracking id, target class and target confidence ratio in multi-target tracking task.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::MOTResult
|
fastdeploy::vision::MOTResult
|
||||||
@@ -21,20 +21,21 @@ struct MOTResult{
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面中检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **ids**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面中所有目标的id,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **ids**: Member variable which indicates the ids of all targets in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single frame, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **class_ids**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面出来的所有目标类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **class_ids**: Member variable which indicates all target classes detected in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.MOTResult
|
fastdeploy.vision.MOTResult
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单帧画面中检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
||||||
- **ids**(list of list(float)):成员变量,表示单帧画面中所有目标的id,其元素个数与`boxes`一致
|
- **ids**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the ids of all targets in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes`.
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单帧画面检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single frame.
|
||||||
- **class_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单帧画面出来的所有目标类别
|
- **class_ids**(list of float): Member variable which indicates all target classes detected in a single frame.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
40
docs/api/vision_results/mot_result_CN.md
Normal file
40
docs/api/vision_results/mot_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](mot_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# MOTResult 多目标跟踪结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
MOTResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明多目标跟踪中的检测出来的目标框、目标跟踪id、目标类别和目标置信度。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy::vision::MOTResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct MOTResult{
|
||||||
|
// left top right bottom
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<int, 4>> boxes;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int> ids;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> scores;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int> class_ids;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面中检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示框的个数,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **ids**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面中所有目标的id,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **scores**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面检测出来的所有目标置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **class_ids**: 成员变量,表示单帧画面出来的所有目标类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```python
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy.vision.MOTResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): 成员变量,表示单帧画面中检测出来的所有目标框坐标。boxes是一个list,其每个元素为一个长度为4的list, 表示为一个框,每个框以4个float数值依次表示xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, 即左上角和右下角坐标
|
||||||
|
- **ids**(list of list(float)):成员变量,表示单帧画面中所有目标的id,其元素个数与`boxes`一致
|
||||||
|
- **scores**(list of float): 成员变量,表示单帧画面检测出来的所有目标置信度
|
||||||
|
- **class_ids**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单帧画面出来的所有目标类别
|
||||||
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](mot_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Multi-target Tracking Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The MOTResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the detected target frame, target tracking id, target class and target confidence ratio in multi-target tracking task.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::MOTResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct MOTResult{
|
|
||||||
// left top right bottom
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<int, 4>> boxes;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int> ids;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> scores;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int> class_ids;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of boxes, each box is represented by 4 float values in order of xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **ids**: Member variable which indicates the ids of all targets in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single frame, where the number of elements is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **class_ids**: Member variable which indicates all target classes detected in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.MOTResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single frame. It is a list, and each element in it is also a list of length 4, representing a box with 4 float values representing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, i.e. the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner.
|
|
||||||
- **ids**(list of list(float)): Member variable which indicates the ids of all targets in a single frame, where the element number is the same as `boxes`.
|
|
||||||
- **scores**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the confidence level of all targets detected in a single frame.
|
|
||||||
- **class_ids**(list of float): Member variable which indicates all target classes detected in a single frame.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](ocr_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](ocr_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# OCRResult OCR预测结果
|
# OCR prediction result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
OCRResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像检测和识别出来的文本框,文本框方向分类,以及文本框内的文本内容
|
The OCRResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the text box detected in the image, text box orientation classification, and the text content.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::OCRResult
|
fastdeploy::vision::OCRResult
|
||||||
@@ -22,22 +22,22 @@ struct OCRResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示单张图内检测出的框的个数,每个框以8个int数值依次表示框的4个坐标点,顺序为左下,右下,右上,左上
|
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of detected boxes. Each box is represented by 8 int values to indicate the 4 coordinates of the box, in the order of lower left, lower right, upper right, upper left.
|
||||||
- **text**: 成员变量,表示多个文本框内被识别出来的文本内容,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **text**: Member variable which indicates the content of the recognized text in multiple text boxes, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **rec_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框内识别出来的文本的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **rec_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the recognized text, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **cls_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框的分类结果的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **cls_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the classification result of the text box, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **cls_labels**: 成员变量,表示文本框的方向分类类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **cls_labels**: Member variable which indicates the directional category of the textbox, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.OCRResult
|
fastdeploy.vision.OCRResult
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示单张图内检测出的框的个数,每个框以8个int数值依次表示框的4个坐标点,顺序为左下,右下,右上,左上
|
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of detected boxes. Each box is represented by 8 int values to indicate the 4 coordinates of the box, in the order of lower left, lower right, upper right, upper left.
|
||||||
- **text**: 成员变量,表示多个文本框内被识别出来的文本内容,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **text**: Member variable which indicates the content of the recognized text in multiple text boxes, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **rec_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框内识别出来的文本的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **rec_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the recognized text, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **cls_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框的分类结果的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **cls_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the classification result of the text box, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
- **cls_labels**: 成员变量,表示文本框的方向分类类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
- **cls_labels**: Member variable which indicates the directional category of the textbox, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
43
docs/api/vision_results/ocr_result_CN.md
Normal file
43
docs/api/vision_results/ocr_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](ocr_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# OCRResult OCR预测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OCRResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像检测和识别出来的文本框,文本框方向分类,以及文本框内的文本内容
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy::vision::OCRResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct OCRResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::array<int, 8>> boxes;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<std::string> text;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> rec_scores;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> cls_scores;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int32_t> cls_labels;
|
||||||
|
ResultType type = ResultType::OCR;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示单张图内检测出的框的个数,每个框以8个int数值依次表示框的4个坐标点,顺序为左下,右下,右上,左上
|
||||||
|
- **text**: 成员变量,表示多个文本框内被识别出来的文本内容,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **rec_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框内识别出来的文本的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **cls_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框的分类结果的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **cls_labels**: 成员变量,表示文本框的方向分类类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```python
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy.vision.OCRResult
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **boxes**: 成员变量,表示单张图片检测出来的所有目标框坐标,`boxes.size()`表示单张图内检测出的框的个数,每个框以8个int数值依次表示框的4个坐标点,顺序为左下,右下,右上,左上
|
||||||
|
- **text**: 成员变量,表示多个文本框内被识别出来的文本内容,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **rec_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框内识别出来的文本的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **cls_scores**: 成员变量,表示文本框的分类结果的置信度,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
|
- **cls_labels**: 成员变量,表示文本框的方向分类类别,其元素个数与`boxes.size()`一致
|
||||||
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](ocr_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# OCR prediction result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The OCRResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, and is used to indicate the text box detected in the image, text box orientation classification, and the text content.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy::vision::OCRResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct OCRResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::array<int, 8>> boxes;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<std::string> text;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> rec_scores;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> cls_scores;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int32_t> cls_labels;
|
|
||||||
ResultType type = ResultType::OCR;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of detected boxes. Each box is represented by 8 int values to indicate the 4 coordinates of the box, in the order of lower left, lower right, upper right, upper left.
|
|
||||||
- **text**: Member variable which indicates the content of the recognized text in multiple text boxes, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **rec_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the recognized text, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **cls_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the classification result of the text box, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **cls_labels**: Member variable which indicates the directional category of the textbox, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
|
||||||
fastdeploy.vision.OCRResult
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **boxes**: Member variable which indicates the coordinates of all detected target boxes in a single image. `boxes.size()` indicates the number of detected boxes. Each box is represented by 8 int values to indicate the 4 coordinates of the box, in the order of lower left, lower right, upper right, upper left.
|
|
||||||
- **text**: Member variable which indicates the content of the recognized text in multiple text boxes, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **rec_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the recognized text, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **cls_scores**: Member variable which indicates the confidence level of the classification result of the text box, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
- **cls_labels**: Member variable which indicates the directional category of the textbox, where the element number is the same as `boxes.size()`.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
|||||||
中文 | [English](segmentation_result_EN.md)
|
English | [中文](segmentation_result_CN.md)
|
||||||
# SegmentationResult 目标检测结果
|
# Segmentation Result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SegmentationResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像中每个像素预测出来的分割类别和分割类别的概率值。
|
The SegmentationResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, indicating the segmentation category and the segmentation category probability predicted in each pixel in the image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 定义
|
## C++ Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy::vision::SegmentationResult`
|
``fastdeploy::vision::SegmentationResult``
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
```c++
|
||||||
struct SegmentationResult {
|
struct SegmentationResult {
|
||||||
@@ -18,16 +18,16 @@ struct SegmentationResult {
|
|||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_map**: 成员变量,表示单张图片每个像素点的分割类别,`label_map.size()`表示图片像素点的个数
|
- **label_map**: Member variable which indicates the segmentation category of each pixel in a single image. `label_map.size()` indicates the number of pixel points of a image.
|
||||||
- **score_map**: 成员变量,与label_map一一对应的所预测的分割类别概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op argmax`)或者经过softmax归一化化后的概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op softmax`或者导出模型时指定`--output_op none`同时模型初始化的时候设置模型[类成员属性](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/)`apply_softmax=True`)
|
- **score_map**: Member variable which indicates the predicted segmentation category probability value (specified as `--output_op argmax` when export) corresponding to label_map, or the probability value normalized by softmax (specified as `--output_op softmax` when export, or as `--output_op when exporting the model). none` when export while setting the [class member attribute](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/) as `apply_softmax=True` during model initialization).
|
||||||
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示输出图片的shape,为H\*W
|
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the output image as H\*W.
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
||||||
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 定义
|
## Python Definition
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult`
|
`fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_map**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片每个像素点的分割类别
|
- **label_map**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the segmentation category of each pixel in a single image.
|
||||||
- **score_map**(list of float): 成员变量,与label_map一一对应的所预测的分割类别概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op argmax`)或者经过softmax归一化化后的概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op softmax`或者导出模型时指定`--output_op none`同时模型初始化的时候设置模型[类成员属性](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/python/)`apply_softmax=true`)
|
- **score_map**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the predicted segmentation category probability value (specified as `--output_op argmax` when export) corresponding to label_map, or the probability value normalized by softmax (specified as `--output_op softmax` when export, or as `--output_op when exporting the model). none` when export while setting the [class member attribute](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/) as `apply_softmax=True` during model initialization).
|
||||||
- **shape**(list of int): 成员变量,表示输出图片的shape,为H\*W
|
- **shape**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the shape of the output image as H\*W.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
33
docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result_CN.md
Normal file
33
docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||||||
|
中文 | [English](segmentation_result.md)
|
||||||
|
# SegmentationResult 目标检测结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SegmentationResult代码定义在`fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`中,用于表明图像中每个像素预测出来的分割类别和分割类别的概率值。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy::vision::SegmentationResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```c++
|
||||||
|
struct SegmentationResult {
|
||||||
|
std::vector<uint8_t> label_map;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> score_map;
|
||||||
|
std::vector<int64_t> shape;
|
||||||
|
bool contain_score_map = false;
|
||||||
|
void Clear();
|
||||||
|
std::string Str();
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **label_map**: 成员变量,表示单张图片每个像素点的分割类别,`label_map.size()`表示图片像素点的个数
|
||||||
|
- **score_map**: 成员变量,与label_map一一对应的所预测的分割类别概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op argmax`)或者经过softmax归一化化后的概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op softmax`或者导出模型时指定`--output_op none`同时模型初始化的时候设置模型[类成员属性](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/)`apply_softmax=True`)
|
||||||
|
- **shape**: 成员变量,表示输出图片的shape,为H\*W
|
||||||
|
- **Clear()**: 成员函数,用于清除结构体中存储的结果
|
||||||
|
- **Str()**: 成员函数,将结构体中的信息以字符串形式输出(用于Debug)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 定义
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **label_map**(list of int): 成员变量,表示单张图片每个像素点的分割类别
|
||||||
|
- **score_map**(list of float): 成员变量,与label_map一一对应的所预测的分割类别概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op argmax`)或者经过softmax归一化化后的概率值(当导出模型时指定`--output_op softmax`或者导出模型时指定`--output_op none`同时模型初始化的时候设置模型[类成员属性](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/python/)`apply_softmax=true`)
|
||||||
|
- **shape**(list of int): 成员变量,表示输出图片的shape,为H\*W
|
||||||
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](segmentation_result.md)
|
|
||||||
# Segmentation Result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The SegmentationResult code is defined in `fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h`, indicating the segmentation category and the segmentation category probability predicted in each pixel in the image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``fastdeploy::vision::SegmentationResult``
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```c++
|
|
||||||
struct SegmentationResult {
|
|
||||||
std::vector<uint8_t> label_map;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<float> score_map;
|
|
||||||
std::vector<int64_t> shape;
|
|
||||||
bool contain_score_map = false;
|
|
||||||
void Clear();
|
|
||||||
std::string Str();
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_map**: Member variable which indicates the segmentation category of each pixel in a single image. `label_map.size()` indicates the number of pixel points of a image.
|
|
||||||
- **score_map**: Member variable which indicates the predicted segmentation category probability value (specified as `--output_op argmax` when export) corresponding to label_map, or the probability value normalized by softmax (specified as `--output_op softmax` when export, or as `--output_op when exporting the model). none` when export while setting the [class member attribute](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/) as `apply_softmax=True` during model initialization).
|
|
||||||
- **shape**: Member variable which indicates the shape of the output image as H\*W.
|
|
||||||
- **Clear()**: Member function used to clear the results stored in the structure.
|
|
||||||
- **Str()**: Member function used to output the information in the structure as string (for Debug).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python Definition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **label_map**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the segmentation category of each pixel in a single image.
|
|
||||||
- **score_map**(list of float): Member variable which indicates the predicted segmentation category probability value (specified as `--output_op argmax` when export) corresponding to label_map, or the probability value normalized by softmax (specified as `--output_op softmax` when export, or as `--output_op when exporting the model). none` when export while setting the [class member attribute](../../../examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/cpp/) as `apply_softmax=True` during model initialization).
|
|
||||||
- **shape**(list of int): Member variable which indicates the shape of the output image as H\*W.
|
|
||||||
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ English | [中文](../../cn/build_and_install/README.md)
|
|||||||
- [Build and Install on RK3588 Platform](rknpu2.md)
|
- [Build and Install on RK3588 Platform](rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
- [Build and Install on A311D Platform](a311d.md)
|
- [Build and Install on A311D Platform](a311d.md)
|
||||||
- [Build and Install on KunlunXin XPU Platform](kunlunxin.md)
|
- [Build and Install on KunlunXin XPU Platform](kunlunxin.md)
|
||||||
|
- [Build and Install on Huawei Ascend Platform](huawei_ascend.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Build options
|
## Build options
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ English | [中文](../../cn/build_and_install/kunlunxin.md)
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
# How to Build KunlunXin XPU Deployment Environment
|
# How to Build KunlunXin XPU Deployment Environment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FastDeploy supports deployment AI on KunlunXin XPU based on Paddle Lite backend. For more detailed information, please refer to: [Paddle Lite Deployment Example](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/lite/develop/demo_guides/kunlunxin_xpu.html#xpu)。
|
FastDeploy supports deployment AI on KunlunXin XPU based on Paddle Lite backend. For more detailed information, please refer to: [Paddle Lite Deployment Example](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/lite/develop/demo_guides/kunlunxin_xpu.html#xpu).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This document describes how to compile the C++ FastDeploy library based on Paddle Lite.
|
This document describes how to compile the C++ FastDeploy library based on Paddle Lite.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ The comparison of the two methods is shown in the following table:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Use FastDeploy one-click model automation compression tool to quantify models
|
### Use FastDeploy one-click model automation compression tool to quantify models
|
||||||
Based on PaddleSlim's Auto Compression Toolkit (ACT), FastDeploy provides users with a one-click model automation compression tool, please refer to the following document for one-click model automation compression.
|
Based on PaddleSlim's Auto Compression Toolkit (ACT), FastDeploy provides users with a one-click model automation compression tool, please refer to the following document for one-click model automation compression.
|
||||||
- [FastDeploy One-Click Model Automation Compression](../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/)
|
- [FastDeploy One-Click Model Automation Compression](../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/README_EN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Benchmark
|
## Benchmark
|
||||||
Currently, FastDeploy supports automated compression, and the Runtime Benchmark and End-to-End Benchmark of the model that completes the deployment test are shown below.
|
Currently, FastDeploy supports automated compression, and the Runtime Benchmark and End-to-End Benchmark of the model that completes the deployment test are shown below.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,42 +1,40 @@
|
|||||||
[English](README_en.md) | 简体中文
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 前端AI应用
|
# Front-end AI application
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
人工智能技术的快速发展带动了计算机视觉、自然语言处理领域的产业升级。另外,随着PC和移动设备上算力的稳步增强、模型压缩技术迭代更新以及各种创新需求的不断催生,在浏览器中部署AI模型实现前端智能已经具备了良好的基础条件。
|
The development of artificial intelligence technology has led to industrial upgrading in the fields of computer vision(CV) and natural language processing(NLP). In addition, the deployment of AI models in browsers to achieve front-end intelligence has already provided good basic conditions with the steady increase in computing power on PCs and mobile devices, iterative updates of model compression technologies, and the continuous emergence of various innovative needs.
|
||||||
针对前端部署AI深度学习模型困难的问题,百度开源了Paddle.js前端深度学习模型部署框架,可以很容易的将深度学习模型部署到前端项目中。
|
In response to the difficulty of deploying AI deep learning models on the front-end, Baidu has open-sourced the Paddle.js front-end deep learning model deployment framework, which can easily deploy deep learning models into front-end projects.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Paddle.js简介
|
# Introduction of Paddle.js
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js)是百度`PaddlePaddle`的web方向子项目,是一个运行在浏览器中的开源深度学习框架。`Paddle.js`可以加载`PaddlePaddle`动转静的模型,经过`Paddle.js`的模型转换工具`paddlejs-converter`转换成浏览器友好的模型,易于在线推理预测使用。`Paddle.js`支持`WebGL/WebGPU/WebAssembly`的浏览器中运行,也可以在百度小程序和微信小程序环境下运行。
|
[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) is a web sub-project of Baidu `PaddlePaddle`, an open source deep learning framework running in the browser. `Paddle.js` can load the deep learning model trained by `PaddlePaddle`, and convert it into a browser-friendly model through the model conversion tool `paddlejs-converter` of `Paddle.js`, which is easy to use for online reasoning and prediction. `Paddle.js` supports running in browsers of `WebGL/WebGPU/WebAssembly`, and can also run in the environment of Baidu applet and WeChat applet.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
简言之,利用Paddle.js,我们可以在浏览器、小程序等前端应用场景上线AI功能,包括但不限于目标检测,图像分割,OCR,物品分类等AI能力。
|
Finally, we can launch AI functions in front-end application scenarios such as browsers and mini-program using `Paddle.js`, including but not limited to AI capabilities such as object detection, image segmentation, OCR, and item classification.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Web Demo使用
|
## Web Demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在浏览器中直接运行官方demo参考[文档](./WebDemo.md)
|
Refer to this [document](./WebDemo.md) for steps to run computer vision demo in the browser.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|demo名称|web demo目录|可视化|
|
|demo|web demo directory|visualization|
|
||||||
|-|-|-|
|
|-|-|-|
|
||||||
|目标检测|[ScrewDetection、FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/)| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874536-b7fa2c0a-d71f-4271-8c40-f9088bfad3c9.png" height="200px">|
|
|object detection|[ScrewDetection、FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/)| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874536-b7fa2c0a-d71f-4271-8c40-f9088bfad3c9.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|人像分割背景替换|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874452-4ef2e770-fbb3-4a35-954b-f871716d6669.png" height="200px">|
|
|human segmentation|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874452-4ef2e770-fbb3-4a35-954b-f871716d6669.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|物体识别|[GestureRecognition、ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874416-454e6bb0-4ebd-4b51-a88a-8c40614290ae.png" height="200px">|
|
|classification|[GestureRecognition、ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874416-454e6bb0-4ebd-4b51-a88a-8c40614290ae.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|OCR|[TextDetection、TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874354-1b5eecb0-f273-403c-aa6c-4463bf6d78db.png" height="200px">|
|
|OCR|[TextDetection、TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874354-1b5eecb0-f273-403c-aa6c-4463bf6d78db.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 微信小程序Demo使用
|
## Wechat Mini-program
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在微信小程序运行官方demo参考[文档](./mini_program/README.md)
|
Run the official demo reference in the WeChat mini-program [document](./mini_program/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|名称|目录|
|
|Name|Directory|
|
||||||
|-|-|
|
|-|-|
|
||||||
|OCR文本检测| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
|OCR Text Detection| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
||||||
|OCR文本识别| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
|OCR Text Recognition| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
||||||
|目标检测| coming soon |
|
|object detection| coming soon |
|
||||||
|图像分割| coming soon |
|
|Image segmentation | coming soon |
|
||||||
|物品分类| coming soon |
|
|Item Category| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Contributor
|
## Contributor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
感谢飞桨开发者专家(PPDE) 陈千鹤(github: [chenqianhe](https://github.com/chenqianhe))贡献的Web demo, 小程序。
|
Thanks to Paddle Paddle Developer Expert (PPDE) Chen Qianhe (github: [chenqianhe](https://github.com/chenqianhe)) for the Web demo, mini-program.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
42
examples/application/js/README_CN.md
Normal file
42
examples/application/js/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 前端AI应用
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
人工智能技术的快速发展带动了计算机视觉、自然语言处理领域的产业升级。另外,随着PC和移动设备上算力的稳步增强、模型压缩技术迭代更新以及各种创新需求的不断催生,在浏览器中部署AI模型实现前端智能已经具备了良好的基础条件。
|
||||||
|
针对前端部署AI深度学习模型困难的问题,百度开源了Paddle.js前端深度学习模型部署框架,可以很容易的将深度学习模型部署到前端项目中。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Paddle.js简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js)是百度`PaddlePaddle`的web方向子项目,是一个运行在浏览器中的开源深度学习框架。`Paddle.js`可以加载`PaddlePaddle`动转静的模型,经过`Paddle.js`的模型转换工具`paddlejs-converter`转换成浏览器友好的模型,易于在线推理预测使用。`Paddle.js`支持`WebGL/WebGPU/WebAssembly`的浏览器中运行,也可以在百度小程序和微信小程序环境下运行。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
简言之,利用Paddle.js,我们可以在浏览器、小程序等前端应用场景上线AI功能,包括但不限于目标检测,图像分割,OCR,物品分类等AI能力。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Web Demo使用
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在浏览器中直接运行官方demo参考[文档](./WebDemo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|demo名称|web demo目录|可视化|
|
||||||
|
|-|-|-|
|
||||||
|
|目标检测|[ScrewDetection、FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/)| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874536-b7fa2c0a-d71f-4271-8c40-f9088bfad3c9.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|
|人像分割背景替换|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874452-4ef2e770-fbb3-4a35-954b-f871716d6669.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|
|物体识别|[GestureRecognition、ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874416-454e6bb0-4ebd-4b51-a88a-8c40614290ae.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|
|OCR|[TextDetection、TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874354-1b5eecb0-f273-403c-aa6c-4463bf6d78db.png" height="200px">|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 微信小程序Demo使用
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在微信小程序运行官方demo参考[文档](./mini_program/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|名称|目录|
|
||||||
|
|-|-|
|
||||||
|
|OCR文本检测| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
||||||
|
|OCR文本识别| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
||||||
|
|目标检测| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|图像分割| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|物品分类| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Contributor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
感谢飞桨开发者专家(PPDE) 陈千鹤(github: [chenqianhe](https://github.com/chenqianhe))贡献的Web demo, 小程序。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](README.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Front-end AI application
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The development of artificial intelligence technology has led to industrial upgrading in the fields of computer vision(CV) and natural language processing(NLP). In addition, the deployment of AI models in browsers to achieve front-end intelligence has already provided good basic conditions with the steady increase in computing power on PCs and mobile devices, iterative updates of model compression technologies, and the continuous emergence of various innovative needs.
|
|
||||||
In response to the difficulty of deploying AI deep learning models on the front-end, Baidu has open-sourced the Paddle.js front-end deep learning model deployment framework, which can easily deploy deep learning models into front-end projects.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Introduction of Paddle.js
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) is a web sub-project of Baidu `PaddlePaddle`, an open source deep learning framework running in the browser. `Paddle.js` can load the deep learning model trained by `PaddlePaddle`, and convert it into a browser-friendly model through the model conversion tool `paddlejs-converter` of `Paddle.js`, which is easy to use for online reasoning and prediction. `Paddle.js` supports running in browsers of `WebGL/WebGPU/WebAssembly`, and can also run in the environment of Baidu applet and WeChat applet.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, we can launch AI functions in front-end application scenarios such as browsers and mini-program using `Paddle.js`, including but not limited to AI capabilities such as object detection, image segmentation, OCR, and item classification.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Web Demo
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Refer to this [document](./WebDemo_en.md) for steps to run computer vision demo in the browser.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|demo|web demo directory|visualization|
|
|
||||||
|-|-|-|
|
|
||||||
|object detection|[ScrewDetection、FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/)| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874536-b7fa2c0a-d71f-4271-8c40-f9088bfad3c9.png" height="200px">|
|
|
||||||
|human segmentation|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874452-4ef2e770-fbb3-4a35-954b-f871716d6669.png" height="200px">|
|
|
||||||
|classification|[GestureRecognition、ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874416-454e6bb0-4ebd-4b51-a88a-8c40614290ae.png" height="200px">|
|
|
||||||
|OCR|[TextDetection、TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/)|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26592129/196874354-1b5eecb0-f273-403c-aa6c-4463bf6d78db.png" height="200px">|
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Wechat Mini-program
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Run the official demo reference in the WeChat mini-program [document](./mini_program/README.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|Name|Directory|
|
|
||||||
|-|-|
|
|
||||||
|OCR Text Detection| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
|
||||||
|OCR Text Recognition| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
|
||||||
|object detection| coming soon |
|
|
||||||
|Image segmentation | coming soon |
|
|
||||||
|Item Category| coming soon |
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Contributor
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Thanks to Paddle Paddle Developer Expert (PPDE) Chen Qianhe (github: [chenqianhe](https://github.com/chenqianhe)) for the Web demo, mini-program.
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,174 +1,176 @@
|
|||||||
[English](WebDemo_en.md) | 简体中文
|
English | [简体中文](WebDemo_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Web Demo介绍
|
# Introduction to Web Demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [简介](#0)
|
- [Introduction](#0)
|
||||||
- [1. 快速开始](#1)
|
- [1. Quick Start](#1)
|
||||||
- [2. npm包调用](#2)
|
- [2. npm package call](#2)
|
||||||
- [3. 模型替换](#3)
|
- [3. Model Replacement](#3)
|
||||||
- [4. 自定义前后处理参数](#4)
|
- [4. custom hyperparameters](#4)
|
||||||
- [5. 其他](#5)
|
- [5. Other](#5)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="0"></a>
|
<a name="0"></a>
|
||||||
## 简介
|
## Introduction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本项目基于[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js)在浏览器中实现目标检测,人像分割,OCR,物品分类等计算机视觉任务。
|
Based on [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js), this project implements computer vision tasks such as target detection, portrait segmentation, OCR, and item classification in the browser.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|demo名称|web demo组件|源码目录|npm包|
|
|demo name|web demo component|source directory|npm package|
|
||||||
|-|-|-|-|
|
|-|-|-|-|
|
||||||
|人脸检测|[FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/FaceDetection/)| [facedetect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect)|[@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect)|
|
|Face Detection|[FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/FaceDetection/)| [facedetect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect)|[@paddle-js-models/ facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect)|
|
||||||
|螺丝钉检测|[ScrewDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/ScrewDetection)| [detect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/detect)|[@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect)|
|
|Screw Detection|[ScrewDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/ScrewDetection)| [detect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/detect)|[@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect)|
|
||||||
|人像分割背景替换|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|[humanseg](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg)|[@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg)|
|
|Portrait segmentation background replacement|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|[humanseg](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg)|[@paddle-js-models/ humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg)|
|
||||||
|手势识别AI猜丁壳|[GestureRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition)|[gesture](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/gesture)|[@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture)|
|
|Gesture Recognition AI Guessing Shell|[GestureRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition)|[gesture](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/gesture)|[@paddle-js- models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture)|
|
||||||
|1000种物品识别|[ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification)|[mobilenet](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet)|[@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet)|
|
|1000 Item Identification|[ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification)|[mobilenet](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet)|[@paddle-js-models/ mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet)|
|
||||||
|文本检测|[TextDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection)|[ocrdetection](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection)|[@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet)|
|
|Text Detection|[TextDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection)|[ocrdetection](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection)|[@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet)|
|
||||||
|文本识别|[TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition)|[ocr](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr)|[@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr)|
|
|Text Recognition|[TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition)|[ocr](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr)|[@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr)|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||||
## 1. 快速开始
|
## 1. Quick Start
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本节介绍如何在浏览器中直接运行官方demo。
|
This section describes how to run the official demo directly in the browser.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**1. 安装Node.js**
|
**1. Install Node.js**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
从`Node.js`官网https://nodejs.org/en/download/ 下载适合自己平台的`Node.js`安装包并安装。
|
Download the `Node.js` installation package suitable for your platform from the `Node.js` official website https://nodejs.org/en/download/ and install it.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**2. 安装demo依赖并启动**
|
**2. Install demo dependencies and start**
|
||||||
在`./web_demo`目录下执行如下指令:
|
Execute the following command in the `./web_demo` directory:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
# 安装依赖
|
# install dependencies
|
||||||
npm install
|
npm install
|
||||||
# 启动demo
|
# start demo
|
||||||
npm run dev
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在浏览器中打开网址 `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` 即可快速体验在浏览器中运行计算机视觉任务。
|
Open the URL `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` in the browser to quickly experience running computer vision tasks in the browser.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||||
## 2. npm包调用
|
## 2. npm package call
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本节介绍npm包的使用方式,每个demo均提供简单易用的接口,用户只需初始化上传图片即可获得结果,使用步骤如下:
|
This section introduces how to use npm packages. Each demo provides an easy-to-use interface. Users only need to initialize and upload images to get the results. The steps are as follows:
|
||||||
1. 调用模块
|
1. Call the module
|
||||||
2. 初始化模型
|
2. Initialize the model
|
||||||
3. 传入输入,执行预测
|
3. Pass in input, perform prediction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以 OCR 为例,在前端项目中,`@paddle-js-models/ocr`包的使用方式如下:
|
Taking OCR as an example, in a front-end project, the `@paddle-js-models/ocr` package is used as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
// 1. 调用ocr模块
|
// 1. Call the ocr module
|
||||||
import * as ocr from '@paddle-js-models/ocr';
|
import * as ocr from '@paddle-js-models/ocr';
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 2. 初始化ocr模型
|
// 2. Initialize the ocr model
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 3. 传入HTMLImageElement类型的图像作为输入并获得结果
|
// 3. Pass in an image of type HTMLImageElement as input and get the result
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img);
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 打印OCR模型得到的文本坐标以及文本内容
|
// Print the text coordinates and text content obtained by the OCR model
|
||||||
console.log(res.text);
|
console.log(res.text);
|
||||||
console.log(res.points);
|
console.log(res.points);
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||||
## 3. 模型替换
|
## 3. Model replacement
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
由于前端环境和计算资源限制,在前端部署深度学习模型时,我们对模型的性能有着更严格的要求,简单来说,模型需要足够轻量化。理论上模型的输入shape越小、模型大小越小,则对应的模型的flops越小,在前端运行也能更流畅。经验总结,使用`Paddle.js`部署的模型存储尽量不超过*5M*,实际情况根据硬件和计算资源情况决定。
|
Due to the limitations of the front-end environment and computing resources, when deploying deep learning models on the front-end, we have stricter requirements on the performance of the models. In short, the models need to be lightweight enough. In theory, the smaller the input shape of the model and the smaller the model size, the smaller the flops of the corresponding model, and the smoother the front-end operation. Based on experience, the model storage deployed with `Paddle.js` should not exceed *5M* as much as possible, and the actual situation depends on the hardware and computing resources.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在实际应用中,常常根据垂类的场景定制化模型,官方的demo支持修改传入参数替换模型。
|
In practical applications, models are often customized according to vertical scenarios, and the official demo supports modifying incoming parameters to replace models.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以OCR demo为例,[ocr.init()函数](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr/src/index.ts#L52)中,包含默认初始化的模型链接,如果要替换模型参考下述步骤。
|
Take the OCR demo as an example, [ocr.init()function](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr/src/index.ts#L52), contains the default initialization model link, if you want to replace the model, please refer to the following steps.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
步骤1:将模型转成js格式:
|
Step 1: Convert the model to js format:
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
# 安装paddlejsconverter
|
# Install paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
# 转换模型格式,输入模型为inference模型
|
# Convert the model format, the input model is the inference model
|
||||||
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=./inference.pdmodel --paramPath=./inference.pdiparams --outputDir=./ --useGPUOpt=True
|
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=./inference.pdmodel --paramPath=./inference.pdiparams --outputDir=./ --useGPUOpt=True
|
||||||
# 注意:useGPUOpt 选项默认不开启,如果模型用在 gpu backend(webgl/webgpu),则开启 useGPUOpt,如果模型运行在(wasm/plain js)则不要开启。
|
# Note: The useGPUOpt option is not enabled by default. If the model is used on the gpu backend (webgl/webgpu), enable useGPUOpt. If the model is running on (wasm/plain js), do not enable it.
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
导出成功后,本地目录下会出现 `model.json chunk_1.dat`等文件,分别是对应js模型的网络结构、模型参数二进制文件。
|
After the export is successful, files such as `model.json chunk_1.dat` will appear in the local directory, which are the network structure and model parameter binary files corresponding to the js model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
步骤2:将导出的js模型上传到支持跨域访问的服务器,服务器的CORS配置参考下图:
|
Step 2: Upload the exported js model to a server that supports cross-domain access. For the CORS configuration of the server, refer to the following image:
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
步骤3:修改代码替换默认的模型。以OCR demo为例,修改OCR web demo中[模型初始化代码](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L64),即
|
Step 3: Modify the code to replace the default model. Take the OCR demo as an example, modify the [model initialization code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L64) in the OCR web demo , i.e.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
修改为:
|
change into:
|
||||||
await ocr.init({modelPath: "https://js-models.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleOCR/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer_js_960/model.json"}); # 第一个参数传入新的文本检测字典类型参数
|
await ocr.init({modelPath: "https://js-models.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleOCR/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer_js_960/model.json"}); # The first parameter passes in the new text Check dictionary type parameter
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
重新在demo目录下执行下述命令,即可体验新的模型效果。
|
Re-execute the following command in the demo directory to experience the new model effect.
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
npm run dev
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||||
## 4. 自定义前后处理参数
|
## 4. custom hyperparameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**自定义前处理参数**
|
**Custom preprocessing parameters**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在不同计算机视觉任务中,不同的模型可能有不同的预处理参数,比如mean,std,keep_ratio等参数,替换模型后也需要对预处理参数进行修改。paddle.js发布的npm包中提供了自定义预处理参数的简单方案。只需要在调用模型初始化函数时,传入自定义的参数即可。
|
In different computer vision tasks, different models may have different preprocessing parameters, such as mean, std, keep_ratio and other parameters. After replacing the model, the preprocessing parameters also need to be modified. A simple solution for customizing preprocessing parameters is provided in the npm package published by paddle.js. You only need to pass in custom parameters when calling the model initialization function.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
# 默认参数初始化
|
# Default parameter initialization
|
||||||
await model.init();
|
await model.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
自定义参数初始化
|
Custom parameter initialization
|
||||||
const Config = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], keepratio: false};
|
const Config = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], keepratio: false};
|
||||||
await model.init(Config);
|
await model.init(Config);
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以OCR文本检测demo为例,修改模型前处理的mean和std参数,只需要在模型初始化时传入自定义的mean和std参数。
|
Taking the OCR text detection demo as an example, to modify the mean and std parameters of the model preprocessing, you only need to pass in the custom mean and std parameters when the model is initialized.
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
修改为:
|
change into:
|
||||||
const detConfig = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]};
|
const detConfig = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]};
|
||||||
await ocr.init(detConfig); # 第一个参数传入新的文本检测模型链接
|
await ocr.init(detConfig); # The first parameter passes in the new text detection model link
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**自定义后处理参数**
|
**Custom postprocessing parameters**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
同理,paddle.js发布的npm包也提供了后处理参数的自定义方案。
|
Similarly, the npm package published by paddle.js also provides a custom solution for post-processing parameters.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
# 默认参数运行
|
# run with default parameters
|
||||||
await model.predict();
|
await model.predict();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 自定义后处理参数
|
# custom post-processing parameters
|
||||||
const postConfig = {thresh: 0.5};
|
const postConfig = {thresh: 0.5};
|
||||||
await model.predict(Config);
|
await model.predict(Config);
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以OCR文本检测 demo为例,修改文本检测后处理的参数实现扩大文本检测框的效果,修改OCR web demo中执行[模型预测代码](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L99),即:
|
Take the OCR text detection demo as an example, modify the parameters of the text detection post-processing to achieve the effect of expanding the text detection frame, and modify the OCR web demo to execute the [model prediction code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L99), ie:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value });
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value });
|
||||||
修改为:
|
change into:
|
||||||
// 定义超参数,将unclip_ratio参数从1.5 增大为3.5
|
// Define hyperparameters, increase the unclip_ratio parameter from 1.5 to 3.5
|
||||||
const detConfig = {shape: 960, thresh: 0.3, box_thresh: 0.6, unclip_ratio:3.5};
|
const detConfig = {shape: 960, thresh: 0.3, box_thresh: 0.6, unclip_ratio:3.5};
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value }, detConfig);
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value }, detConfig);
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
注:不同的任务有不同的后处理参数,详细参数参考npm包中的API。
|
Note: Different tasks have different post-processing parameters. For detailed parameters, please refer to the API in the npm package.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||||
## 5. 其他
|
## 5. Others
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`Paddle.js`转换后的模型不仅支持浏览器中使用,也可以在百度小程序和微信小程序环境下运行。
|
The converted model of `Paddle.js` can not only be used in the browser, but also can be run in the Baidu mini-program and WeChat mini-program environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|名称|目录|
|
|Name|Directory|
|
||||||
|-|-|
|
|-|-|
|
||||||
|OCR文本检测| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
|OCR Text Detection| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
||||||
|OCR文本识别| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
|OCR Text Recognition| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
||||||
|目标检测| coming soon |
|
|target detection| coming soon |
|
||||||
|图像分割| coming soon |
|
| Image segmentation | coming soon |
|
||||||
|物品分类| coming soon |
|
|Item Category| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
174
examples/application/js/WebDemo_CN.md
Normal file
174
examples/application/js/WebDemo_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](WebDemo.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Web Demo介绍
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [简介](#0)
|
||||||
|
- [1. 快速开始](#1)
|
||||||
|
- [2. npm包调用](#2)
|
||||||
|
- [3. 模型替换](#3)
|
||||||
|
- [4. 自定义前后处理参数](#4)
|
||||||
|
- [5. 其他](#5)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="0"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本项目基于[Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js)在浏览器中实现目标检测,人像分割,OCR,物品分类等计算机视觉任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|demo名称|web demo组件|源码目录|npm包|
|
||||||
|
|-|-|-|-|
|
||||||
|
|人脸检测|[FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/FaceDetection/)| [facedetect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect)|[@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect)|
|
||||||
|
|螺丝钉检测|[ScrewDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/ScrewDetection)| [detect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/detect)|[@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect)|
|
||||||
|
|人像分割背景替换|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|[humanseg](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg)|[@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg)|
|
||||||
|
|手势识别AI猜丁壳|[GestureRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition)|[gesture](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/gesture)|[@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture)|
|
||||||
|
|1000种物品识别|[ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification)|[mobilenet](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet)|[@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet)|
|
||||||
|
|文本检测|[TextDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection)|[ocrdetection](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection)|[@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet)|
|
||||||
|
|文本识别|[TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition)|[ocr](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr)|[@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr)|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 1. 快速开始
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本节介绍如何在浏览器中直接运行官方demo。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. 安装Node.js**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
从`Node.js`官网https://nodejs.org/en/download/ 下载适合自己平台的`Node.js`安装包并安装。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. 安装demo依赖并启动**
|
||||||
|
在`./web_demo`目录下执行如下指令:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# 安装依赖
|
||||||
|
npm install
|
||||||
|
# 启动demo
|
||||||
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在浏览器中打开网址 `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` 即可快速体验在浏览器中运行计算机视觉任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 2. npm包调用
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本节介绍npm包的使用方式,每个demo均提供简单易用的接口,用户只需初始化上传图片即可获得结果,使用步骤如下:
|
||||||
|
1. 调用模块
|
||||||
|
2. 初始化模型
|
||||||
|
3. 传入输入,执行预测
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以 OCR 为例,在前端项目中,`@paddle-js-models/ocr`包的使用方式如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
// 1. 调用ocr模块
|
||||||
|
import * as ocr from '@paddle-js-models/ocr';
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 2. 初始化ocr模型
|
||||||
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 3. 传入HTMLImageElement类型的图像作为输入并获得结果
|
||||||
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 打印OCR模型得到的文本坐标以及文本内容
|
||||||
|
console.log(res.text);
|
||||||
|
console.log(res.points);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 3. 模型替换
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
由于前端环境和计算资源限制,在前端部署深度学习模型时,我们对模型的性能有着更严格的要求,简单来说,模型需要足够轻量化。理论上模型的输入shape越小、模型大小越小,则对应的模型的flops越小,在前端运行也能更流畅。经验总结,使用`Paddle.js`部署的模型存储尽量不超过*5M*,实际情况根据硬件和计算资源情况决定。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在实际应用中,常常根据垂类的场景定制化模型,官方的demo支持修改传入参数替换模型。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以OCR demo为例,[ocr.init()函数](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr/src/index.ts#L52)中,包含默认初始化的模型链接,如果要替换模型参考下述步骤。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
步骤1:将模型转成js格式:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# 安装paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
|
pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
|
# 转换模型格式,输入模型为inference模型
|
||||||
|
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=./inference.pdmodel --paramPath=./inference.pdiparams --outputDir=./ --useGPUOpt=True
|
||||||
|
# 注意:useGPUOpt 选项默认不开启,如果模型用在 gpu backend(webgl/webgpu),则开启 useGPUOpt,如果模型运行在(wasm/plain js)则不要开启。
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
导出成功后,本地目录下会出现 `model.json chunk_1.dat`等文件,分别是对应js模型的网络结构、模型参数二进制文件。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
步骤2:将导出的js模型上传到支持跨域访问的服务器,服务器的CORS配置参考下图:
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
步骤3:修改代码替换默认的模型。以OCR demo为例,修改OCR web demo中[模型初始化代码](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L64),即
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
|
修改为:
|
||||||
|
await ocr.init({modelPath: "https://js-models.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleOCR/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer_js_960/model.json"}); # 第一个参数传入新的文本检测字典类型参数
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
重新在demo目录下执行下述命令,即可体验新的模型效果。
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 4. 自定义前后处理参数
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**自定义前处理参数**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在不同计算机视觉任务中,不同的模型可能有不同的预处理参数,比如mean,std,keep_ratio等参数,替换模型后也需要对预处理参数进行修改。paddle.js发布的npm包中提供了自定义预处理参数的简单方案。只需要在调用模型初始化函数时,传入自定义的参数即可。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# 默认参数初始化
|
||||||
|
await model.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
自定义参数初始化
|
||||||
|
const Config = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], keepratio: false};
|
||||||
|
await model.init(Config);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以OCR文本检测demo为例,修改模型前处理的mean和std参数,只需要在模型初始化时传入自定义的mean和std参数。
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
await ocr.init();
|
||||||
|
修改为:
|
||||||
|
const detConfig = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]};
|
||||||
|
await ocr.init(detConfig); # 第一个参数传入新的文本检测模型链接
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**自定义后处理参数**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
同理,paddle.js发布的npm包也提供了后处理参数的自定义方案。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# 默认参数运行
|
||||||
|
await model.predict();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 自定义后处理参数
|
||||||
|
const postConfig = {thresh: 0.5};
|
||||||
|
await model.predict(Config);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以OCR文本检测 demo为例,修改文本检测后处理的参数实现扩大文本检测框的效果,修改OCR web demo中执行[模型预测代码](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L99),即:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value });
|
||||||
|
修改为:
|
||||||
|
// 定义超参数,将unclip_ratio参数从1.5 增大为3.5
|
||||||
|
const detConfig = {shape: 960, thresh: 0.3, box_thresh: 0.6, unclip_ratio:3.5};
|
||||||
|
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value }, detConfig);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
注:不同的任务有不同的后处理参数,详细参数参考npm包中的API。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="5"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 5. 其他
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`Paddle.js`转换后的模型不仅支持浏览器中使用,也可以在百度小程序和微信小程序环境下运行。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|名称|目录|
|
||||||
|
|-|-|
|
||||||
|
|OCR文本检测| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
||||||
|
|OCR文本识别| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
||||||
|
|目标检测| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|图像分割| coming soon |
|
||||||
|
|物品分类| coming soon |
|
||||||
@@ -1,176 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](WebDemo.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Introduction to Web Demo
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Introduction](#0)
|
|
||||||
- [1. Quick Start](#1)
|
|
||||||
- [2. npm package call](#2)
|
|
||||||
- [3. Model Replacement](#3)
|
|
||||||
- [4. custom hyperparameters](#4)
|
|
||||||
- [5. Other](#5)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="0"></a>
|
|
||||||
## Introduction
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Based on [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js), this project implements computer vision tasks such as target detection, portrait segmentation, OCR, and item classification in the browser.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|demo name|web demo component|source directory|npm package|
|
|
||||||
|-|-|-|-|
|
|
||||||
|Face Detection|[FaceDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/FaceDetection/)| [facedetect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect)|[@paddle-js-models/ facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect)|
|
|
||||||
|Screw Detection|[ScrewDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/detection/ScrewDetection)| [detect](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/detect)|[@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect)|
|
|
||||||
|Portrait segmentation background replacement|[HumanSeg](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg)|[humanseg](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg)|[@paddle-js-models/ humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg)|
|
|
||||||
|Gesture Recognition AI Guessing Shell|[GestureRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition)|[gesture](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/gesture)|[@paddle-js- models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture)|
|
|
||||||
|1000 Item Identification|[ItemIdentification](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification)|[mobilenet](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet)|[@paddle-js-models/ mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet)|
|
|
||||||
|Text Detection|[TextDetection](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection)|[ocrdetection](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection)|[@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet)|
|
|
||||||
|Text Recognition|[TextRecognition](./web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition)|[ocr](./package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr)|[@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr)|
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 1. Quick Start
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This section describes how to run the official demo directly in the browser.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**1. Install Node.js**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Download the `Node.js` installation package suitable for your platform from the `Node.js` official website https://nodejs.org/en/download/ and install it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**2. Install demo dependencies and start**
|
|
||||||
Execute the following command in the `./web_demo` directory:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
# install dependencies
|
|
||||||
npm install
|
|
||||||
# start demo
|
|
||||||
npm run dev
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Open the URL `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` in the browser to quickly experience running computer vision tasks in the browser.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 2. npm package call
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This section introduces how to use npm packages. Each demo provides an easy-to-use interface. Users only need to initialize and upload images to get the results. The steps are as follows:
|
|
||||||
1. Call the module
|
|
||||||
2. Initialize the model
|
|
||||||
3. Pass in input, perform prediction
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Taking OCR as an example, in a front-end project, the `@paddle-js-models/ocr` package is used as follows:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
// 1. Call the ocr module
|
|
||||||
import * as ocr from '@paddle-js-models/ocr';
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 2. Initialize the ocr model
|
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 3. Pass in an image of type HTMLImageElement as input and get the result
|
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Print the text coordinates and text content obtained by the OCR model
|
|
||||||
console.log(res.text);
|
|
||||||
console.log(res.points);
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 3. Model replacement
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Due to the limitations of the front-end environment and computing resources, when deploying deep learning models on the front-end, we have stricter requirements on the performance of the models. In short, the models need to be lightweight enough. In theory, the smaller the input shape of the model and the smaller the model size, the smaller the flops of the corresponding model, and the smoother the front-end operation. Based on experience, the model storage deployed with `Paddle.js` should not exceed *5M* as much as possible, and the actual situation depends on the hardware and computing resources.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In practical applications, models are often customized according to vertical scenarios, and the official demo supports modifying incoming parameters to replace models.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Take the OCR demo as an example, [ocr.init()function](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/package/packages/paddlejs-models/ocr/src/index.ts#L52), contains the default initialization model link, if you want to replace the model, please refer to the following steps.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Step 1: Convert the model to js format:
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
# Install paddlejsconverter
|
|
||||||
pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
|
||||||
# Convert the model format, the input model is the inference model
|
|
||||||
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=./inference.pdmodel --paramPath=./inference.pdiparams --outputDir=./ --useGPUOpt=True
|
|
||||||
# Note: The useGPUOpt option is not enabled by default. If the model is used on the gpu backend (webgl/webgpu), enable useGPUOpt. If the model is running on (wasm/plain js), do not enable it.
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After the export is successful, files such as `model.json chunk_1.dat` will appear in the local directory, which are the network structure and model parameter binary files corresponding to the js model.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Step 2: Upload the exported js model to a server that supports cross-domain access. For the CORS configuration of the server, refer to the following image:
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Step 3: Modify the code to replace the default model. Take the OCR demo as an example, modify the [model initialization code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/js/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L64) in the OCR web demo , i.e.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
|
||||||
change into:
|
|
||||||
await ocr.init({modelPath: "https://js-models.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleOCR/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer_js_960/model.json"}); # The first parameter passes in the new text Check dictionary type parameter
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Re-execute the following command in the demo directory to experience the new model effect.
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
npm run dev
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 4. custom hyperparameters
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Custom preprocessing parameters**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In different computer vision tasks, different models may have different preprocessing parameters, such as mean, std, keep_ratio and other parameters. After replacing the model, the preprocessing parameters also need to be modified. A simple solution for customizing preprocessing parameters is provided in the npm package published by paddle.js. You only need to pass in custom parameters when calling the model initialization function.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
# Default parameter initialization
|
|
||||||
await model.init();
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Custom parameter initialization
|
|
||||||
const Config = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], keepratio: false};
|
|
||||||
await model.init(Config);
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Taking the OCR text detection demo as an example, to modify the mean and std parameters of the model preprocessing, you only need to pass in the custom mean and std parameters when the model is initialized.
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
await ocr.init();
|
|
||||||
change into:
|
|
||||||
const detConfig = {mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]};
|
|
||||||
await ocr.init(detConfig); # The first parameter passes in the new text detection model link
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Custom postprocessing parameters**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Similarly, the npm package published by paddle.js also provides a custom solution for post-processing parameters.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
# run with default parameters
|
|
||||||
await model.predict();
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# custom post-processing parameters
|
|
||||||
const postConfig = {thresh: 0.5};
|
|
||||||
await model.predict(Config);
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Take the OCR text detection demo as an example, modify the parameters of the text detection post-processing to achieve the effect of expanding the text detection frame, and modify the OCR web demo to execute the [model prediction code](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/application/web_demo/src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition/TextRecognition.vue#L99), ie:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value });
|
|
||||||
change into:
|
|
||||||
// Define hyperparameters, increase the unclip_ratio parameter from 1.5 to 3.5
|
|
||||||
const detConfig = {shape: 960, thresh: 0.3, box_thresh: 0.6, unclip_ratio:3.5};
|
|
||||||
const res = await ocr.recognize(img, { canvas: canvas.value }, detConfig);
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Note: Different tasks have different post-processing parameters. For detailed parameters, please refer to the API in the npm package.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="5"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 5. Others
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The converted model of `Paddle.js` can not only be used in the browser, but also can be run in the Baidu mini-program and WeChat mini-program environment.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|Name|Directory|
|
|
||||||
|-|-|
|
|
||||||
|OCR Text Detection| [ocrdetecXcx](./mini_program/ocrdetectXcx/) |
|
|
||||||
|OCR Text Recognition| [ocrXcx](./mini_program/ocrXcx/) |
|
|
||||||
|target detection| coming soon |
|
|
||||||
| Image segmentation | coming soon |
|
|
||||||
|Item Category| coming soon |
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
[中文版](./DEVELOPMENT_cn.md)
|
English | [简体中文](DEVELOPMENT_CN.md)
|
||||||
# paddlejs-converter
|
# paddlejs-converter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
paddlejs-converter is a model transformation tool for Paddle.js. Its role is to convert PaddlePaddle models (also known as fluid models) into a browser-friendly format that Paddle.js can use to load and predict usage in browsers as well as other environments. In addition, paddlejs-converter provides powerful model optimization capabilities to help developers optimize the model structure and improve runtime performance.
|
paddlejs-converter is a model transformation tool for Paddle.js. Its role is to convert PaddlePaddle models (also known as fluid models) into a browser-friendly format that Paddle.js can use to load and predict usage in browsers as well as other environments. In addition, paddlejs-converter provides powerful model optimization capabilities to help developers optimize the model structure and improve runtime performance.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
[English](./README.md)
|
[English](DEVELOPMENT.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
# paddlejs-converter
|
# paddlejs-converter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
paddlejs-converter 是适用于 Paddle.js 的模型转换工具,其作用是将 PaddlePaddle 模型(或称为 fluid 模型)转化为浏览器友好的格式,以供Paddle.js在浏览器等环境中加载预测使用。此外,paddlejs-converter 还提供了强大的模型优化能力,帮助开发者对模型结构进行优化,提高运行时性能。
|
paddlejs-converter 是适用于 Paddle.js 的模型转换工具,其作用是将 PaddlePaddle 模型(或称为 fluid 模型)转化为浏览器友好的格式,以供Paddle.js在浏览器等环境中加载预测使用。此外,paddlejs-converter 还提供了强大的模型优化能力,帮助开发者对模型结构进行优化,提高运行时性能。
|
||||||
@@ -1,35 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
简体中文 | [English](RNN_EN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](RNN_CN.md)
|
||||||
# RNN算子计算过程
|
# The computation process of RNN operator
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 一、RNN理解
|
## 1. Understanding of RNN
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**RNN** 是循环神经网络,由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成,擅长对序列数据进行处理。
|
**RNN** is a recurrent neural network, including an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, which is specialized in processing sequential data.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
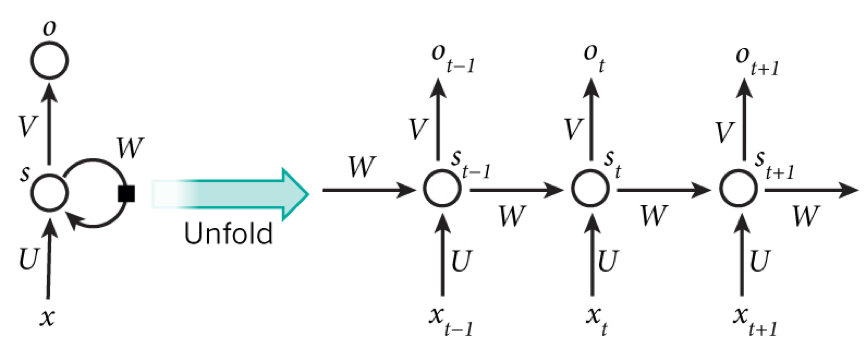
|

|
||||||
paddle官网文档:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/RNN_cn.html#rnn
|
paddle official document: https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/RNN_cn.html#rnn
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
paddle源码实现:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/fluid/operators/rnn_op.h#L812
|
paddle source code implementation: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/fluid/operators/rnn_op.h#L812
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##二、RNN计算方式
|
## 2. How to compute RNN
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t 时刻,输入层为  ,隐藏层为  ,输出层为  。由上图可知, 的值不仅仅取决于  ,还取决于  。计算公式如下:
|
At moment t, the input layer is , hidden layer is , output layer is . As the picture above, isn't just decided by ,it is also related to . The formula is as follows.:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
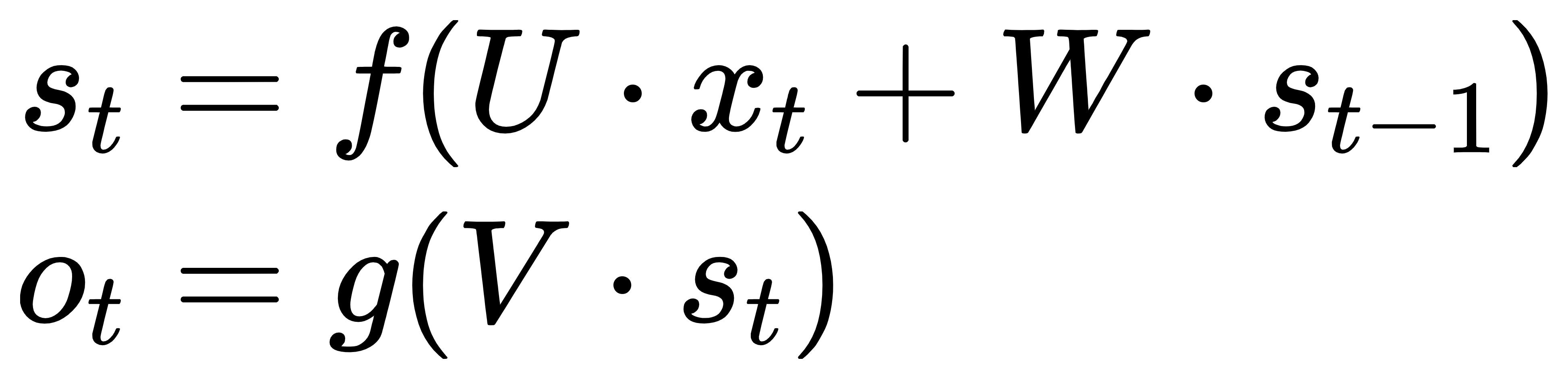
|
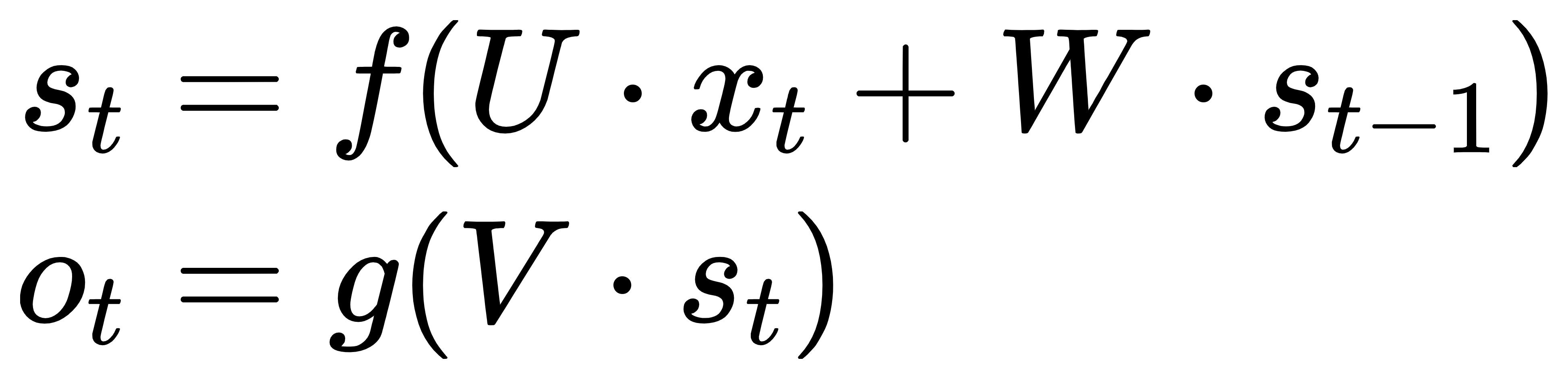
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 三、pdjs中RNN算子实现
|
## 3. RNN operator implementation in pdjs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
因为 RNN 有梯度消失问题,不能获取更多上下文信息,所以 CRNN 中使用的是 **LSTM(Long Short Term Memory)**,LSTM 是一种特殊的 RNN,能够保存长期的依赖关系。
|
Because the gradient disappearance problem exists in RNN, and more contextual information cannot be obtained, **LSTM (Long Short Term Memory)** is used in CRNN, which is a special kind of RNN that can preserve long-term dependencies.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
基于图像的序列,两个方向的上下文是相互有用且互补的。由于 LSTM 是单向的,所以将两个 LSTM,一个向前和一个向后组合到一个**双向 LSTM** 中。此外,可以堆叠多层双向 LSTM。ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer 识别模型就是使用的双层双向 LSTM 结构。计算过程如下图所示:
|
Based on the image sequence, the two directions of context are mutually useful and complementary. Since the LSTM is unidirectional, two LSTMs, one forward and one backward, are combined into a **bidirectional LSTM**. In addition, multiple layers of bidirectional LSTMs can be stacked. ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer recognition model is using a two-layer bidirectional LSTM structure. The calculation process is shown as follows.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 以ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer 模型 rnn算子为例:
|
#### Take ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer model, rnn operator as an example
|
||||||
```javascript
|
```javascript
|
||||||
{
|
{
|
||||||
Attr: {
|
Attr: {
|
||||||
mode: 'LSTM'
|
mode: 'LSTM'
|
||||||
// 是否双向,为true则正向反向都需要遍历
|
// Whether bidirectional, if true, it is necessary to traverse both forward and reverse.
|
||||||
is_bidirec: true
|
is_bidirec: true
|
||||||
// 隐藏层层数,代表循环次数
|
// Number of hidden layers, representing the number of loops.
|
||||||
num_layers: 2
|
num_layers: 2
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -59,25 +59,22 @@ paddle源码实现:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/
|
|||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 整体计算过程
|
#### Overall computation process
|
||||||
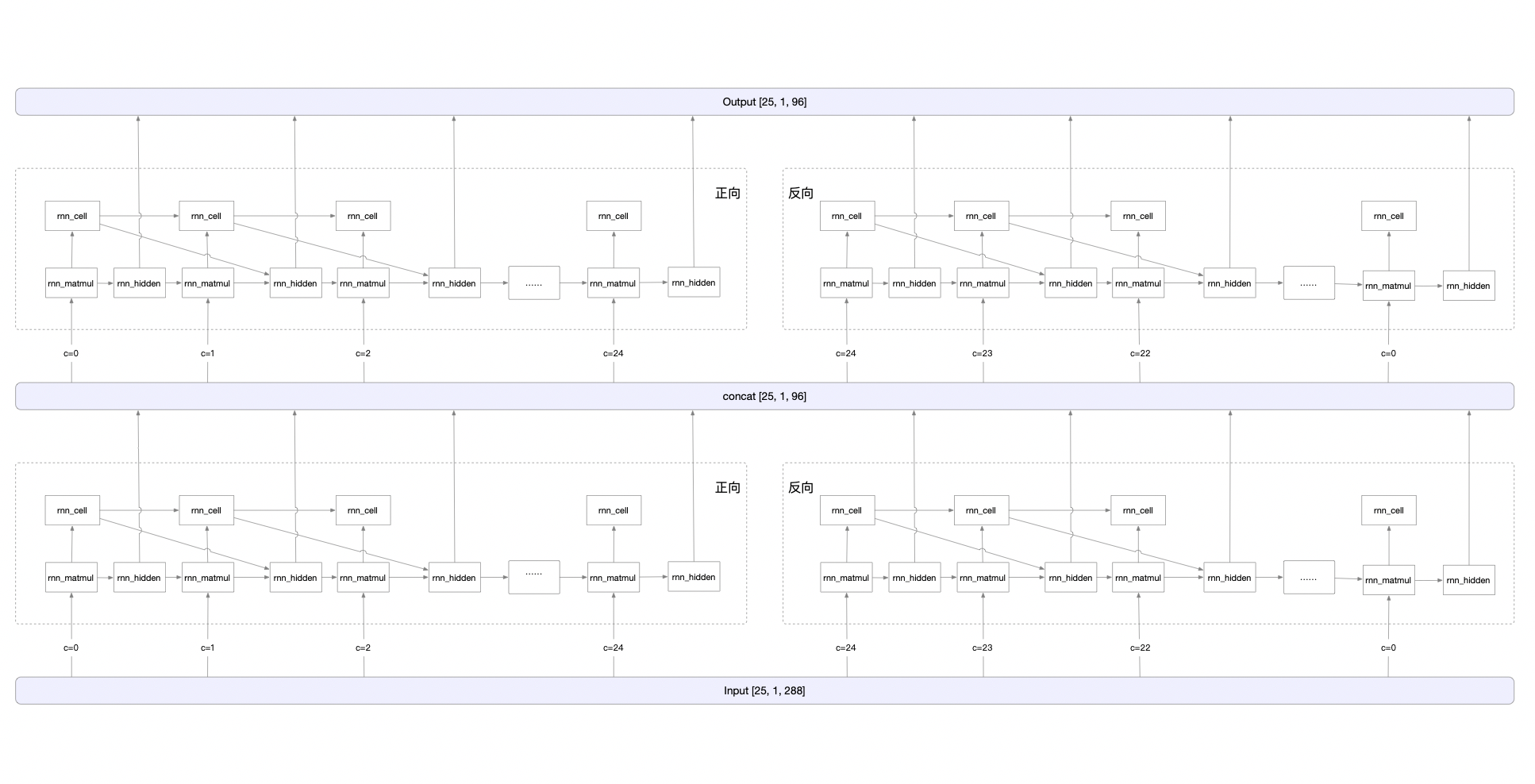
|

|
||||||
#### rnn 计算中新增op:
|
#### Add op in rnn calculation
|
||||||
1)rnn_origin
|
1) rnn_origin
|
||||||
|
Formula: blas.MatMul(Input, WeightList_ih, blas_ih) + blas.MatMul(PreState, WeightList_hh, blas_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
计算公式: blas.MatMul(Input, WeightList_ih, blas_ih) + blas.MatMul(PreState, WeightList_hh, blas_hh)
|
2) rnn_matmul
|
||||||
|
Formula: rnn_matmul = rnn_origin + Matmul( $ S_{t-1} $, WeightList_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2)rnn_matmul
|
3) rnn_cell
|
||||||
|
Method: Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
||||||
计算公式:rnn_matmul = rnn_origin + Matmul( $ S_{t-1} $, WeightList_hh)
|
For details, please refer to [rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3)rnn_cell
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
|
||||||
详见算子实现:[rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4)rnn_hidden
|
4) rnn_hidden
|
||||||
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
||||||
详见算子实现:[rnn_hidden](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_hidden.ts)
|
For details, please refer to [rnn_hidden](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_hidden.ts).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
83
examples/application/js/converter/RNN_CN.md
Normal file
83
examples/application/js/converter/RNN_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](RNN.md)
|
||||||
|
# RNN算子计算过程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 一、RNN理解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**RNN** 是循环神经网络,由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成,擅长对序列数据进行处理。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
paddle官网文档:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/RNN_cn.html#rnn
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
paddle源码实现:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/fluid/operators/rnn_op.h#L812
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
##二、RNN计算方式
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
t 时刻,输入层为  ,隐藏层为  ,输出层为  。由上图可知, 的值不仅仅取决于  ,还取决于  。计算公式如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
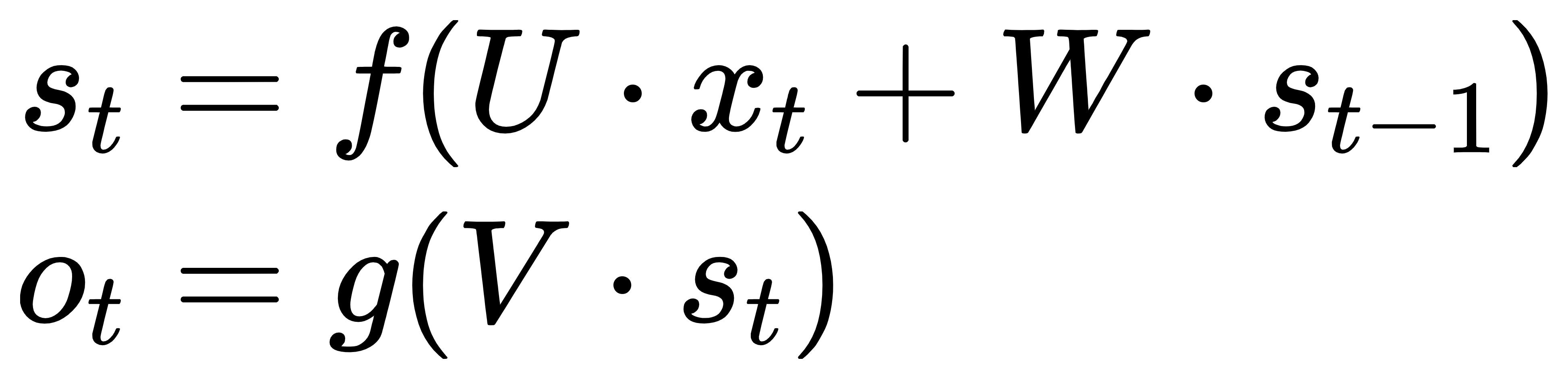
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 三、pdjs中RNN算子实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
因为 RNN 有梯度消失问题,不能获取更多上下文信息,所以 CRNN 中使用的是 **LSTM(Long Short Term Memory)**,LSTM 是一种特殊的 RNN,能够保存长期的依赖关系。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
基于图像的序列,两个方向的上下文是相互有用且互补的。由于 LSTM 是单向的,所以将两个 LSTM,一个向前和一个向后组合到一个**双向 LSTM** 中。此外,可以堆叠多层双向 LSTM。ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer 识别模型就是使用的双层双向 LSTM 结构。计算过程如下图所示:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 以ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer 模型 rnn算子为例:
|
||||||
|
```javascript
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
Attr: {
|
||||||
|
mode: 'LSTM'
|
||||||
|
// 是否双向,为true则正向反向都需要遍历
|
||||||
|
is_bidirec: true
|
||||||
|
// 隐藏层层数,代表循环次数
|
||||||
|
num_layers: 2
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: [
|
||||||
|
transpose_1.tmp_0[25, 1, 288]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PreState: [
|
||||||
|
fill_constant_batch_size_like_0.tmp_0[4, 1, 48],
|
||||||
|
fill_constant_batch_size_like_1.tmp_0[4, 1, 48]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
WeightList: [
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_0.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_0.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_1.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_1.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_2.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_2.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_3.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_3.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_0.b_0[192], lstm_cell_0.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_1.b_0[192], lstm_cell_1.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_2.b_0[192], lstm_cell_2.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_3.b_0[192], lstm_cell_3.b_1[192]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Output: [
|
||||||
|
lstm_0.tmp_0[25, 1, 96]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 整体计算过程
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
#### rnn 计算中新增op:
|
||||||
|
1)rnn_origin
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
计算公式: blas.MatMul(Input, WeightList_ih, blas_ih) + blas.MatMul(PreState, WeightList_hh, blas_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2)rnn_matmul
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
计算公式:rnn_matmul = rnn_origin + Matmul( $ S_{t-1} $, WeightList_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3)rnn_cell
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
||||||
|
详见算子实现:[rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4)rnn_hidden
|
||||||
|
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
||||||
|
详见算子实现:[rnn_hidden](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_hidden.ts)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](RNN.md)
|
|
||||||
# The computation process of RNN operator
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 1. Understanding of RNN
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**RNN** is a recurrent neural network, including an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, which is specialized in processing sequential data.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
paddle official document: https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/RNN_cn.html#rnn
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
paddle source code implementation: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/fluid/operators/rnn_op.h#L812
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 2. How to compute RNN
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
At moment t, the input layer is , hidden layer is , output layer is . As the picture above, isn't just decided by ,it is also related to . The formula is as follows.:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
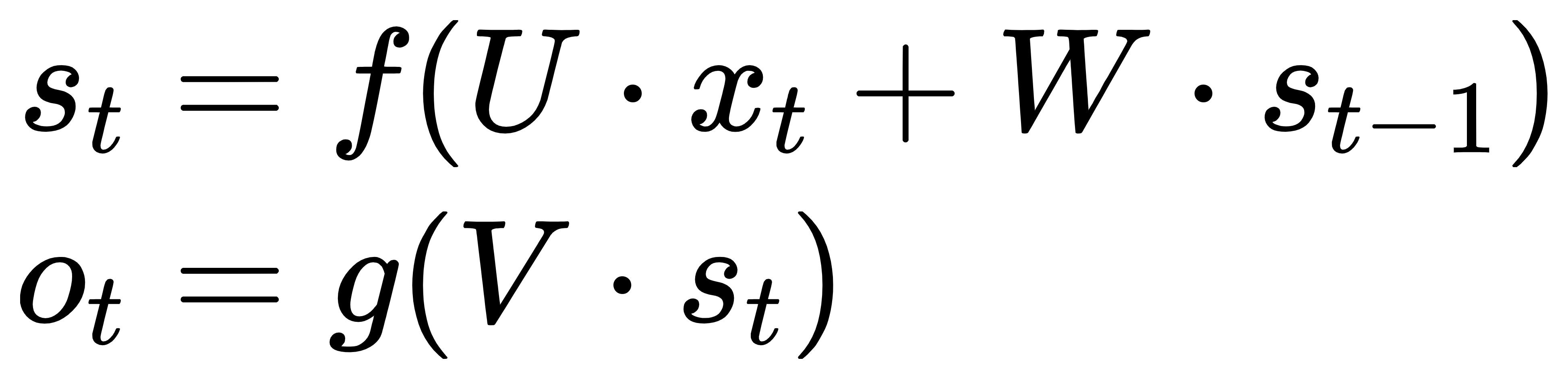
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 3. RNN operator implementation in pdjs
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Because the gradient disappearance problem exists in RNN, and more contextual information cannot be obtained, **LSTM (Long Short Term Memory)** is used in CRNN, which is a special kind of RNN that can preserve long-term dependencies.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Based on the image sequence, the two directions of context are mutually useful and complementary. Since the LSTM is unidirectional, two LSTMs, one forward and one backward, are combined into a **bidirectional LSTM**. In addition, multiple layers of bidirectional LSTMs can be stacked. ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer recognition model is using a two-layer bidirectional LSTM structure. The calculation process is shown as follows.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Take ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer model, rnn operator as an example
|
|
||||||
```javascript
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
Attr: {
|
|
||||||
mode: 'LSTM'
|
|
||||||
// Whether bidirectional, if true, it is necessary to traverse both forward and reverse.
|
|
||||||
is_bidirec: true
|
|
||||||
// Number of hidden layers, representing the number of loops.
|
|
||||||
num_layers: 2
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Input: [
|
|
||||||
transpose_1.tmp_0[25, 1, 288]
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
PreState: [
|
|
||||||
fill_constant_batch_size_like_0.tmp_0[4, 1, 48],
|
|
||||||
fill_constant_batch_size_like_1.tmp_0[4, 1, 48]
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
WeightList: [
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_0.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_0.w_1[192, 48],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_1.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_1.w_1[192, 48],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_2.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_2.w_1[192, 48],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_3.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_3.w_1[192, 48],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_0.b_0[192], lstm_cell_0.b_1[192],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_1.b_0[192], lstm_cell_1.b_1[192],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_2.b_0[192], lstm_cell_2.b_1[192],
|
|
||||||
lstm_cell_3.b_0[192], lstm_cell_3.b_1[192]
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Output: [
|
|
||||||
lstm_0.tmp_0[25, 1, 96]
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Overall computation process
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
#### Add op in rnn calculation
|
|
||||||
1) rnn_origin
|
|
||||||
Formula: blas.MatMul(Input, WeightList_ih, blas_ih) + blas.MatMul(PreState, WeightList_hh, blas_hh)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2) rnn_matmul
|
|
||||||
Formula: rnn_matmul = rnn_origin + Matmul( $ S_{t-1} $, WeightList_hh)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3) rnn_cell
|
|
||||||
Method: Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
|
||||||
For details, please refer to [rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4) rnn_hidden
|
|
||||||
Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
|
||||||
For details, please refer to [rnn_hidden](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_hidden.ts).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,84 +1,84 @@
|
|||||||
[English](README_en.md) | 简体中文
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Paddle.js微信小程序Demo
|
# Paddle.js WeChat mini-program Demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [1.简介](#1)
|
- [1. Introduction](#1)
|
||||||
- [2. 项目启动](#2)
|
- [2. Project Start](#2)
|
||||||
* [2.1 准备工作](#21)
|
* [2.1 Preparations](#21)
|
||||||
* [2.2 启动步骤](#22)
|
* [2.2 Startup steps](#22)
|
||||||
* [2.3 效果展示](#23)
|
* [2.3 visualization](#23)
|
||||||
- [3. 模型推理pipeline](#3)
|
- [3. Model inference pipeline](#3)
|
||||||
- [4. 常见问题](#4)
|
- [4. FAQ](#4)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||||
## 1.简介
|
## 1 Introduction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下包含文本检测、文本识别小程序demo,通过使用 [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) 以及 [Paddle.js微信小程序插件](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxopen/plugindevdoc?appid=wx7138a7bb793608c3&token=956931339&lang=zh_CN) 完成在小程序上利用用户终端算力实现文本检测框选效果。
|
This directory contains the text detection, text recognition mini-program demo, by using [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) and [Paddle.js WeChat mini-program plugin](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxopen/plugindevdoc?appid=wx7138a7bb793608c3&token=956931339&lang=zh_CN) to complete the text detection frame selection effect on the mini-program using the computing power of the user terminal.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||||
## 2. 项目启动
|
## 2. Project start
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="21"></a>
|
<a name="21"></a>
|
||||||
### 2.1 准备工作
|
### 2.1 Preparations
|
||||||
* [申请微信小程序账号](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/)
|
* [Apply for a WeChat mini-program account](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/)
|
||||||
* [微信小程序开发者工具](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/download.html)
|
* [WeChat Mini Program Developer Tools](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/download.html)
|
||||||
* 前端开发环境准备:node、npm
|
* Front-end development environment preparation: node, npm
|
||||||
* 小程序管理后台配置服务器域名,或打开开发者工具【不校验合法域名】
|
* Configure the server domain name in the mini-program management background, or open the developer tool [do not verify the legal domain name]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
详情参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxamp/devprofile/get_profile?token=1132303404&lang=zh_CN)
|
For details, please refer to [document.](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxamp/devprofile/get_profile?token=1132303404&lang=zh_CN)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="22"></a>
|
<a name="22"></a>
|
||||||
### 2.2 启动步骤
|
### 2.2 Startup steps
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **1. 克隆Demo代码**
|
#### **1. Clone the demo code**
|
||||||
```sh
|
````sh
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/application/js/mini_program
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/application/js/mini_program
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **2. 进入小程序目录,安装依赖**
|
#### **2. Enter the mini-program directory and install dependencies**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
````sh
|
||||||
# 运行文本识别demo,进入到ocrXcx目录
|
# Run the text recognition demo and enter the ocrXcx directory
|
||||||
cd ./ocrXcx && npm install
|
cd ./ocrXcx && npm install
|
||||||
# 运行文本检测demo,进入到ocrdetectXcx目录
|
# Run the text detection demo and enter the ocrdetectXcx directory
|
||||||
# cd ./ocrdetectXcx && npm install
|
# cd ./ocrdetectXcx && npm install
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **3. 微信小程序导入代码**
|
#### **3. WeChat mini-program import code**
|
||||||
打开微信开发者工具 --> 导入 --> 选定目录,输入相关信息
|
Open WeChat Developer Tools --> Import --> Select a directory and enter relevant information
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **4. 添加 Paddle.js微信小程序插件**
|
#### **4. Add Paddle.js WeChat mini-program plugin**
|
||||||
小程序管理界面 --> 设置 --> 第三方设置 --> 插件管理 --> 添加插件 --> 搜索 `wx7138a7bb793608c3` 并添加
|
Mini Program Management Interface --> Settings --> Third Party Settings --> Plugin Management --> Add Plugins --> Search for `wx7138a7bb793608c3` and add
|
||||||
[参考文档](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/framework/plugin/using.html)
|
[Reference document](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/framework/plugin/using.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **5. 构建依赖**
|
#### **5. Build dependencies**
|
||||||
点击开发者工具中的菜单栏:工具 --> 构建 npm
|
Click on the menu bar in the developer tools: Tools --> Build npm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
原因:node_modules 目录不会参与编译、上传和打包中,小程序想要使用 npm 包必须走一遍“构建 npm”的过程,构建完成会生成一个 miniprogram_npm 目录,里面会存放构建打包后的 npm 包,也就是小程序真正使用的 npm 包。*
|
Reason: The node_modules directory will not be involved in compiling, uploading and packaging. If a small program wants to use npm packages, it must go through the process of "building npm". After the construction is completed, a miniprogram_npm directory will be generated, which will store the built and packaged npm packages. It is the npm package that the mini-program actually uses. *
|
||||||
[参考文档](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/npm.html)
|
[Reference Documentation](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/npm.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="23"></a>
|
<a name="23"></a>
|
||||||
### 2.3 效果展示
|
### 2.3 visualization
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/43414102/157648579-cdbbee61-9866-4364-9edd-a97ac0eda0c1.png" width="300px">
|
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/43414102/157648579-cdbbee61-9866-4364-9edd-a97ac0eda0c1.png" width="300px">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||||
## 3. 模型推理pipeline
|
## 3. Model inference pipeline
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```typescript
|
```typescript
|
||||||
// 引入 paddlejs 和 paddlejs-plugin,注册小程序环境变量和合适的 backend
|
// Introduce paddlejs and paddlejs-plugin, register the mini-program environment variables and the appropriate backend
|
||||||
import * as paddlejs from '@paddlejs/paddlejs-core';
|
import * as paddlejs from '@paddlejs/paddlejs-core';
|
||||||
import '@paddlejs/paddlejs-backend-webgl';
|
import '@paddlejs/paddlejs-backend-webgl';
|
||||||
const plugin = requirePlugin('paddlejs-plugin');
|
const plugin = requirePlugin('paddlejs-plugin');
|
||||||
plugin.register(paddlejs, wx);
|
plugin.register(paddlejs, wx);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 初始化推理引擎
|
// Initialize the inference engine
|
||||||
const runner = new paddlejs.Runner({modelPath, feedShape, mean, std});
|
const runner = new paddlejs.Runner({modelPath, feedShape, mean, std});
|
||||||
await runner.init();
|
await runner.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 获取图像信息
|
// get image information
|
||||||
wx.canvasGetImageData({
|
wx.canvasGetImageData({
|
||||||
canvasId: canvasId,
|
canvasId: canvasId,
|
||||||
x: 0,
|
x: 0,
|
||||||
@@ -86,41 +86,40 @@ wx.canvasGetImageData({
|
|||||||
width: canvas.width,
|
width: canvas.width,
|
||||||
height: canvas.height,
|
height: canvas.height,
|
||||||
success(res) {
|
success(res) {
|
||||||
// 推理预测
|
// inference prediction
|
||||||
runner.predict({
|
runner.predict({
|
||||||
data: res.data,
|
data: res.data,
|
||||||
width: canvas.width,
|
width: canvas.width,
|
||||||
height: canvas.height,
|
height: canvas.height,
|
||||||
}, function (data) {
|
}, function (data) {
|
||||||
// 获取推理结果
|
// get the inference result
|
||||||
console.log(data)
|
console.log(data)
|
||||||
});
|
});
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
});
|
});
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||||
## 4. 常见问题
|
## 4. FAQ
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.1 出现报错 `Invalid context type [webgl2] for Canvas#getContext`
|
- 4.1 An error occurs `Invalid context type [webgl2] for Canvas#getContext`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**答:** 可以不管,不影响正常代码运行和demo功能
|
**A:** You can leave it alone, it will not affect the normal code operation and demo function
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.2 预览看不到结果
|
- 4.2 Preview can't see the result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**答:** 建议尝试真机调试
|
**A:** It is recommended to try real machine debugging
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.3 微信开发者工具出现黑屏,然后出现超多报错
|
- 4.3 A black screen appears in the WeChat developer tool, and then there are too many errors
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**答:** 重启微信开发者工具
|
**A:** Restart WeChat Developer Tools
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.4 模拟和真机调试结果不一致;模拟检测不到文本等
|
- 4.4 The debugging results of the simulation and the real machine are inconsistent; the simulation cannot detect the text, etc.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**答:** 可以以真机为准;模拟检测不到文本等可以尝试随意改动下代码(增删换行等)再点击编译
|
**A:** The real machine can prevail;
|
||||||
|
If the simulation cannot detect the text, etc., you can try to change the code at will (add, delete, newline, etc.) and then click to compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.5 手机调试或运行时出现 长时间无反应等提示
|
- 4.5 Prompts such as no response for a long time appear when the phone is debugged or running
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**答:** 请继续等待,模型推理需要一定时间
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**A:** Please continue to wait, model inference will take some time
|
||||||
|
|||||||
126
examples/application/js/mini_program/README_CN.md
Normal file
126
examples/application/js/mini_program/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Paddle.js微信小程序Demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [1.简介](#1)
|
||||||
|
- [2. 项目启动](#2)
|
||||||
|
* [2.1 准备工作](#21)
|
||||||
|
* [2.2 启动步骤](#22)
|
||||||
|
* [2.3 效果展示](#23)
|
||||||
|
- [3. 模型推理pipeline](#3)
|
||||||
|
- [4. 常见问题](#4)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 1.简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下包含文本检测、文本识别小程序demo,通过使用 [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) 以及 [Paddle.js微信小程序插件](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxopen/plugindevdoc?appid=wx7138a7bb793608c3&token=956931339&lang=zh_CN) 完成在小程序上利用用户终端算力实现文本检测框选效果。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 2. 项目启动
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="21"></a>
|
||||||
|
### 2.1 准备工作
|
||||||
|
* [申请微信小程序账号](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/)
|
||||||
|
* [微信小程序开发者工具](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/download.html)
|
||||||
|
* 前端开发环境准备:node、npm
|
||||||
|
* 小程序管理后台配置服务器域名,或打开开发者工具【不校验合法域名】
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
详情参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxamp/devprofile/get_profile?token=1132303404&lang=zh_CN)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="22"></a>
|
||||||
|
### 2.2 启动步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### **1. 克隆Demo代码**
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/application/js/mini_program
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### **2. 进入小程序目录,安装依赖**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
# 运行文本识别demo,进入到ocrXcx目录
|
||||||
|
cd ./ocrXcx && npm install
|
||||||
|
# 运行文本检测demo,进入到ocrdetectXcx目录
|
||||||
|
# cd ./ocrdetectXcx && npm install
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### **3. 微信小程序导入代码**
|
||||||
|
打开微信开发者工具 --> 导入 --> 选定目录,输入相关信息
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### **4. 添加 Paddle.js微信小程序插件**
|
||||||
|
小程序管理界面 --> 设置 --> 第三方设置 --> 插件管理 --> 添加插件 --> 搜索 `wx7138a7bb793608c3` 并添加
|
||||||
|
[参考文档](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/framework/plugin/using.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### **5. 构建依赖**
|
||||||
|
点击开发者工具中的菜单栏:工具 --> 构建 npm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
原因:node_modules 目录不会参与编译、上传和打包中,小程序想要使用 npm 包必须走一遍“构建 npm”的过程,构建完成会生成一个 miniprogram_npm 目录,里面会存放构建打包后的 npm 包,也就是小程序真正使用的 npm 包。*
|
||||||
|
[参考文档](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/npm.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="23"></a>
|
||||||
|
### 2.3 效果展示
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/43414102/157648579-cdbbee61-9866-4364-9edd-a97ac0eda0c1.png" width="300px">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="3"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 3. 模型推理pipeline
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```typescript
|
||||||
|
// 引入 paddlejs 和 paddlejs-plugin,注册小程序环境变量和合适的 backend
|
||||||
|
import * as paddlejs from '@paddlejs/paddlejs-core';
|
||||||
|
import '@paddlejs/paddlejs-backend-webgl';
|
||||||
|
const plugin = requirePlugin('paddlejs-plugin');
|
||||||
|
plugin.register(paddlejs, wx);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 初始化推理引擎
|
||||||
|
const runner = new paddlejs.Runner({modelPath, feedShape, mean, std});
|
||||||
|
await runner.init();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 获取图像信息
|
||||||
|
wx.canvasGetImageData({
|
||||||
|
canvasId: canvasId,
|
||||||
|
x: 0,
|
||||||
|
y: 0,
|
||||||
|
width: canvas.width,
|
||||||
|
height: canvas.height,
|
||||||
|
success(res) {
|
||||||
|
// 推理预测
|
||||||
|
runner.predict({
|
||||||
|
data: res.data,
|
||||||
|
width: canvas.width,
|
||||||
|
height: canvas.height,
|
||||||
|
}, function (data) {
|
||||||
|
// 获取推理结果
|
||||||
|
console.log(data)
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<a name="4"></a>
|
||||||
|
## 4. 常见问题
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 4.1 出现报错 `Invalid context type [webgl2] for Canvas#getContext`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**答:** 可以不管,不影响正常代码运行和demo功能
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 4.2 预览看不到结果
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**答:** 建议尝试真机调试
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 4.3 微信开发者工具出现黑屏,然后出现超多报错
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**答:** 重启微信开发者工具
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 4.4 模拟和真机调试结果不一致;模拟检测不到文本等
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**答:** 可以以真机为准;模拟检测不到文本等可以尝试随意改动下代码(增删换行等)再点击编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 4.5 手机调试或运行时出现 长时间无反应等提示
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**答:** 请继续等待,模型推理需要一定时间
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [中文](README.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Paddle.js WeChat mini-program Demo
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [1. Introduction](#1)
|
|
||||||
- [2. Project Start](#2)
|
|
||||||
* [2.1 Preparations](#21)
|
|
||||||
* [2.2 Startup steps](#22)
|
|
||||||
* [2.3 visualization](#23)
|
|
||||||
- [3. Model inference pipeline](#3)
|
|
||||||
- [4. FAQ](#4)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 1 Introduction
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This directory contains the text detection, text recognition mini-program demo, by using [Paddle.js](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.js) and [Paddle.js WeChat mini-program plugin](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxopen/plugindevdoc?appid=wx7138a7bb793608c3&token=956931339&lang=zh_CN) to complete the text detection frame selection effect on the mini-program using the computing power of the user terminal.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 2. Project start
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="21"></a>
|
|
||||||
### 2.1 Preparations
|
|
||||||
* [Apply for a WeChat mini-program account](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/)
|
|
||||||
* [WeChat Mini Program Developer Tools](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/download.html)
|
|
||||||
* Front-end development environment preparation: node, npm
|
|
||||||
* Configure the server domain name in the mini-program management background, or open the developer tool [do not verify the legal domain name]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For details, please refer to [document.](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wxamp/devprofile/get_profile?token=1132303404&lang=zh_CN)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="22"></a>
|
|
||||||
### 2.2 Startup steps
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **1. Clone the demo code**
|
|
||||||
````sh
|
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy
|
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/application/js/mini_program
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **2. Enter the mini-program directory and install dependencies**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````sh
|
|
||||||
# Run the text recognition demo and enter the ocrXcx directory
|
|
||||||
cd ./ocrXcx && npm install
|
|
||||||
# Run the text detection demo and enter the ocrdetectXcx directory
|
|
||||||
# cd ./ocrdetectXcx && npm install
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **3. WeChat mini-program import code**
|
|
||||||
Open WeChat Developer Tools --> Import --> Select a directory and enter relevant information
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **4. Add Paddle.js WeChat mini-program plugin**
|
|
||||||
Mini Program Management Interface --> Settings --> Third Party Settings --> Plugin Management --> Add Plugins --> Search for `wx7138a7bb793608c3` and add
|
|
||||||
[Reference document](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/framework/plugin/using.html)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### **5. Build dependencies**
|
|
||||||
Click on the menu bar in the developer tools: Tools --> Build npm
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Reason: The node_modules directory will not be involved in compiling, uploading and packaging. If a small program wants to use npm packages, it must go through the process of "building npm". After the construction is completed, a miniprogram_npm directory will be generated, which will store the built and packaged npm packages. It is the npm package that the mini-program actually uses. *
|
|
||||||
[Reference Documentation](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/npm.html)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="23"></a>
|
|
||||||
### 2.3 visualization
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/43414102/157648579-cdbbee61-9866-4364-9edd-a97ac0eda0c1.png" width="300px">
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 3. Model inference pipeline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```typescript
|
|
||||||
// Introduce paddlejs and paddlejs-plugin, register the mini-program environment variables and the appropriate backend
|
|
||||||
import * as paddlejs from '@paddlejs/paddlejs-core';
|
|
||||||
import '@paddlejs/paddlejs-backend-webgl';
|
|
||||||
const plugin = requirePlugin('paddlejs-plugin');
|
|
||||||
plugin.register(paddlejs, wx);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Initialize the inference engine
|
|
||||||
const runner = new paddlejs.Runner({modelPath, feedShape, mean, std});
|
|
||||||
await runner.init();
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// get image information
|
|
||||||
wx.canvasGetImageData({
|
|
||||||
canvasId: canvasId,
|
|
||||||
x: 0,
|
|
||||||
y: 0,
|
|
||||||
width: canvas.width,
|
|
||||||
height: canvas.height,
|
|
||||||
success(res) {
|
|
||||||
// inference prediction
|
|
||||||
runner.predict({
|
|
||||||
data: res.data,
|
|
||||||
width: canvas.width,
|
|
||||||
height: canvas.height,
|
|
||||||
}, function (data) {
|
|
||||||
// get the inference result
|
|
||||||
console.log(data)
|
|
||||||
});
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
});
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="4"></a>
|
|
||||||
## 4. FAQ
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.1 An error occurs `Invalid context type [webgl2] for Canvas#getContext`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**A:** You can leave it alone, it will not affect the normal code operation and demo function
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.2 Preview can't see the result
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**A:** It is recommended to try real machine debugging
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.3 A black screen appears in the WeChat developer tool, and then there are too many errors
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**A:** Restart WeChat Developer Tools
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.4 The debugging results of the simulation and the real machine are inconsistent; the simulation cannot detect the text, etc.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**A:** The real machine can prevail;
|
|
||||||
If the simulation cannot detect the text, etc., you can try to change the code at will (add, delete, newline, etc.) and then click to compile
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 4.5 Prompts such as no response for a long time appear when the phone is debugged or running
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**A:** Please continue to wait, model inference will take some time
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,43 +1,41 @@
|
|||||||
[English](README_en.md) | 简体中文
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Paddle.js Model Module介绍
|
# Introduction to Paddle.js Demo Module
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该部分是基于 Paddle.js 进行开发的模型库,主要提供 Web 端可直接引入使用模型的能力。
|
This part is a model library developed based on Paddle.js, which mainly provides the ability to directly introduce and use models on the web side.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| demo名称 | 源码目录 | npm包 |
|
| demo name | source directory | npm package |
|
||||||
| ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
| - | - | - |
|
||||||
| 人脸检测 | [facedetect](./packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect) | [@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect) |
|
| face detection | [facedetect](./packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect) | [@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect) |
|
||||||
| 螺丝钉检测 | [detect](./packages/paddlejs-models/detect) | [@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect) |
|
| Screw detection | [detect](./packages/paddlejs-models/detect) | [@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect ) |
|
||||||
| 人像分割背景替换 | [humanseg](./packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg) | [@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg) |
|
| Portrait segmentation background replacement | [humanseg](./packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg) | [@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg) |
|
||||||
| 手势识别AI猜丁壳 | [gesture](./packages/paddlejs-models/gesture) | [@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture) |
|
| Gesture Recognition AI Guessing Shell | [gesture](./packages/paddlejs-models/gesture) | [@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture) |
|
||||||
| 1000种物品识别 | [mobilenet](./packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet) | [@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet) |
|
| 1000 Item Recognition | [mobilenet](./packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet) | [@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet) |
|
||||||
| 文本检测 | [ocrdetection](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection) | [@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet) |
|
| Text Detection | [ocrdetection](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection) | [@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet ) |
|
||||||
| 文本识别 | [ocr](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocr) | [@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr) |
|
| Text Recognition | [ocr](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocr) | [@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 开发使用
|
## Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该部分是使用 `pnpm` 搭建的 Menorepo
|
This part is Menorepo built with `pnpm`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 安装依赖
|
### Install dependencies
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
````sh
|
||||||
pnpm i
|
pnpm i
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 开发
|
### Development
|
||||||
参考 Package.json 使用 `yalc` 进行开发测试。
|
See Package.json for development testing with `yalc`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
````sh
|
||||||
pnpm run dev:xxx
|
pnpm run dev:xxx
|
||||||
```
|
````
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 整体简介
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 使用 rollup 一次性打包生成 commonjs 和 es 规范的代码;同时具有可扩展性;目前由于依赖的cv库有些问题;就没有配置umd打包。
|
|
||||||
2. 打包时基于 api-extractor 实现 d.ts 文件生成,实现支持 ts 引入生成我们的包
|
|
||||||
3. 基于 jest 支持测试并显示测试相关覆盖率等
|
|
||||||
4. 基于 ts 和 eslint 维护代码风格,保证代码更好开发
|
|
||||||
5. 基于 conventional-changelog-cli 实现自定义关键词生成对应生成changelog
|
|
||||||
6. 基于 yalc 实现本地打包开发测试
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Overall Introduction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Use rollup to package the code of commonjs and es specifications at one time; at the same time, it is extensible; at present, there are some problems with the dependent cv library; there is no configuration for umd packaging.
|
||||||
|
2. The d.ts file is generated based on api-extractor during packaging, and the introduction of ts is supported to generate our package
|
||||||
|
3. Support testing based on jest and display test related coverage, etc.
|
||||||
|
4. Maintain code style based on ts and eslint to ensure better code development
|
||||||
|
5. Generate custom keywords based on conventional-changelog-cli and generate changelog accordingly
|
||||||
|
6. Implement local packaging development and testing based on yalc
|
||||||
|
|||||||
43
examples/application/js/package/README_CN.md
Normal file
43
examples/application/js/package/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Paddle.js Model Module介绍
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该部分是基于 Paddle.js 进行开发的模型库,主要提供 Web 端可直接引入使用模型的能力。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| demo名称 | 源码目录 | npm包 |
|
||||||
|
| ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||||
|
| 人脸检测 | [facedetect](./packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect) | [@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect) |
|
||||||
|
| 螺丝钉检测 | [detect](./packages/paddlejs-models/detect) | [@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect) |
|
||||||
|
| 人像分割背景替换 | [humanseg](./packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg) | [@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg) |
|
||||||
|
| 手势识别AI猜丁壳 | [gesture](./packages/paddlejs-models/gesture) | [@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture) |
|
||||||
|
| 1000种物品识别 | [mobilenet](./packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet) | [@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet) |
|
||||||
|
| 文本检测 | [ocrdetection](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection) | [@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet) |
|
||||||
|
| 文本识别 | [ocr](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocr) | [@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 开发使用
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该部分是使用 `pnpm` 搭建的 Menorepo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 安装依赖
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
pnpm i
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 开发
|
||||||
|
参考 Package.json 使用 `yalc` 进行开发测试。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
pnpm run dev:xxx
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 整体简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 使用 rollup 一次性打包生成 commonjs 和 es 规范的代码;同时具有可扩展性;目前由于依赖的cv库有些问题;就没有配置umd打包。
|
||||||
|
2. 打包时基于 api-extractor 实现 d.ts 文件生成,实现支持 ts 引入生成我们的包
|
||||||
|
3. 基于 jest 支持测试并显示测试相关覆盖率等
|
||||||
|
4. 基于 ts 和 eslint 维护代码风格,保证代码更好开发
|
||||||
|
5. 基于 conventional-changelog-cli 实现自定义关键词生成对应生成changelog
|
||||||
|
6. 基于 yalc 实现本地打包开发测试
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](README.md)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Introduction to Paddle.js Demo Module
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This part is a model library developed based on Paddle.js, which mainly provides the ability to directly introduce and use models on the web side.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| demo name | source directory | npm package |
|
|
||||||
| - | - | - |
|
|
||||||
| face detection | [facedetect](./packages/paddlejs-models/facedetect) | [@paddle-js-models/facedetect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/facedetect) |
|
|
||||||
| Screw detection | [detect](./packages/paddlejs-models/detect) | [@paddle-js-models/detect](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/detect ) |
|
|
||||||
| Portrait segmentation background replacement | [humanseg](./packages/paddlejs-models/humanseg) | [@paddle-js-models/humanseg](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/humanseg) |
|
|
||||||
| Gesture Recognition AI Guessing Shell | [gesture](./packages/paddlejs-models/gesture) | [@paddle-js-models/gesture](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/gesture) |
|
|
||||||
| 1000 Item Recognition | [mobilenet](./packages/paddlejs-models/mobilenet) | [@paddle-js-models/mobilenet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/mobilenet) |
|
|
||||||
| Text Detection | [ocrdetection](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocrdetection) | [@paddle-js-models/ocrdet](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocrdet ) |
|
|
||||||
| Text Recognition | [ocr](./packages/paddlejs-models/ocr) | [@paddle-js-models/ocr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@paddle-js-models/ocr) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Usage
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This part is Menorepo built with `pnpm`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Install dependencies
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````sh
|
|
||||||
pnpm i
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Development
|
|
||||||
See Package.json for development testing with `yalc`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
````sh
|
|
||||||
pnpm run dev:xxx
|
|
||||||
````
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Overall Introduction
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Use rollup to package the code of commonjs and es specifications at one time; at the same time, it is extensible; at present, there are some problems with the dependent cv library; there is no configuration for umd packaging.
|
|
||||||
2. The d.ts file is generated based on api-extractor during packaging, and the introduction of ts is supported to generate our package
|
|
||||||
3. Support testing based on jest and display test related coverage, etc.
|
|
||||||
4. Maintain code style based on ts and eslint to ensure better code development
|
|
||||||
5. Generate custom keywords based on conventional-changelog-cli and generate changelog accordingly
|
|
||||||
6. Implement local packaging development and testing based on yalc
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,78 +1,79 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# Paddle.js-demo
|
# Paddle.js-demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Demo 目录
|
## Demo Directory
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 分类 | 名称 | 目录 |
|
| Classification | Name | Directory |
|
||||||
|:----:| :--------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
|
|:----:| :--------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||||
| CV | 人像扣图 | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
| CV | Portrait matting | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
||||||
| CV | 人像分割背景替换 | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
| CV | Portrait segmentation background replacement | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
||||||
| CV | 手势识别AI猜丁壳 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition |
|
| CV | Gesture recognition AI 'Rock Paper Scissors' | /src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition |
|
||||||
| CV | 1000种物品识别 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification |
|
| CV | Identify 1000 items | /src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification |
|
||||||
| CV | 酒瓶识别 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/WineBottleIdentification |
|
| CV | Wine bottle recognition | /src/pages/cv/recognition/WineBottleIdentification |
|
||||||
| CV | 文本检测 | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection |
|
| CV | Text detection | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection |
|
||||||
| CV | 文本识别 | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition |
|
| CV | Text Recognition | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 开发简介
|
## Introduction to Development
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 安装依赖
|
### Install dependencies
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
```sh
|
||||||
npm install
|
npm install
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 开发
|
### Development
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
```sh
|
||||||
npm run dev
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 查看页面
|
### Page View
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
访问 `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` 进入主页
|
Visit `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` and enter homepage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 构建
|
### Construction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
```sh
|
||||||
npm run build
|
npm run build
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### [ESLint](https://eslint.org/) 格式化
|
### [ESLint](https://eslint.org/) Formatting
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```sh
|
```sh
|
||||||
npm run lint
|
npm run lint
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 工程风格
|
### Project style
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 项目使用TypeScript
|
1. Use TypeScript
|
||||||
2. 推荐使用 Vue 的组合式 API,可以根据 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue' 模板创建新的组件
|
2. Vue's compositional API is recommended. Creating new components according to the 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue' template
|
||||||
3. CSS 使用 Less
|
3. use Less for CSS
|
||||||
4. eslint 使用的是 Vue 推荐的,一般情况请尽量符合对应的要求
|
4. Use what Vue recommends for eslint. Try to meet the requirements.
|
||||||
5. store 使用的是 [Pinia](https://pinia.web3doc.top/)
|
5. Use [Pinia](https://pinia.web3doc.top/) for store
|
||||||
6. router 使用的是 [vue-router](https://router.vuejs.org/zh/)
|
6. Use [vue-router](https://router.vuejs.org/zh/) for router
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### src 目录简介
|
### Brief introduction to src
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
├─assets 资源文件
|
├─assets
|
||||||
├─components 全局组件
|
├─components
|
||||||
├─router 路由
|
├─router
|
||||||
├─stores 存储库
|
├─stores
|
||||||
└─pages
|
└─pages
|
||||||
└─cv cv相关demo
|
└─cv demo of cv
|
||||||
├─ocr ocr相关demo
|
├─ocr demo of ocr
|
||||||
│ ├─TextDetection
|
│ ├─TextDetection
|
||||||
│ └─TextRecognition
|
│ └─TextRecognition
|
||||||
├─...
|
├─...
|
||||||
├─recognition 识别相关demo
|
├─recognition demo of recognition
|
||||||
│ ├─GestureRecognition
|
│ ├─GestureRecognition
|
||||||
│ ├─ItemIdentification
|
│ ├─ItemIdentification
|
||||||
│ ├─...
|
│ ├─...
|
||||||
│ └─WineBottleIdentification
|
│ └─WineBottleIdentification
|
||||||
└─segmentation 分割相关demo
|
└─segmentation demo of segmentation
|
||||||
├─PortraitBackgroundReplacement
|
├─PortraitBackgroundReplacement
|
||||||
├─...
|
├─...
|
||||||
└─PortraitMatting
|
└─PortraitMatting
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
新增组件在对应类别下新增即可,可以参考模板 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue'
|
Add new components under corresponding categories. Refer to 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue' for its template
|
||||||
|
|||||||
79
examples/application/js/web_demo/README_CN.md
Normal file
79
examples/application/js/web_demo/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# Paddle.js-demo
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Demo 目录
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 分类 | 名称 | 目录 |
|
||||||
|
|:----:| :--------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 人像扣图 | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 人像分割背景替换 | /src/pages/cv/segmentation/HumanSeg |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 手势识别AI猜丁壳 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/GestureRecognition |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 1000种物品识别 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/ItemIdentification |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 酒瓶识别 | /src/pages/cv/recognition/WineBottleIdentification |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 文本检测 | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextDetection |
|
||||||
|
| CV | 文本识别 | /src/pages/cv/ocr/TextRecognition |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 开发简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 安装依赖
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
npm install
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 开发
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
npm run dev
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 查看页面
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
访问 `http://localhost:5173/main/index.html` 进入主页
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 构建
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
npm run build
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### [ESLint](https://eslint.org/) 格式化
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```sh
|
||||||
|
npm run lint
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 工程风格
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 项目使用TypeScript
|
||||||
|
2. 推荐使用 Vue 的组合式 API,可以根据 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue' 模板创建新的组件
|
||||||
|
3. CSS 使用 Less
|
||||||
|
4. eslint 使用的是 Vue 推荐的,一般情况请尽量符合对应的要求
|
||||||
|
5. store 使用的是 [Pinia](https://pinia.web3doc.top/)
|
||||||
|
6. router 使用的是 [vue-router](https://router.vuejs.org/zh/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### src 目录简介
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
├─assets 资源文件
|
||||||
|
├─components 全局组件
|
||||||
|
├─router 路由
|
||||||
|
├─stores 存储库
|
||||||
|
└─pages
|
||||||
|
└─cv cv相关demo
|
||||||
|
├─ocr ocr相关demo
|
||||||
|
│ ├─TextDetection
|
||||||
|
│ └─TextRecognition
|
||||||
|
├─...
|
||||||
|
├─recognition 识别相关demo
|
||||||
|
│ ├─GestureRecognition
|
||||||
|
│ ├─ItemIdentification
|
||||||
|
│ ├─...
|
||||||
|
│ └─WineBottleIdentification
|
||||||
|
└─segmentation 分割相关demo
|
||||||
|
├─PortraitBackgroundReplacement
|
||||||
|
├─...
|
||||||
|
└─PortraitMatting
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
新增组件在对应类别下新增即可,可以参考模板 'src/pages/ExampleFile.vue'
|
||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
([简体中文](./README_cn.md)|English)
|
[简体中文](README_CN.md) | English
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# PP-TTS Streaming Text-to-Speech Python Example
|
# PP-TTS Streaming Text-to-Speech Python Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
(简体中文|[English](./README.md))
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# PP-TTS流式语音合成Python示例
|
# PP-TTS流式语音合成Python示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
([简体中文](./README_cn.md)|English)
|
[简体中文](README_CN.md) | English
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# PP-TTS Streaming Text-to-Speech Serving
|
# PP-TTS Streaming Text-to-Speech Serving
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
(简体中文|[English](./README.md))
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# PP-TTS流式语音合成服务化部署
|
# PP-TTS流式语音合成服务化部署
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ This document completes the high-performance deployment of the Diffusion model w
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
This example needs the deployment model after exporting the training model. Here are two ways to obtain the deployment model:
|
This example needs the deployment model after exporting the training model. Here are two ways to obtain the deployment model:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Methods for model export. Please refer to [Model Export](./export_EN.md) to export deployment model.
|
- Methods for model export. Please refer to [Model Export](export.md) to export deployment model.
|
||||||
- Download the deployment model. To facilitate developers to test the example, we have pre-exported some of the `Diffusion` models, so you can just download models and test them quickly:
|
- Download the deployment model. To facilitate developers to test the example, we have pre-exported some of the `Diffusion` models, so you can just download models and test them quickly:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Model | Scheduler |
|
| Model | Scheduler |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
|
|||||||
简体中文 | [English](export_EN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](export_CN.md)
|
||||||
# Diffusion模型导出教程
|
# Diffusion Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本项目支持两种模型导出方式:[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)模型导出以及[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)模型导出。下面分别介绍这两种模型导出方式。
|
The project supports two methods of model export, [PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) model export and [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) model export. Here we introduce each of these two methods.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## PPDiffusers 模型导出
|
## PPDiffusers Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)是一款支持跨模态(如图像与语音)训练和推理的扩散模型(Diffusion Model)工具箱,其借鉴了🤗 Huggingface团队的[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)的优秀设计,并且依托[PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle)框架和[PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP)自然语言处理库。下面介绍如何使用FastDeploy将PPDiffusers提供的Diffusion模型进行高性能部署。
|
[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit that supports cross-modal (e.g., image and speech) training and inference. It builds on the design of [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by the 🤗 Huggingface team, and relies on [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle) framework and the [PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP) natural language processing library. The following describes how to use FastDeploy to deploy the Diffusion model provided by PPDiffusers for high performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 依赖安装
|
### Dependency Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
模型导出需要依赖`paddlepaddle`, `paddlenlp`以及`ppdiffusers`,可使用`pip`执行下面的命令进行快速安装。
|
The model export depends on `paddlepaddle`, `paddlenlp` and `ppdiffusers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
pip install -r requirements_paddle.txt
|
pip install -r requirements_paddle.txt
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 模型导出
|
### Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___注意:模型导出过程中,需要下载StableDiffusion模型。为了使用该模型与权重,你必须接受该模型所要求的License,请访问HuggingFace的[model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), 仔细阅读里面的License,然后签署该协议。___
|
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Tips: Stable Diffusion是基于以下的License: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
可执行以下命令行完成模型导出。
|
You can run the following lines to export model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
python export_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
python export_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
输出的模型目录结构如下:
|
The output model directory is as follows:
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
||||||
├── text_encoder
|
├── text_encoder
|
||||||
@@ -44,47 +44,47 @@ stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
|||||||
└── inference.pdmodel
|
└── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 参数说明
|
#### Parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`export_model.py` 各命令行参数的说明。
|
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_model.py`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
| Parameter |Description |
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | ppdiffuers提供的diffusion预训练模型。默认为:"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 "。更多diffusion预训练模型可参考[ppdiffuser模型列表](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion)。|
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers. Default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [ppdiffuser model list](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion).|
|
||||||
|--output_path | 导出的模型目录。 |
|
|--output_path | Exported directory |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Diffusers 模型导出
|
## Diffusers Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)是一款由HuggingFace打造的支持跨模态(如图像与语音)训练和推理的扩散模型(Diffusion Model)工具箱。其底层的模型代码提供PyTorch实现的版本以及Flax实现的版本两种版本。本示例将介绍如何使用FastDeploy将PyTorch实现的Diffusion模型进行高性能部署。
|
[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit built by HuggingFace to support cross-modal (e.g. image and speech) training and inference. The underlying model code is available in both a PyTorch implementation and a Flax implementation. This example shows how to use FastDeploy to deploy a PyTorch implementation of Diffusion Model for high performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 依赖安装
|
### Dependency Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
模型导出需要依赖`onnx`, `torch`, `diffusers`以及`transformers`,可使用`pip`执行下面的命令进行快速安装。
|
The model export depends on `onnx`, `torch`, `diffusers` and `transformers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
|
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 模型导出
|
### Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___注意:模型导出过程中,需要下载StableDiffusion模型。为了使用该模型与权重,你必须接受该模型所要求的License,并且获取HF Hub授予的Token。请访问HuggingFace的[model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), 仔细阅读里面的License,然后签署该协议。___
|
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required, and get the Token granted by HF Hub. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Tips: Stable Diffusion是基于以下的License: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
若第一次导出模型,需要先登录HuggingFace客户端。执行以下命令进行登录:
|
If you are exporting a model for the first time, you need to log in to the HuggingFace client first. Run the following command to log in:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
huggingface-cli login
|
huggingface-cli login
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
完成登录后,执行以下命令行完成模型导出。
|
After finishing the login, you can run the following lines to export model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
python export_torch_to_onnx_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path torch_diffusion_model
|
python export_torch_to_onnx_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path torch_diffusion_model
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
输出的模型目录结构如下:
|
The output model directory is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
torch_diffusion_model/
|
torch_diffusion_model/
|
||||||
@@ -96,11 +96,11 @@ torch_diffusion_model/
|
|||||||
└── inference.onnx
|
└── inference.onnx
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 参数说明
|
#### Parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`export_torch_to_onnx_model.py` 各命令行参数的说明。
|
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_torch_to_onnx_model.py`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
| Parameter |Description |
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | ppdiffuers提供的diffusion预训练模型。默认为:"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 "。更多diffusion预训练模型可参考[HuggingFace模型列表说明](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)。|
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> |The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers, default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [HuggingFace model list](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4).|
|
||||||
|--output_path | 导出的模型目录。 |
|
|--output_path |Exported directory |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
106
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/export_CN.md
Normal file
106
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/export_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文|[English](export.md)
|
||||||
|
# Diffusion模型导出教程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本项目支持两种模型导出方式:[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)模型导出以及[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)模型导出。下面分别介绍这两种模型导出方式。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PPDiffusers 模型导出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)是一款支持跨模态(如图像与语音)训练和推理的扩散模型(Diffusion Model)工具箱,其借鉴了🤗 Huggingface团队的[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)的优秀设计,并且依托[PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle)框架和[PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP)自然语言处理库。下面介绍如何使用FastDeploy将PPDiffusers提供的Diffusion模型进行高性能部署。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 依赖安装
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
模型导出需要依赖`paddlepaddle`, `paddlenlp`以及`ppdiffusers`,可使用`pip`执行下面的命令进行快速安装。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install -r requirements_paddle.txt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 模型导出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___注意:模型导出过程中,需要下载StableDiffusion模型。为了使用该模型与权重,你必须接受该模型所要求的License,请访问HuggingFace的[model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), 仔细阅读里面的License,然后签署该协议。___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion是基于以下的License: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
可执行以下命令行完成模型导出。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
python export_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
输出的模型目录结构如下:
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
||||||
|
├── text_encoder
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
├── unet
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
└── vae_decoder
|
||||||
|
├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
└── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 参数说明
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`export_model.py` 各命令行参数的说明。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | ppdiffuers提供的diffusion预训练模型。默认为:"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 "。更多diffusion预训练模型可参考[ppdiffuser模型列表](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion)。|
|
||||||
|
|--output_path | 导出的模型目录。 |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Diffusers 模型导出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)是一款由HuggingFace打造的支持跨模态(如图像与语音)训练和推理的扩散模型(Diffusion Model)工具箱。其底层的模型代码提供PyTorch实现的版本以及Flax实现的版本两种版本。本示例将介绍如何使用FastDeploy将PyTorch实现的Diffusion模型进行高性能部署。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 依赖安装
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
模型导出需要依赖`onnx`, `torch`, `diffusers`以及`transformers`,可使用`pip`执行下面的命令进行快速安装。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 模型导出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___注意:模型导出过程中,需要下载StableDiffusion模型。为了使用该模型与权重,你必须接受该模型所要求的License,并且获取HF Hub授予的Token。请访问HuggingFace的[model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), 仔细阅读里面的License,然后签署该协议。___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion是基于以下的License: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
若第一次导出模型,需要先登录HuggingFace客户端。执行以下命令进行登录:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
huggingface-cli login
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
完成登录后,执行以下命令行完成模型导出。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
python export_torch_to_onnx_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path torch_diffusion_model
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
输出的模型目录结构如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
torch_diffusion_model/
|
||||||
|
├── text_encoder
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
├── unet
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
└── vae_decoder
|
||||||
|
└── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 参数说明
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`export_torch_to_onnx_model.py` 各命令行参数的说明。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | ppdiffuers提供的diffusion预训练模型。默认为:"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 "。更多diffusion预训练模型可参考[HuggingFace模型列表说明](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)。|
|
||||||
|
|--output_path | 导出的模型目录。 |
|
||||||
@@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](export.md)
|
|
||||||
# Diffusion Model Export
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The project supports two methods of model export, [PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) model export and [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) model export. Here we introduce each of these two methods.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## PPDiffusers Model Export
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit that supports cross-modal (e.g., image and speech) training and inference. It builds on the design of [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by the 🤗 Huggingface team, and relies on [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle) framework and the [PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP) natural language processing library. The following describes how to use FastDeploy to deploy the Diffusion model provided by PPDiffusers for high performance.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Dependency Installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The model export depends on `paddlepaddle`, `paddlenlp` and `ppdiffusers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
pip install -r requirements_paddle.txt
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Model Export
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can run the following lines to export model.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
python export_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The output model directory is as follows:
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
|
||||||
├── text_encoder
|
|
||||||
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
|
||||||
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
|
||||||
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
|
||||||
├── unet
|
|
||||||
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
|
||||||
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
|
||||||
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
|
||||||
└── vae_decoder
|
|
||||||
├── inference.pdiparams
|
|
||||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
|
||||||
└── inference.pdmodel
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Parameters
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_model.py`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Parameter |Description |
|
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|
||||||
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers. Default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [ppdiffuser model list](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion).|
|
|
||||||
|--output_path | Exported directory |
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Diffusers Model Export
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit built by HuggingFace to support cross-modal (e.g. image and speech) training and inference. The underlying model code is available in both a PyTorch implementation and a Flax implementation. This example shows how to use FastDeploy to deploy a PyTorch implementation of Diffusion Model for high performance.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Dependency Installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The model export depends on `onnx`, `torch`, `diffusers` and `transformers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Model Export
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required, and get the Token granted by HF Hub. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you are exporting a model for the first time, you need to log in to the HuggingFace client first. Run the following command to log in:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
huggingface-cli login
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After finishing the login, you can run the following lines to export model.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
python export_torch_to_onnx_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path torch_diffusion_model
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The output model directory is as follows:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
torch_diffusion_model/
|
|
||||||
├── text_encoder
|
|
||||||
│ └── inference.onnx
|
|
||||||
├── unet
|
|
||||||
│ └── inference.onnx
|
|
||||||
└── vae_decoder
|
|
||||||
└── inference.onnx
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Parameters
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_torch_to_onnx_model.py`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Parameter |Description |
|
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|
||||||
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> |The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers, default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [HuggingFace model list](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4).|
|
|
||||||
|--output_path |Exported directory |
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# C++推理
|
# C++ Inference
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||||||
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# Python推理
|
# Python Inference
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# RKYOLO C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# RKYOLO C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer_xxxxx.cc`快速完成RKYOLO模型在Rockchip板子上上通过二代NPU加速部署的示例。
|
This directory provides examples that `infer_xxxxx.cc` fast finishes the deployment of RKYOLO models on Rockchip board through 2-nd generation NPU
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Two steps before deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Download the precompiled deployment library or deploy FastDeploy repository from scratch according to your development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
Refer to [RK2 generation NPU deployment repository compilation](../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate the base directory file
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
The routine consists of the following parts
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # Folder to save images
|
||||||
├── infer_rkyolo.cc
|
├── infer_rkyolo.cc
|
||||||
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
├── model # Folder to save model files
|
||||||
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
└── thirdpartys # Folder to save sdk
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
Generate a directory first
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
mkdir images
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
@@ -30,24 +31,23 @@ mkdir model
|
|||||||
mkdir thirdpartys
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and copy SDK to the thirdpartys folder
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成
|
Refer to [RK2 generation NPU deployment repository compilation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md). It will generate fastdeploy-0.0.3 directory in the build directory after compilation. Move it to the thirdpartys directory.
|
||||||
fastdeploy-0.0.3目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy model files and configuration files to the model folder
|
||||||
在Paddle动态图模型 -> Paddle静态图模型 -> ONNX模型的过程中,将生成ONNX文件以及对应的yaml配置文件,请将配置文件存放到model文件夹内。
|
In the process of Paddle dynamic graph model -> Paddle static graph model -> ONNX model, the ONNX file and the corresponding yaml configuration file will be generated. Please save the configuration file in the model folder.
|
||||||
转换为RKNN后的模型文件也需要拷贝至model。
|
Copy onverted RKNN model files to model。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare test images and image folder
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compilation example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ make -j8
|
|||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running routine
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd ./build/install
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
@@ -64,6 +64,6 @@ cd ./build/install
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
- [Model Description](../../)
|
||||||
- [Python部署](../python)
|
- [Python Deployment](../python)
|
||||||
- [视觉模型预测结果](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
- [Vision Model Prediction Results](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
70
examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
70
examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# RKYOLO C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer_xxxxx.cc`快速完成RKYOLO模型在Rockchip板子上上通过二代NPU加速部署的示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer_rkyolo.cc
|
||||||
|
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
|
mkdir model
|
||||||
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy-0.0.3目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
在Paddle动态图模型 -> Paddle静态图模型 -> ONNX模型的过程中,将生成ONNX文件以及对应的yaml配置文件,请将配置文件存放到model文件夹内。
|
||||||
|
转换为RKNN后的模型文件也需要拷贝至model。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
|
./infer_picodet model/ images/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](../python)
|
||||||
|
- [视觉模型预测结果](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
@@ -1,34 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
# RKYOLO Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# RKYOLO Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Two steps before deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
- 1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成Picodet在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.py` fast finishes the deployment of Picodet on RKNPU. The script is as follows
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the example code for deployment
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# copy model
|
# copy model
|
||||||
cp -r ./model /path/to/FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
cp -r ./model /path/to/FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./model/ \
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./model/ \
|
||||||
--image 000000014439.jpg
|
--image 000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 注意事项
|
## Note
|
||||||
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,
|
The model needs to be in NHWC format on RKNPU. The normalized image will be embedded in the RKNN model. Therefore, when we deploy with FastDeploy, call DisablePermute(C++) or `disable_permute(Python)` to disable normalization and data format conversion during preprocessing.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [PaddleDetection 模型介绍](..)
|
- [PaddleDetection Model Description](..)
|
||||||
- [PaddleDetection C++部署](../cpp)
|
- [PaddleDetection C++ Deployment](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
- [model prediction Results](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
- [转换PaddleDetection RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Convert PaddleDetection RKNN Model Files](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
35
examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
35
examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# RKYOLO Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成Picodet在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# copy model
|
||||||
|
cp -r ./model /path/to/FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/rkyolo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./model/ \
|
||||||
|
--image 000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 注意事项
|
||||||
|
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,需要先调用DisablePermute(C++) `disable_permute(Python)`,在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [PaddleDetection 模型介绍](..)
|
||||||
|
- [PaddleDetection C++部署](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
|
- [转换PaddleDetection RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,45 +1,46 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv5 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 Quantification Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 YOLOv5 量化模型在 RV1126 上的部署推理加速。
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.cc` fast finishes the deployment of YOLOv5 on RV1126.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Prepare the deployment
|
||||||
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
### Prepare FastDeploy cross-compilation environment
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
1. For the environment of software, hardware and cross-compilation, refer to [FastDeploy cross-compilation environment preparation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Prepare the quantification model
|
||||||
可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署,也可以按照如下步骤准备量化模型:
|
Users can directly deploy quantized models provided by FastDeploy or prepare quantification models as the following steps:
|
||||||
1. 按照 [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.1) 官方导出方式导出 ONNX 模型,或者直接使用如下命令下载
|
1. Refer to [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.1) to officially convert the ONNX model or use the following command to download it.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://paddle-slim-models.bj.bcebos.com/act/yolov5s.onnx
|
wget https://paddle-slim-models.bj.bcebos.com/act/yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
2. 准备 300 张左右量化用的图片,也可以使用如下命令下载我们准备好的数据。
|
2. Prepare 300 or so images for quantization.And we can also download the prepared data using the following command:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
||||||
tar -xf COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
tar -xf COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
3. 使用 FastDeploy 提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署。
|
3. Users can use the [ One-click auto-compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to automatically conduct quantification model for deployment.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
fastdeploy compress --config_path=./configs/detection/yolov5s_quant.yaml --method='PTQ' --save_dir='./yolov5s_ptq_model_new/'
|
fastdeploy compress --config_path=./configs/detection/yolov5s_quant.yaml --method='PTQ' --save_dir='./yolov5s_ptq_model_new/'
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
4. YOLOv5 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了 YOLOv5 模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
4. The YOLOv5 model requires heterogeneous computing. Refer to [Heterogeneous Computing](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md). Since FastDeploy already provides the YOLOv5 model, we can first test the heterogeneous files to verify whether the accuracy meets the requirements.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 先下载我们提供的模型,解压后将其中的 subgraph.txt 文件拷贝到新量化的模型目录中
|
# Download the model, unzip it, and copy the subgraph.txt file to your newly quantized model directory
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
tar -xvf yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
tar -xvf yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
Refer to [model quantification](../../quantize/README.md) for more information
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 在 RV1126 上部署量化后的 YOLOv5 检测模型
|
## Deploy quantized YOLOv5 detection model on RV1126
|
||||||
请按照以下步骤完成在 RV1126 上部署 YOLOv5 量化模型:
|
Refer to the following steps:
|
||||||
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
1. For cross compiling FastDeploy repo, refer to [cross compiling FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
2. Copy the compiled repo to your current directory through the following command:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
3. Download models and images for deployment in the current location:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
@@ -50,26 +51,26 @@ wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/0000000
|
|||||||
cp -r 000000014439.jpg images
|
cp -r 000000014439.jpg images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
4. Compile the deployment example through the following command:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
mkdir build && cd build
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
||||||
make -j8
|
make -j8
|
||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
# Successful compilation generates the install folder, containing a running demo and repo required for deployment
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 YOLOv5 检测模型到 Rockchip RV1126,可使用如下命令:
|
5. Deploy YOLOv5 detection model to Rockchip RV1126 based on adb. Refer to the following command:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 进入 install 目录
|
# Enter the install directory
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
# The following commands represent: bash run_with_adb.sh running demo model path image path DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo yolov5s_ptq_model 000000014439.jpg $DEVICE_ID
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo yolov5s_ptq_model 000000014439.jpg $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
部署成功后,vis_result.jpg 保存的结果如下:
|
vis_result.jpg after successful deployment:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/203706969-dd58493c-6635-4ee7-9421-41c2e0c9524b.png">
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/203706969-dd58493c-6635-4ee7-9421-41c2e0c9524b.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
需要特别注意的是,在 RV1126 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
Note that the deployment model on RV1126 is the quantized model. Refer to [Model Quantification](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
76
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
76
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 YOLOv5 量化模型在 RV1126 上的部署推理加速。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署,也可以按照如下步骤准备量化模型:
|
||||||
|
1. 按照 [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.1) 官方导出方式导出 ONNX 模型,或者直接使用如下命令下载
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddle-slim-models.bj.bcebos.com/act/yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
2. 准备 300 张左右量化用的图片,也可以使用如下命令下载我们准备好的数据。
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar -xf COCO_val_320.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
3. 使用 FastDeploy 提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署。
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy compress --config_path=./configs/detection/yolov5s_quant.yaml --method='PTQ' --save_dir='./yolov5s_ptq_model_new/'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
4. YOLOv5 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了 YOLOv5 模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 先下载我们提供的模型,解压后将其中的 subgraph.txt 文件拷贝到新量化的模型目录中
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 在 RV1126 上部署量化后的 YOLOv5 检测模型
|
||||||
|
请按照以下步骤完成在 RV1126 上部署 YOLOv5 量化模型:
|
||||||
|
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov5s_ptq_model.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
cp -r yolov5s_ptq_model models
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
cp -r 000000014439.jpg images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 YOLOv5 检测模型到 Rockchip RV1126,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 进入 install 目录
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
|
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo yolov5s_ptq_model 000000014439.jpg $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
部署成功后,vis_result.jpg 保存的结果如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/203706969-dd58493c-6635-4ee7-9421-41c2e0c9524b.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
需要特别注意的是,在 RV1126 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,37 +1,38 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv6量化模型 C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6 Quantification Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv6s量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.cc` fast finishes the deployment of YOLOv6 quantification models on CPU/GPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Prepare the deployment
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparation
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Install FastDeploy Python whl package. Refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Prepare the quantification model
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. Users can directly deploy quantized models provided by FastDeploy.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 2. ii. Or users can use the [One-click auto-compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to automatically conduct quantification model for deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的YOLOv6s模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Example: quantized YOLOv6 model
|
||||||
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
The compilation and deployment can be completed by executing the following command in this directory. FastDeploy version 0.7.0 or above (x.x.x>=0.7.0) is required to support this model.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
# Download the FastDeploy precompiled library. Users can choose your appropriate version in the `FastDeploy Precompiled Library` mentioned above
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
make -j
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov6s量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download yolov6 quantification model files and test images provided by FastDeploy
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
# Use ONNX Runtime quantification model on CPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 0
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 0
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 1
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 1
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 2
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 2
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
38
examples/vision/detection/yolov6/quantize/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
38
examples/vision/detection/yolov6/quantize/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6量化模型 C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv6s量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的YOLOv6s模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov6s量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 0
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 1
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov6s_qat_model 000000014439.jpg 2
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,30 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv6量化模型 Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv6量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
# YOLOv6 Quantification Model Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.py` fast finishes the deployment of YOLOv6 quantification models on CPU/GPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Prepare the deployment
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparation
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Install FastDeploy Python whl package. Refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Prepare the quantification model
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. Users can directly deploy quantized models provided by FastDeploy.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 2. ii. Or users can use the [One-click auto-compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to automatically conduct quantification model for deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的YOLOv6s模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Example: quantized YOLOv6 model
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
#下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the example code for deployment
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd examples/slim/yolov6/python
|
cd examples/slim/yolov6/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov6s量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download yolov6 quantification model files and test images provided by FastDeploy
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
# Use ONNX Runtime quantification model on CPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6量化模型 Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv6量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的YOLOv6s模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
#下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd examples/slim/yolov6/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov6s量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov6s_qat_model_new.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov6s_qat_model.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov6s_qat_model --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,37 +1,38 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv7量化模型 C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv7 Quantification Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv7量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.cc` fast finishes the deployment of YOLOv7 quantification models on CPU/GPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Prepare the deployment
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparation
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Install FastDeploy Python whl package. Refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Prepare the quantification model
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. Users can directly deploy quantized models provided by FastDeploy.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 2. Or users can use the [One-click auto-compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to automatically conduct quantification model for deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的YOLOv7模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Example: quantized YOLOv7 model
|
||||||
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
The compilation and deployment can be completed by executing the following command in this directory. FastDeploy version 0.7.0 or above (x.x.x>=0.7.0) is required to support this model.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
# Download the FastDeploy precompiled library. Users can choose your appropriate version in the `FastDeploy Precompiled Library` mentioned above
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
make -j
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov7量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download yolov7 quantification model files and test images provided by FastDeploy
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
# Use ONNX Runtime quantification model on CPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 0
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 0
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 1
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 1
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 2
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 2
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
38
examples/vision/detection/yolov7/quantize/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
38
examples/vision/detection/yolov7/quantize/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv7量化模型 C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv7量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的YOLOv7模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov7量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 0
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 1
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo yolov7_quant 000000014439.jpg 2
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,30 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv7量化模型 Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv7量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
# YOLOv7 Quantification Model Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.py` fast finishes the deployment of YOLOv7 quantification models on CPU/GPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Prepare the deployment
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparation
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. i. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. ii. Install FastDeploy Python whl package. Refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Prepare the quantification model
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. Users can directly deploy quantized models provided by FastDeploy.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 2. Or users can use the [ One-click auto-compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to automatically conduct quantification model for deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的YOLOv7模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Example: quantized YOLOv7 model
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
#下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the example code for deployment
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd examples/vision/detection/yolov7/quantize/python
|
cd examples/vision/detection/yolov7/quantize/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov7量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download yolov7 quantification model files and test images provided by FastDeploy
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
# Use ONNX Runtime quantification model on CPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
||||||
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-TensorRT quantification model on GPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv7量化模型 Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成YOLOv7量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的YOLOv7模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
#下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd examples/vision/detection/yolov7/quantize/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#下载FastDeloy提供的yolov7量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf yolov7_quant.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用ONNX Runtime推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device cpu --backend ort
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend trt
|
||||||
|
# 在GPU上使用Paddle-TensorRT推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model yolov7_quant --image 000000014439.jpg --device gpu --backend pptrt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# SCRFD C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# SCRFD C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成SCRFD在NPU加速部署的示例。
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.cc` fast finishes the deployment of SCRFD on NPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Two steps before deployment:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. The environment of software and hardware should meet the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Download the precompiled deployment repo or deploy the FastDeploy repository from scratch according to your development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
Refer to [RK2 generation NPU deployment repository compilation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md) for the steps above
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate the base directory file
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
It consists of the following parts
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # The folder to save images
|
||||||
├── infer.cc
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
├── model # The folder to save model files
|
||||||
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
└── thirdpartys # The folder to save sdk
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
Generate the directory first
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
mkdir images
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
@@ -30,23 +31,22 @@ mkdir model
|
|||||||
mkdir thirdpartys
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and copy the SDK into the thirdpartys folder
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成
|
Refer to [RK2 generation NPU deployment repository compilation](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md). It will enerate fastdeploy-0.7.0 directory in the build directory after compilation. Move it to the thirdpartys directory.
|
||||||
fastdeploy-0.7.0目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy the model files to the model folder
|
||||||
请参考[SCRFD模型转换文档](../README.md)转换SCRFD ONNX模型到RKNN模型,再将RKNN模型移动到model文件夹。
|
Refer to [SCRFD model conversion](../README.md) to convert SCRFD ONNX model to RKNN model and move it to the model folder.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare test images to the image folder
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
cp test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg ./images
|
cp test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg ./images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compile example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -54,17 +54,17 @@ cmake ..
|
|||||||
make -j8
|
make -j8
|
||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running routines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd ./build/install
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PWD}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
|
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PWD}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
|
||||||
./rknpu_test
|
./rknpu_test
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
运行完成可视化结果如下图所示
|
The visualized result after running is as follows
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../README.md)
|
- [Model Description](../../README.md)
|
||||||
- [Python部署](../python/README.md)
|
- [Python Deployment](../python/README.md)
|
||||||
- [视觉模型预测结果](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
- [Vision Model Prediction Results](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
71
examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
71
examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# SCRFD C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成SCRFD在NPU加速部署的示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
|
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
|
mkdir model
|
||||||
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成
|
||||||
|
fastdeploy-0.7.0目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
请参考[SCRFD模型转换文档](../README.md)转换SCRFD ONNX模型到RKNN模型,再将RKNN模型移动到model文件夹。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
|
cp test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg ./images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
|
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PWD}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
|
||||||
|
./rknpu_test
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
运行完成可视化结果如下图所示
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../README.md)
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](../python/README.md)
|
||||||
|
- [视觉模型预测结果](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,44 +1,45 @@
|
|||||||
# SCRFD Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# SCRFD Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Two steps before deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
- 1. Software and hardware should meet the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成SCRFD在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
This directory provides examples that `infer.py` fast finishes the deployment of SCRFD on RKNPU. The script is as follows
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 拷贝模型文件
|
## Copy model files
|
||||||
请参考[SCRFD模型转换文档](../README.md)转换SCRFD ONNX模型到RKNN模型,再将RKNN模型移动到该目录下。
|
Refer to [SCRFD model conversion](../README.md) to convert SCRFD ONNX model to RKNN model and move it to this directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行example
|
## Run example
|
||||||
拷贝模型文件后,请输入以下命令,运行RKNPU2 Python example
|
After copying model files, enter the following command to run it: RKNPU2 Python example
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the example code for deployment
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images
|
||||||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./scrfd_500m_bnkps_shape640x640_rk3588.rknn \
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./scrfd_500m_bnkps_shape640x640_rk3588.rknn \
|
||||||
--image test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
--image test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 可视化
|
## Visualization
|
||||||
运行完成可视化结果如下图所示
|
The visualized result after running is as follows
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 注意事项
|
## Note
|
||||||
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,
|
The model needs to be in NHWC format on RKNPU. The normalized image will be embedded in the RKNN model. Therefore, when we deploy with FastDeploy,
|
||||||
需要先调用DisablePermute(C++)或`disable_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
call DisablePermute(C++) or `disable_permute(Python) to disable normalization and data format conversion during preprocessing.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [SCRFD 模型介绍](../README.md)
|
- [SCRFD Model Description](../README.md)
|
||||||
- [SCRFD C++部署](../cpp/README.md)
|
- [SCRFD C++ Deployment](../cpp/README.md)
|
||||||
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
- [Model Prediction Results](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
||||||
- [转换SCRFD RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Convert SCRFD RKNN Model Files](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
45
examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
45
examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# SCRFD Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成SCRFD在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 拷贝模型文件
|
||||||
|
请参考[SCRFD模型转换文档](../README.md)转换SCRFD ONNX模型到RKNN模型,再将RKNN模型移动到该目录下。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行example
|
||||||
|
拷贝模型文件后,请输入以下命令,运行RKNPU2 Python example
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit/main/examples/lite/resources/test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./scrfd_500m_bnkps_shape640x640_rk3588.rknn \
|
||||||
|
--image test_lite_face_detector_3.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 可视化
|
||||||
|
运行完成可视化结果如下图所示
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/67993288/184301789-1981d065-208f-4a6b-857c-9a0f9a63e0b1.jpg">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 注意事项
|
||||||
|
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,
|
||||||
|
需要先调用DisablePermute(C++)或`disable_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [SCRFD 模型介绍](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
- [SCRFD C++部署](../cpp/README.md)
|
||||||
|
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/README.md)
|
||||||
|
- [转换SCRFD RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -33,13 +33,13 @@ docker pull registry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/fastdeploy:1.0.2-gpu-cuda11.4-trt
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Users can also compile the image by themselves according to their own needs, referring to the following documents:
|
Users can also compile the image by themselves according to their own needs, referring to the following documents:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [FastDeploy Serving Deployment Image Compilation](docs/zh_CN/compile.md)
|
- [FastDeploy Serving Deployment Image Compilation](docs/EN/compile-en.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Other Tutorials
|
## Other Tutorials
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [How to Prepare Serving Model Repository](docs/zh_CN/model_repository.md)
|
- [How to Prepare Serving Model Repository](docs/EN/model_repository-en.md)
|
||||||
- [Serving Deployment Configuration for Runtime](docs/zh_CN/model_configuration.md)
|
- [Serving Deployment Configuration for Runtime](docs/EN/model_configuration-en.md)
|
||||||
- [Demo of Serving Deployment](docs/zh_CN/demo.md)
|
- [Demo of Serving Deployment](docs/EN/demo-en.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Serving Deployment Demo
|
### Serving Deployment Demo
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user