mirror of
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
synced 2025-10-04 16:22:57 +08:00
[Doc]Add English version of documents in examples/ (#1042)
* 第一次提交 * 补充一处漏翻译 * deleted: docs/en/quantize.md * Update one translation * Update en version * Update one translation in code * Standardize one writing * Standardize one writing * Update some en version * Fix a grammer problem * Update en version for api/vision result * Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/charl-u/FastDeploy into develop * Checkout the link in README in vision_results/ to the en documents * Modify a title * Add link to serving/docs/ * Finish translation of demo.md * Update english version of serving/docs/ * Update title of readme * Update some links * Modify a title * Update some links * Update en version of java android README * Modify some titles * Modify some titles * Modify some titles * modify article to document * update some english version of documents in examples * Add english version of documents in examples/visions * Sync to current branch * Add english version of documents in examples
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](../../en/build_and_install/sophgo.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
# SOPHGO 部署库编译
|
# SOPHGO 部署库编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## SOPHGO 环境准备
|
## SOPHGO 环境准备
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [中文](../../cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
# How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment
|
# How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## SOPHGO Environment Preparation
|
## SOPHGO Environment Preparation
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ Please check out the FastDeploy C++ deployment library is already in your enviro
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
This document shows an inference sample on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
This document shows an inference sample on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 1. Obtaining the Module
|
## 1. Obtaining the Model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ Please check out the FastDeploy is already installed in your environment. You ca
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
This document shows an inference sample on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
This document shows an inference sample on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 1. Obtaining the Module
|
## 1. Obtaining the model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``` python
|
``` python
|
||||||
import fastdeploy as fd
|
import fastdeploy as fd
|
||||||
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ results = runtime.infer({
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
print(results[0].shape)
|
print(results[0].shape)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
When loading is complete, you can get the following output information indicating the initialized backend and the hardware devices.
|
When loading is complete, you will get the following output information indicating the initialized backend and the hardware devices.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# PaddleJsConverter
|
# PaddleJsConverter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Installation
|
## Installation
|
||||||
@@ -26,4 +27,4 @@ pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
|||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=user_model_path --paramPath=user_model_params_path --outputDir=model_saved_path --useGPUOpt=True
|
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=user_model_path --paramPath=user_model_params_path --outputDir=model_saved_path --useGPUOpt=True
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
注意:useGPUOpt 选项默认不开启,如果模型用在 gpu backend(webgl/webgpu),则开启 useGPUOpt,如果模型运行在(wasm/plain js)则不要开启。
|
Note: The option useGPUOpt is not turned on by default. Turn on useGPUOpt if the model is used on gpu backend (webgl/webgpu), don't turn on if is running on (wasm/plain js).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
30
examples/application/js/converter/README_CN.md
Normal file
30
examples/application/js/converter/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleJsConverter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System Requirements:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* paddlepaddle >= 2.0.0
|
||||||
|
* paddlejslite >= 0.0.2
|
||||||
|
* Python3: 3.5.1+ / 3.6 / 3.7
|
||||||
|
* Python2: 2.7.15+
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install PaddleJsConverter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/paddlejsconverter" alt="version">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# or
|
||||||
|
pip3 install paddlejsconverter
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
paddlejsconverter --modelPath=user_model_path --paramPath=user_model_params_path --outputDir=model_saved_path --useGPUOpt=True
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
注意:useGPUOpt 选项默认不开启,如果模型用在 gpu backend(webgl/webgpu),则开启 useGPUOpt,如果模型运行在(wasm/plain js)则不要开启。
|
||||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](RNN_EN.md)
|
||||||
# RNN算子计算过程
|
# RNN算子计算过程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 一、RNN理解
|
## 一、RNN理解
|
||||||
@@ -73,7 +74,7 @@ paddle源码实现:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
||||||
详见算子实现:[rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts)
|
详见算子实现:[rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts)
|
||||||
)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4)rnn_hidden
|
4)rnn_hidden
|
||||||
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
计算方式:将rnn_matmul op输出结果分割成4份,每份执行不同激活函数计算,最后输出lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]。x∈[0, 3],y∈[0, 24]。
|
||||||
|
|||||||
80
examples/application/js/converter/RNN_EN.md
Normal file
80
examples/application/js/converter/RNN_EN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](RNN.md)
|
||||||
|
# The computation process of RNN operator
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 1. Understanding of RNN
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**RNN** is a recurrent neural network, including an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, which is specialized in processing sequential data.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
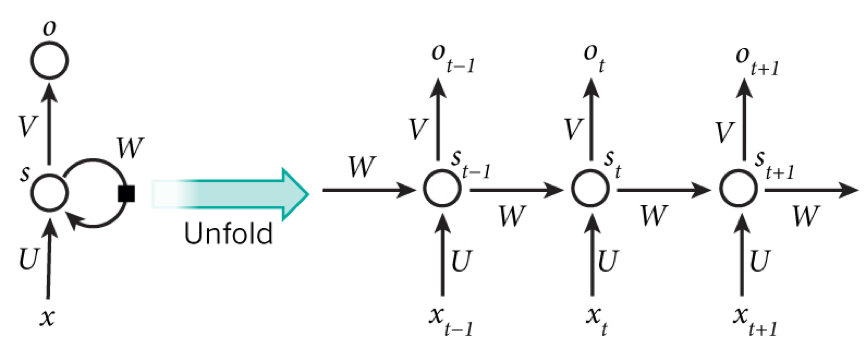
|
||||||
|
paddle official document: https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/RNN_cn.html#rnn
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
paddle source code implementation: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/fluid/operators/rnn_op.h#L812
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 2. How to compute RNN
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
At moment t, the input layer is , hidden layer is , output layer is . As the picture above, isn't just decided by ,it is also related to . The formula is as follows.:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
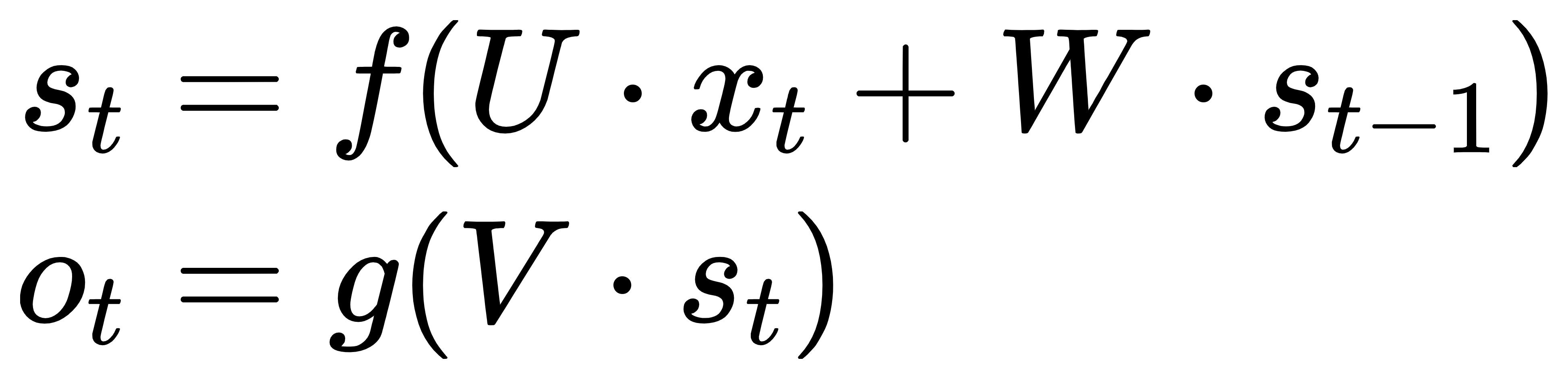
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 3. RNN operator implementation in pdjs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Because the gradient disappearance problem exists in RNN, and more contextual information cannot be obtained, **LSTM (Long Short Term Memory)** is used in CRNN, which is a special kind of RNN that can preserve long-term dependencies.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Based on the image sequence, the two directions of context are mutually useful and complementary. Since the LSTM is unidirectional, two LSTMs, one forward and one backward, are combined into a **bidirectional LSTM**. In addition, multiple layers of bidirectional LSTMs can be stacked. ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer recognition model is using a two-layer bidirectional LSTM structure. The calculation process is shown as follows.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Take ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer model, rnn operator as an example
|
||||||
|
```javascript
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
Attr: {
|
||||||
|
mode: 'LSTM'
|
||||||
|
// Whether bidirectional, if true, it is necessary to traverse both forward and reverse.
|
||||||
|
is_bidirec: true
|
||||||
|
// Number of hidden layers, representing the number of loops.
|
||||||
|
num_layers: 2
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: [
|
||||||
|
transpose_1.tmp_0[25, 1, 288]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PreState: [
|
||||||
|
fill_constant_batch_size_like_0.tmp_0[4, 1, 48],
|
||||||
|
fill_constant_batch_size_like_1.tmp_0[4, 1, 48]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
WeightList: [
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_0.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_0.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_1.w_0[192, 288], lstm_cell_1.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_2.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_2.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_3.w_0[192, 96], lstm_cell_3.w_1[192, 48],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_0.b_0[192], lstm_cell_0.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_1.b_0[192], lstm_cell_1.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_2.b_0[192], lstm_cell_2.b_1[192],
|
||||||
|
lstm_cell_3.b_0[192], lstm_cell_3.b_1[192]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Output: [
|
||||||
|
lstm_0.tmp_0[25, 1, 96]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Overall computation process
|
||||||
|
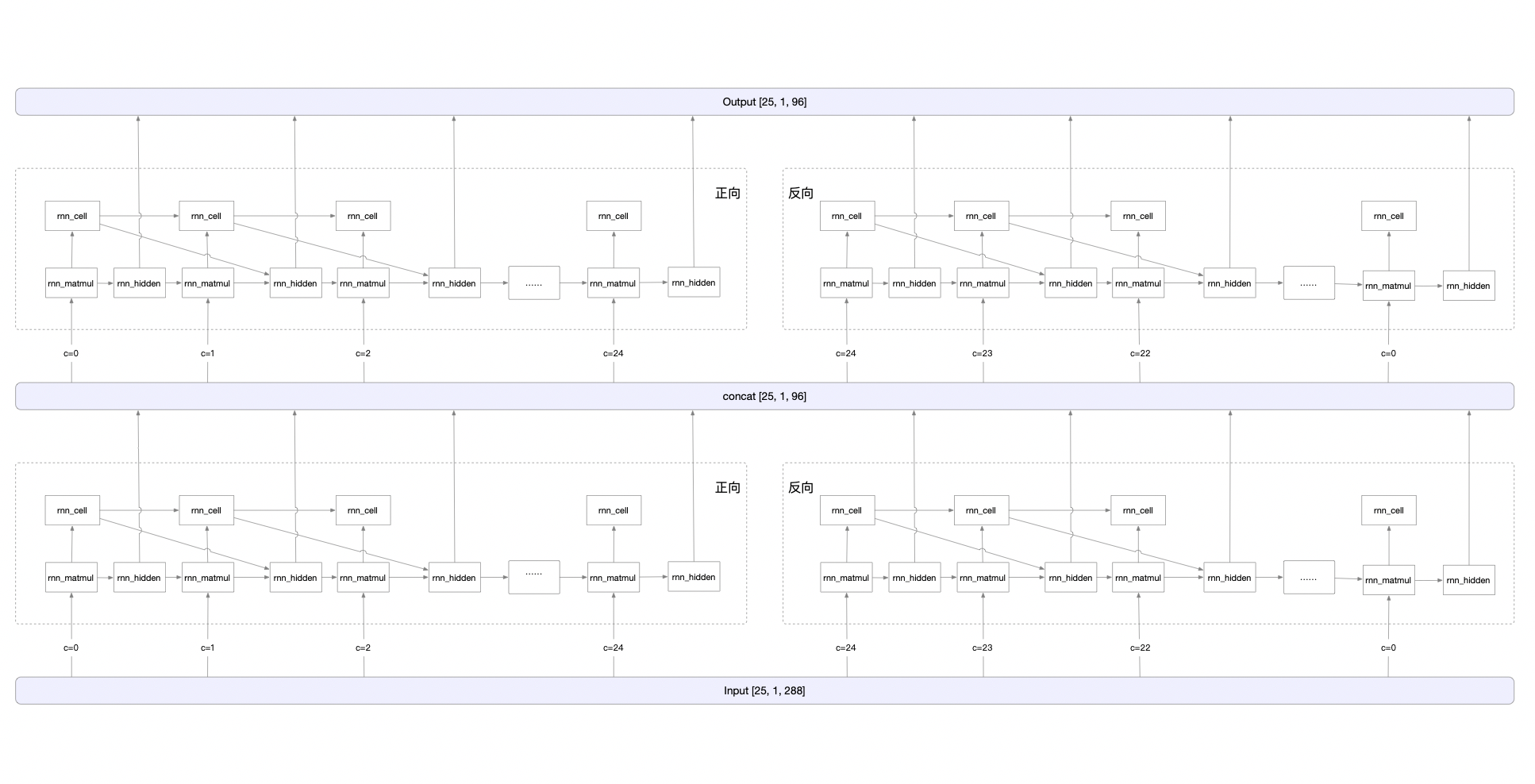
|
||||||
|
#### Add op in rnn calculation
|
||||||
|
1) rnn_origin
|
||||||
|
Formula: blas.MatMul(Input, WeightList_ih, blas_ih) + blas.MatMul(PreState, WeightList_hh, blas_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2) rnn_matmul
|
||||||
|
Formula: rnn_matmul = rnn_origin + Matmul( $ S_{t-1} $, WeightList_hh)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3) rnn_cell
|
||||||
|
Method: Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_c[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
||||||
|
For details, please refer to [rnn_cell](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_cell.ts).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4) rnn_hidden
|
||||||
|
Split the rnn_matmul op output into 4 copies, each copy performs a different activation function calculation, and finally outputs lstm_x_y.tmp_h[1, 1, 48]. x∈[0, 3], y∈[0, 24].
|
||||||
|
For details, please refer to [rnn_hidden](../paddlejs-backend-webgl/src/ops/shader/rnn/rnn_hidden.ts).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ humanseg.drawMask(data, canvas3, back_canvas);
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```js
|
```js
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 引入 humanseg sdk
|
// import humanseg sdk
|
||||||
import * as humanseg from '@paddle-js-models/humanseg/lib/index_gpu';
|
import * as humanseg from '@paddle-js-models/humanseg/lib/index_gpu';
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// load humanseg model, use 398x224 shape model, and preheat
|
// load humanseg model, use 398x224 shape model, and preheat
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSpeech 流式语音合成
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSpeech Streaming Text-to-Speech
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 本文示例的实现来自[PaddleSpeech 流式语音合成](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech/tree/r1.2).
|
- The examples in this document are from [PaddleSpeech Streaming Text-to-Speech](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech/tree/r1.2).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 详细部署文档
|
## Detailed deployment document
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Python部署](python)
|
- [Python deployment](python)
|
||||||
- [Serving部署](serving)
|
- [Serving deployment](serving)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
10
examples/audio/pp-tts/README_CN.md
Normal file
10
examples/audio/pp-tts/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSpeech 流式语音合成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 本文示例的实现来自[PaddleSpeech 流式语音合成](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech/tree/r1.2).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 详细部署文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](python)
|
||||||
|
- [Serving部署](serving)
|
||||||
@@ -1,63 +1,64 @@
|
|||||||
# FastDeploy Diffusion模型高性能部署
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# FastDeploy Diffusion Model High-Performance Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本部署示例使用⚡️`FastDeploy`在Huggingface团队[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)项目设计的`DiffusionPipeline`基础上,完成Diffusion模型的高性能部署。
|
This document completes the high-performance deployment of the Diffusion model with ⚡️`FastDeploy`, based on `DiffusionPipeline` in project [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) designed by Huggingface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 部署模型准备
|
### Preperation for Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本示例需要使用训练模型导出后的部署模型。有两种部署模型的获取方式:
|
This example needs the deployment model after exporting the training model. Here are two ways to obtain the deployment model:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 模型导出方式,可参考[模型导出文档](./export.md)导出部署模型。
|
- Methods for model export. Please refer to [Model Export](./export_EN.md) to export deployment model.
|
||||||
- 下载部署模型。为了方便开发者快速测试本示例,我们已经将部分`Diffusion`模型预先导出,开发者只要下载模型就可以快速测试:
|
- Download the deployment model. To facilitate developers to test the example, we have pre-exported some of the `Diffusion` models, so you can just download models and test them quickly:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 模型 | Scheduler |
|
| Model | Scheduler |
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
| [CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4.tgz) | PNDM |
|
| [CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4.tgz) | PNDM |
|
||||||
| [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5.tgz) | EulerAncestral |
|
| [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5.tgz) | EulerAncestral |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 环境依赖
|
## Environment Dependency
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在示例中使用了PaddleNLP的CLIP模型的分词器,所以需要执行以下命令安装依赖。
|
In the example, the word splitter in CLIP model of PaddleNLP is required, so you need to run the following line to install the dependency.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
pip install paddlenlp paddlepaddle-gpu
|
pip install paddlenlp paddlepaddle-gpu
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 快速体验
|
### Quick Experience
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
我们经过部署模型准备,可以开始进行测试。下面将指定模型目录以及推理引擎后端,运行`infer.py`脚本,完成推理。
|
We are ready to start testing after model deployment. Here we will specify the model directory as well as the inference engine backend, and run the `infer.py` script to complete the inference.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-4/ --scheduler "pndm" --backend paddle
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-4/ --scheduler "pndm" --backend paddle
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
得到的图像文件为fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png。生成的图片示例如下(每次生成的图片都不相同,示例仅作参考):
|
The image file is fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png. An example of the generated image is as follows (the generated image is different each time, the example is for reference only):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
如果使用stable-diffusion-v1-5模型,则可执行以下命令完成推理:
|
If the stable-diffusion-v1-5 model is used, you can run these to complete the inference.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# GPU上推理
|
# Inference on GPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在昆仑芯XPU上推理
|
# Inference on KunlunXin XPU
|
||||||
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle-kunlunxin
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle-kunlunxin
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 参数说明
|
#### Parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`infer.py` 除了以上示例的命令行参数,还支持更多命令行参数的设置。以下为各命令行参数的说明。
|
`infer.py` supports more command line parameters than the above example. The following is a description of each command line parameter.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
| Parameter |Description |
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
| --model_dir | 导出后模型的目录。 |
|
| --model_dir | Directory of the exported model. |
|
||||||
| --model_format | 模型格式。默认为`'paddle'`,可选列表:`['paddle', 'onnx']`。 |
|
| --model_format | Model format. Default is `'paddle'`, optional list: `['paddle', 'onnx']`. |
|
||||||
| --backend | 推理引擎后端。默认为`paddle`,可选列表:`['onnx_runtime', 'paddle', 'paddle-kunlunxin']`,当模型格式为`onnx`时,可选列表为`['onnx_runtime']`。 |
|
| --backend | Inference engine backend. Default is`paddle`, optional list: `['onnx_runtime', 'paddle', 'paddle-kunlunxin']`, when the model format is `onnx`, optional list is`['onnx_runtime']`. |
|
||||||
| --scheduler | StableDiffusion 模型的scheduler。默认为`'pndm'`。可选列表:`['pndm', 'euler_ancestral']`,StableDiffusio模型对应的scheduler可参考[ppdiffuser模型列表](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion)。|
|
| --scheduler | Scheduler in StableDiffusion model. Default is`'pndm'`, optional list `['pndm', 'euler_ancestral']`. The scheduler corresponding to the StableDiffusio model can be found in [ppdiffuser model list](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion).|
|
||||||
| --unet_model_prefix | UNet模型前缀。默认为`unet`。 |
|
| --unet_model_prefix | UNet model prefix, default is `unet`. |
|
||||||
| --vae_model_prefix | VAE模型前缀。默认为`vae_decoder`。 |
|
| --vae_model_prefix | VAE model prefix, defalut is `vae_decoder`. |
|
||||||
| --text_encoder_model_prefix | TextEncoder模型前缀。默认为`text_encoder`。 |
|
| --text_encoder_model_prefix | TextEncoder model prefix, default is `text_encoder`. |
|
||||||
| --inference_steps | UNet模型运行的次数,默认为100。 |
|
| --inference_steps | Running times of UNet model, default is 100. |
|
||||||
| --image_path | 生成图片的路径。默认为`fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png`。 |
|
| --image_path | Path to the generated images, defalut is `fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png`. |
|
||||||
| --device_id | gpu设备的id。若`device_id`为-1,视为使用cpu推理。 |
|
| --device_id | gpu id. If `device_id` is -1, cpu is used for inference. |
|
||||||
| --use_fp16 | 是否使用fp16精度。默认为`False`。使用tensorrt或者paddle-tensorrt后端时可以设为`True`开启。 |
|
| --use_fp16 | Indicates if fp16 is used, default is `False`. Can be set to `True` when using tensorrt or paddle-tensorrt backend. |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
64
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/README_CN.md
Normal file
64
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# FastDeploy Diffusion模型高性能部署
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本部署示例使用⚡️`FastDeploy`在Huggingface团队[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)项目设计的`DiffusionPipeline`基础上,完成Diffusion模型的高性能部署。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 部署模型准备
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本示例需要使用训练模型导出后的部署模型。有两种部署模型的获取方式:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 模型导出方式,可参考[模型导出文档](./export.md)导出部署模型。
|
||||||
|
- 下载部署模型。为了方便开发者快速测试本示例,我们已经将部分`Diffusion`模型预先导出,开发者只要下载模型就可以快速测试:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 模型 | Scheduler |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
| [CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4.tgz) | PNDM |
|
||||||
|
| [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/stable-diffusion/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5.tgz) | EulerAncestral |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 环境依赖
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在示例中使用了PaddleNLP的CLIP模型的分词器,所以需要执行以下命令安装依赖。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install paddlenlp paddlepaddle-gpu
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 快速体验
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我们经过部署模型准备,可以开始进行测试。下面将指定模型目录以及推理引擎后端,运行`infer.py`脚本,完成推理。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-4/ --scheduler "pndm" --backend paddle
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
得到的图像文件为fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png。生成的图片示例如下(每次生成的图片都不相同,示例仅作参考):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果使用stable-diffusion-v1-5模型,则可执行以下命令完成推理:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# GPU上推理
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在昆仑芯XPU上推理
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model_dir stable-diffusion-v1-5/ --scheduler "euler_ancestral" --backend paddle-kunlunxin
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 参数说明
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`infer.py` 除了以上示例的命令行参数,还支持更多命令行参数的设置。以下为各命令行参数的说明。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 参数 |参数说明 |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
| --model_dir | 导出后模型的目录。 |
|
||||||
|
| --model_format | 模型格式。默认为`'paddle'`,可选列表:`['paddle', 'onnx']`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --backend | 推理引擎后端。默认为`paddle`,可选列表:`['onnx_runtime', 'paddle', 'paddle-kunlunxin']`,当模型格式为`onnx`时,可选列表为`['onnx_runtime']`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --scheduler | StableDiffusion 模型的scheduler。默认为`'pndm'`。可选列表:`['pndm', 'euler_ancestral']`,StableDiffusio模型对应的scheduler可参考[ppdiffuser模型列表](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion)。|
|
||||||
|
| --unet_model_prefix | UNet模型前缀。默认为`unet`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --vae_model_prefix | VAE模型前缀。默认为`vae_decoder`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --text_encoder_model_prefix | TextEncoder模型前缀。默认为`text_encoder`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --inference_steps | UNet模型运行的次数,默认为100。 |
|
||||||
|
| --image_path | 生成图片的路径。默认为`fd_astronaut_rides_horse.png`。 |
|
||||||
|
| --device_id | gpu设备的id。若`device_id`为-1,视为使用cpu推理。 |
|
||||||
|
| --use_fp16 | 是否使用fp16精度。默认为`False`。使用tensorrt或者paddle-tensorrt后端时可以设为`True`开启。 |
|
||||||
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
|||||||
# StableDiffusion C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# StableDiffusion C++ Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before deployment, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [Environment requirements for FastDeploy](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库和samples代码,参考[FastDeploy预编译库](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Download pre-compiled libraries and samples according to the development environment. Please refer to [FastDeploy pre-compiled libraries](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`*_infer.cc`快速完成StableDiffusion各任务的C++部署示例。
|
This directory provides `*_infer.cc` to quickly complete C++ deployment examples for each task of StableDiffusion.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Inpaint任务
|
## Inpaint Task
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
StableDiffusion Inpaint任务是一个根据提示文本补全图片的任务,具体而言就是用户给定提示文本,原始图片以及原始图片的mask图片,该任务输出补全后的图片。
|
The StableDiffusion Inpaint task is a task that completes the image based on the prompt text. User provides the prompt text, the original image and the mask image of the original image, and the task outputs the completed image.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
13
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
13
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# StableDiffusion C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库和samples代码,参考[FastDeploy预编译库](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`*_infer.cc`快速完成StableDiffusion各任务的C++部署示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Inpaint任务
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
StableDiffusion Inpaint任务是一个根据提示文本补全图片的任务,具体而言就是用户给定提示文本,原始图片以及原始图片的mask图片,该任务输出补全后的图片。
|
||||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](export_EN.md)
|
||||||
# Diffusion模型导出教程
|
# Diffusion模型导出教程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本项目支持两种模型导出方式:[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)模型导出以及[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)模型导出。下面分别介绍这两种模型导出方式。
|
本项目支持两种模型导出方式:[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers)模型导出以及[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)模型导出。下面分别介绍这两种模型导出方式。
|
||||||
|
|||||||
106
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/export_EN.md
Normal file
106
examples/multimodal/stable_diffusion/export_EN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](export.md)
|
||||||
|
# Diffusion Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The project supports two methods of model export, [PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) model export and [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) model export. Here we introduce each of these two methods.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PPDiffusers Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[PPDiffusers](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit that supports cross-modal (e.g., image and speech) training and inference. It builds on the design of [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by the 🤗 Huggingface team, and relies on [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle) framework and the [PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP) natural language processing library. The following describes how to use FastDeploy to deploy the Diffusion model provided by PPDiffusers for high performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Dependency Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The model export depends on `paddlepaddle`, `paddlenlp` and `ppdiffusers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install -r requirements_paddle.txt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can run the following lines to export model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
python export_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The output model directory is as follows:
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
stable-diffusion-v1-4/
|
||||||
|
├── text_encoder
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
├── unet
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
│ ├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
└── vae_decoder
|
||||||
|
├── inference.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
├── inference.pdiparams.info
|
||||||
|
└── inference.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_model.py`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Parameter |Description |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> | The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers. Default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [ppdiffuser model list](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/ppdiffusers/examples/textual_inversion).|
|
||||||
|
|--output_path | Exported directory |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Diffusers Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) is a Diffusion Model toolkit built by HuggingFace to support cross-modal (e.g. image and speech) training and inference. The underlying model code is available in both a PyTorch implementation and a Flax implementation. This example shows how to use FastDeploy to deploy a PyTorch implementation of Diffusion Model for high performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Dependency Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The model export depends on `onnx`, `torch`, `diffusers` and `transformers`, which can be installed quickly by running the following command using `pip`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Model Export
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Note: The StableDiffusion model needs to be downloaded during the model export process. In order to use the model and weights, you must accept the License required, and get the Token granted by HF Hub. Please visit HuggingFace's [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), to read the License carefully, and then sign the agreement.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
___Tips: Stable Diffusion is based on these Licenses: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which this license is based.___
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you are exporting a model for the first time, you need to log in to the HuggingFace client first. Run the following command to log in:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
huggingface-cli login
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
After finishing the login, you can run the following lines to export model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
python export_torch_to_onnx_model.py --pretrained_model_name_or_path CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 --output_path torch_diffusion_model
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The output model directory is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
torch_diffusion_model/
|
||||||
|
├── text_encoder
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
├── unet
|
||||||
|
│ └── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
└── vae_decoder
|
||||||
|
└── inference.onnx
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Parameters
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here is description of each command line parameter in `export_torch_to_onnx_model.py`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Parameter |Description |
|
||||||
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
|
|<div style="width: 230pt">--pretrained_model_name_or_path </div> |The diffusion pretrained model provided by ppdiffuers, default is "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4". For more diffusion pretrained models, please refer to [HuggingFace model list](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4).|
|
||||||
|
|--output_path |Exported directory |
|
||||||
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# FastDeploy Runtime examples
|
# FastDeploy Runtime examples
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FastDeploy Runtime 推理示例如下
|
FastDeploy Runtime examples are as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Python 示例
|
## Python Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
||||||
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
||||||
@@ -15,7 +16,7 @@ FastDeploy Runtime 推理示例如下
|
|||||||
| python/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.py | Python | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
| python/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.py | Python | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
| python/infer_torchscript_poros.py | Python | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
| python/infer_torchscript_poros.py | Python | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## C++ 示例
|
## C++ Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
||||||
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
||||||
@@ -28,7 +29,7 @@ FastDeploy Runtime 推理示例如下
|
|||||||
| cpp/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.cc | C++ | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
| cpp/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.cc | C++ | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
| cpp/infer_torchscript_poros.cc | C++ | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
| cpp/infer_torchscript_poros.cc | C++ | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 详细部署文档
|
## Detailed deployment documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Python部署](python)
|
- [Python deployment](python)
|
||||||
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
- [C++ deployment](cpp)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
35
examples/runtime/README_CN.md
Normal file
35
examples/runtime/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# FastDeploy Runtime examples
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FastDeploy Runtime 推理示例如下
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Python 示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
||||||
|
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_paddle_paddle_inference.py | Python | Deploy Paddle model with Paddle Inference(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_paddle_tensorrt.py | Python | Deploy Paddle model with TensorRT(GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_paddle_openvino.py | Python | Deploy Paddle model with OpenVINO(CPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_paddle_onnxruntime.py | Python | Deploy Paddle model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_onnx_openvino.py | Python | Deploy ONNX model with OpenVINO(CPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_onnx_tensorrt.py | Python | Deploy ONNX model with TensorRT(GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.py | Python | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| python/infer_torchscript_poros.py | Python | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## C++ 示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Example Code | Program Language | Description |
|
||||||
|
| :------- | :------- | :---- |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_paddle_paddle_inference.cc | C++ | Deploy Paddle model with Paddle Inference(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_paddle_tensorrt.cc | C++ | Deploy Paddle model with TensorRT(GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_paddle_openvino.cc | C++ | Deploy Paddle model with OpenVINO(CPU |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc | C++ | Deploy Paddle model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_onnx_openvino.cc | C++ | Deploy ONNX model with OpenVINO(CPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_onnx_tensorrt.cc | C++ | Deploy ONNX model with TensorRT(GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_onnx_onnxruntime.cc | C++ | Deploy ONNX model with ONNX Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
| cpp/infer_torchscript_poros.cc | C++ | Deploy TorchScript model with Poros Runtime(CPU/GPU) |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 详细部署文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](python)
|
||||||
|
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
||||||
@@ -1,22 +1,23 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# C++推理
|
# C++推理
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在运行demo前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [Environment requirements for FastDeploy](../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
- 2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库和samples代码,参考[FastDeploy预编译库](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Download pre-compiled libraries and samples according to the development environment. Please refer to [FastDeploy pre-compiled libraries](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文档以 PaddleClas 分类模型 MobileNetV2 为例展示CPU上的推理示例
|
This document shows an inference example on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 1. 获取模型
|
## 1. Obtaining the Model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf mobilenetv2.tgz
|
tar xvf mobilenetv2.tgz
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 2. 配置后端
|
## 2. Backend Configuration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
如下C++代码保存为`infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc`
|
The following C++ code is saved as `infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``` c++
|
``` c++
|
||||||
#include "fastdeploy/runtime.h"
|
#include "fastdeploy/runtime.h"
|
||||||
@@ -66,35 +67,35 @@ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
|
|||||||
return 0;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
加载完成,会输出提示如下,说明初始化的后端,以及运行的硬件设备
|
When loading is complete, the following prompt will be output, indicating the initialized backend, and the running hardware devices.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 3. 准备CMakeLists.txt
|
## 3. Prepare for CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FastDeploy中包含多个依赖库,直接采用`g++`或编译器编译较为繁杂,推荐使用cmake进行编译配置。示例配置如下,
|
FastDeploy contains several dependencies, it is complicated to compile directly with `g++` or compiler, so we recommend using cmake for compiling configuration. The sample configuration is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```cmake
|
```cmake
|
||||||
PROJECT(runtime_demo C CXX)
|
PROJECT(runtime_demo C CXX)
|
||||||
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED (VERSION 3.12)
|
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED (VERSION 3.12)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 指定下载解压后的fastdeploy库路径
|
# Specify the path to the fastdeploy library after downloading and unpacking.
|
||||||
option(FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR "Path of downloaded fastdeploy sdk.")
|
option(FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR "Path of downloaded fastdeploy sdk.")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
include(${FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR}/FastDeploy.cmake)
|
include(${FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR}/FastDeploy.cmake)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 添加FastDeploy依赖头文件
|
# Add FastDeploy dependency headers.
|
||||||
include_directories(${FASTDEPLOY_INCS})
|
include_directories(${FASTDEPLOY_INCS})
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
add_executable(runtime_demo ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/infer_onnx_openvino.cc)
|
add_executable(runtime_demo ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/infer_onnx_openvino.cc)
|
||||||
# 添加FastDeploy库依赖
|
# Adding FastDeploy library dependencies.
|
||||||
target_link_libraries(runtime_demo ${FASTDEPLOY_LIBS})
|
target_link_libraries(runtime_demo ${FASTDEPLOY_LIBS})
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 4. 编译可执行程序
|
## 4. Compile executable program
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
打开命令行终端,进入`infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc`和`CMakeLists.txt`所在的目录,执行如下命令
|
Open the terminal, go to the directory where `infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc` and `CMakeLists.txt` are located, and run the following command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build & cd build
|
mkdir build & cd build
|
||||||
@@ -102,20 +103,20 @@ cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=$fastdeploy_cpp_sdk
|
|||||||
make -j
|
make -j
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```fastdeploy_cpp_sdk``` 为FastDeploy C++部署库路径
|
```fastdeploy_cpp_sdk``` is path to FastDeploy C++ deployment libraries.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
编译完成后,使用如下命令执行可得到预测结果
|
After compiling, run the following command and get the results.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
./runtime_demo
|
./runtime_demo
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
执行时如提示`error while loading shared libraries: libxxx.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file...`,说明程序执行时没有找到FastDeploy的库路径,可通过执行如下命令,将FastDeploy的库路径添加到环境变量之后,重新执行二进制程序。
|
If you are prompted with `error while loading shared libraries: libxxx.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file... `, it means that the path to FastDeploy libraries is not found, you can run the program again after adding the path to the environment variable by executing the following command.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
source /Path/to/fastdeploy_cpp_sdk/fastdeploy_init.sh
|
source /Path/to/fastdeploy_cpp_sdk/fastdeploy_init.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本示例代码在各平台(Windows/Linux/Mac)上通用,但编译过程仅支持(Linux/Mac),Windows上使用msbuild进行编译,具体使用方式参考[Windows平台使用FastDeploy C++ SDK](../../../docs/cn/faq/use_sdk_on_windows.md)
|
This sample code is common on all platforms (Windows/Linux/Mac), but the compilation process is only supported on (Linux/Mac),while using msbuild to compile on Windows. Please refer to [FastDeploy C++ SDK on Windows](../../../docs/en/faq/use_sdk_on_windows.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Runtime Python 示例](../python)
|
- [A Python example for Runtime](../python)
|
||||||
- [切换模型推理的硬件和后端](../../../docs/cn/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
- [Switching hardware and backend for model inference](../../../docs/en/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
122
examples/runtime/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
122
examples/runtime/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# C++推理
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在运行demo前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库和samples代码,参考[FastDeploy预编译库](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文档以 PaddleClas 分类模型 MobileNetV2 为例展示CPU上的推理示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 1. 获取模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf mobilenetv2.tgz
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 2. 配置后端
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如下C++代码保存为`infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
``` c++
|
||||||
|
#include "fastdeploy/runtime.h"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
namespace fd = fastdeploy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
|
||||||
|
std::string model_file = "mobilenetv2/inference.pdmodel";
|
||||||
|
std::string params_file = "mobilenetv2/inference.pdiparams";
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// setup option
|
||||||
|
fd::RuntimeOption runtime_option;
|
||||||
|
runtime_option.SetModelPath(model_file, params_file, fd::ModelFormat::PADDLE);
|
||||||
|
runtime_option.UseOrtBackend();
|
||||||
|
runtime_option.SetCpuThreadNum(12);
|
||||||
|
// init runtime
|
||||||
|
std::unique_ptr<fd::Runtime> runtime =
|
||||||
|
std::unique_ptr<fd::Runtime>(new fd::Runtime());
|
||||||
|
if (!runtime->Init(runtime_option)) {
|
||||||
|
std::cerr << "--- Init FastDeploy Runitme Failed! "
|
||||||
|
<< "\n--- Model: " << model_file << std::endl;
|
||||||
|
return -1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
std::cout << "--- Init FastDeploy Runitme Done! "
|
||||||
|
<< "\n--- Model: " << model_file << std::endl;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// init input tensor shape
|
||||||
|
fd::TensorInfo info = runtime->GetInputInfo(0);
|
||||||
|
info.shape = {1, 3, 224, 224};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
std::vector<fd::FDTensor> input_tensors(1);
|
||||||
|
std::vector<fd::FDTensor> output_tensors(1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
std::vector<float> inputs_data;
|
||||||
|
inputs_data.resize(1 * 3 * 224 * 224);
|
||||||
|
for (size_t i = 0; i < inputs_data.size(); ++i) {
|
||||||
|
inputs_data[i] = std::rand() % 1000 / 1000.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
input_tensors[0].SetExternalData({1, 3, 224, 224}, fd::FDDataType::FP32, inputs_data.data());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//get input name
|
||||||
|
input_tensors[0].name = info.name;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
runtime->Infer(input_tensors, &output_tensors);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
output_tensors[0].PrintInfo();
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
加载完成,会输出提示如下,说明初始化的后端,以及运行的硬件设备
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 3. 准备CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FastDeploy中包含多个依赖库,直接采用`g++`或编译器编译较为繁杂,推荐使用cmake进行编译配置。示例配置如下,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cmake
|
||||||
|
PROJECT(runtime_demo C CXX)
|
||||||
|
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED (VERSION 3.12)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 指定下载解压后的fastdeploy库路径
|
||||||
|
option(FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR "Path of downloaded fastdeploy sdk.")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
include(${FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR}/FastDeploy.cmake)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 添加FastDeploy依赖头文件
|
||||||
|
include_directories(${FASTDEPLOY_INCS})
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
add_executable(runtime_demo ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/infer_onnx_openvino.cc)
|
||||||
|
# 添加FastDeploy库依赖
|
||||||
|
target_link_libraries(runtime_demo ${FASTDEPLOY_LIBS})
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 4. 编译可执行程序
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
打开命令行终端,进入`infer_paddle_onnxruntime.cc`和`CMakeLists.txt`所在的目录,执行如下命令
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build & cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=$fastdeploy_cpp_sdk
|
||||||
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```fastdeploy_cpp_sdk``` 为FastDeploy C++部署库路径
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
编译完成后,使用如下命令执行可得到预测结果
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./runtime_demo
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
执行时如提示`error while loading shared libraries: libxxx.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file...`,说明程序执行时没有找到FastDeploy的库路径,可通过执行如下命令,将FastDeploy的库路径添加到环境变量之后,重新执行二进制程序。
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
source /Path/to/fastdeploy_cpp_sdk/fastdeploy_init.sh
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本示例代码在各平台(Windows/Linux/Mac)上通用,但编译过程仅支持(Linux/Mac),Windows上使用msbuild进行编译,具体使用方式参考[Windows平台使用FastDeploy C++ SDK](../../../docs/cn/faq/use_sdk_on_windows.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Runtime Python 示例](../python)
|
||||||
|
- [切换模型推理的硬件和后端](../../../docs/cn/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,13 +1,14 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
# Python推理
|
# Python推理
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在运行demo前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before running demo, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [Environment requirements for FastDeploy](../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Install FastDeploy Python whl package, please refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文档以 PaddleClas 分类模型 MobileNetV2 为例展示 CPU 上的推理示例
|
This document shows an inference example on the CPU using the PaddleClas classification model MobileNetV2 as an example.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 1. 获取模型
|
## 1. Obtaining the model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``` python
|
``` python
|
||||||
import fastdeploy as fd
|
import fastdeploy as fd
|
||||||
@@ -16,7 +17,7 @@ model_url = "https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz"
|
|||||||
fd.download_and_decompress(model_url, path=".")
|
fd.download_and_decompress(model_url, path=".")
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 2. 配置后端
|
## 2. Backend Configuration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``` python
|
``` python
|
||||||
option = fd.RuntimeOption()
|
option = fd.RuntimeOption()
|
||||||
@@ -24,30 +25,30 @@ option = fd.RuntimeOption()
|
|||||||
option.set_model_path("mobilenetv2/inference.pdmodel",
|
option.set_model_path("mobilenetv2/inference.pdmodel",
|
||||||
"mobilenetv2/inference.pdiparams")
|
"mobilenetv2/inference.pdiparams")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# **** CPU 配置 ****
|
# **** CPU Configuration ****
|
||||||
option.use_cpu()
|
option.use_cpu()
|
||||||
option.use_ort_backend()
|
option.use_ort_backend()
|
||||||
option.set_cpu_thread_num(12)
|
option.set_cpu_thread_num(12)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 初始化构造runtime
|
# Initialise runtime
|
||||||
runtime = fd.Runtime(option)
|
runtime = fd.Runtime(option)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 获取模型输入名
|
# Get model input name
|
||||||
input_name = runtime.get_input_info(0).name
|
input_name = runtime.get_input_info(0).name
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 构造随机数据进行推理
|
# Constructing random data for inference
|
||||||
results = runtime.infer({
|
results = runtime.infer({
|
||||||
input_name: np.random.rand(1, 3, 224, 224).astype("float32")
|
input_name: np.random.rand(1, 3, 224, 224).astype("float32")
|
||||||
})
|
})
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print(results[0].shape)
|
print(results[0].shape)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
加载完成,会输出提示如下,说明初始化的后端,以及运行的硬件设备
|
When loading is complete, you will get the following output information indicating the initialized backend and the hardware devices.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Runtime C++ 示例](../cpp)
|
- [A C++ example for Runtime C++](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [切换模型推理的硬件和后端](../../../docs/cn/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
- [Switching hardware and backend for model inference](../../../docs/en/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
54
examples/runtime/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
54
examples/runtime/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|||||||
|
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||||
|
# Python推理
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在运行demo前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文档以 PaddleClas 分类模型 MobileNetV2 为例展示 CPU 上的推理示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 1. 获取模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
``` python
|
||||||
|
import fastdeploy as fd
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
model_url = "https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/mobilenetv2.tgz"
|
||||||
|
fd.download_and_decompress(model_url, path=".")
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 2. 配置后端
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
``` python
|
||||||
|
option = fd.RuntimeOption()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
option.set_model_path("mobilenetv2/inference.pdmodel",
|
||||||
|
"mobilenetv2/inference.pdiparams")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# **** CPU 配置 ****
|
||||||
|
option.use_cpu()
|
||||||
|
option.use_ort_backend()
|
||||||
|
option.set_cpu_thread_num(12)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 初始化构造runtime
|
||||||
|
runtime = fd.Runtime(option)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 获取模型输入名
|
||||||
|
input_name = runtime.get_input_info(0).name
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 构造随机数据进行推理
|
||||||
|
results = runtime.infer({
|
||||||
|
input_name: np.random.rand(1, 3, 224, 224).astype("float32")
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
print(results[0].shape)
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
加载完成,会输出提示如下,说明初始化的后端,以及运行的硬件设备
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[INFO] fastdeploy/fastdeploy_runtime.cc(283)::Init Runtime initialized with Backend::OrtBackend in device Device::CPU.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Runtime C++ 示例](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [切换模型推理的硬件和后端](../../../docs/cn/faq/how_to_change_backend.md)
|
||||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ tar xvfz ernie-3.0-medium-zh-afqmc.tgz
|
|||||||
# GPU Inference
|
# GPU Inference
|
||||||
./seq_cls_infer_demo --device gpu --model_dir ernie-3.0-medium-zh-afqmc
|
./seq_cls_infer_demo --device gpu --model_dir ernie-3.0-medium-zh-afqmc
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# KunlunXin XPU 推理
|
# KunlunXin XPU Inference
|
||||||
./seq_cls_infer_demo --device kunlunxin --model_dir ernie-3.0-medium-zh-afqmc
|
./seq_cls_infer_demo --device kunlunxin --model_dir ernie-3.0-medium-zh-afqmc
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
The result returned after running is as follows:
|
The result returned after running is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -30,18 +30,18 @@ mv msra_ner_pruned_infer_model/float32.pdiparams models/ernie_tokencls_model/1/m
|
|||||||
After download and move, the models directory of the classification tasks is as follows:
|
After download and move, the models directory of the classification tasks is as follows:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
models
|
models
|
||||||
├── ernie_seqcls # 分类任务的pipeline
|
├── ernie_seqcls # Pipeline for classification task
|
||||||
│ ├── 1
|
│ ├── 1
|
||||||
│ └── config.pbtxt # 通过这个文件组合前后处理和模型推理
|
│ └── config.pbtxt # Combine pre and post processing and model inference
|
||||||
├── ernie_seqcls_model # 分类任务的模型推理
|
├── ernie_seqcls_model # Model inference for classification task
|
||||||
│ ├── 1
|
│ ├── 1
|
||||||
│ │ └── model.onnx
|
│ │ └── model.onnx
|
||||||
│ └── config.pbtxt
|
│ └── config.pbtxt
|
||||||
├── ernie_seqcls_postprocess # 分类任务后处理
|
├── ernie_seqcls_postprocess # Post-processing of classification task
|
||||||
│ ├── 1
|
│ ├── 1
|
||||||
│ │ └── model.py
|
│ │ └── model.py
|
||||||
│ └── config.pbtxt
|
│ └── config.pbtxt
|
||||||
└── ernie_tokenizer # 预处理分词
|
└── ernie_tokenizer # Pre-processing splitting
|
||||||
├── 1
|
├── 1
|
||||||
│ └── model.py
|
│ └── model.py
|
||||||
└── config.pbtxt
|
└── config.pbtxt
|
||||||
@@ -63,9 +63,9 @@ docker run -it --net=host --name fastdeploy_server --shm-size="1g" -v /path/ser
|
|||||||
The serving directory contains the configuration to start the pipeline service and the code to send the prediction request, including
|
The serving directory contains the configuration to start the pipeline service and the code to send the prediction request, including
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
models # 服务化启动需要的模型仓库,包含模型和服务配置文件
|
models # Model repository needed for serving startup, containing model and service configuration files
|
||||||
seq_cls_rpc_client.py # 新闻分类任务发送pipeline预测请求的脚本
|
seq_cls_rpc_client.py # Script for sending pipeline prediction requests for news classification task
|
||||||
token_cls_rpc_client.py # 序列标注任务发送pipeline预测请求的脚本
|
token_cls_rpc_client.py # Script for sequence annotation task to send pipeline prediction requests
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*Attention*:Attention: When starting the service, each python backend process of Server requests 64M memory by default, and the docker started by default cannot start more than one python backend node. There are two solutions:
|
*Attention*:Attention: When starting the service, each python backend process of Server requests 64M memory by default, and the docker started by default cannot start more than one python backend node. There are two solutions:
|
||||||
@@ -76,13 +76,13 @@ token_cls_rpc_client.py # 序列标注任务发送pipeline预测请求的脚
|
|||||||
### Classification Task
|
### Classification Task
|
||||||
Execute the following command in the container to start the service:
|
Execute the following command in the container to start the service:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# 默认启动models下所有模型
|
# Enable all models by default
|
||||||
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models
|
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 可通过参数只启动分类任务
|
# You can only enable classification task via parameters
|
||||||
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models --model-control-mode=explicit --load-model=ernie_seqcls
|
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models --model-control-mode=explicit --load-model=ernie_seqcls
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
输出打印如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
I1019 09:41:15.375496 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1183] successfully loaded 'ernie_tokenizer' version 1
|
I1019 09:41:15.375496 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1183] successfully loaded 'ernie_tokenizer' version 1
|
||||||
I1019 09:41:15.375987 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1022] loading: ernie_seqcls:1
|
I1019 09:41:15.375987 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1022] loading: ernie_seqcls:1
|
||||||
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ Execute the following command in the container to start the sequence labelling s
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models --model-control-mode=explicit --load-model=ernie_tokencls --backend-config=python,shm-default-byte-size=10485760
|
fastdeployserver --model-repository=/models --model-control-mode=explicit --load-model=ernie_tokencls --backend-config=python,shm-default-byte-size=10485760
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
输出打印如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
I1019 09:41:15.375496 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1183] successfully loaded 'ernie_tokenizer' version 1
|
I1019 09:41:15.375496 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1183] successfully loaded 'ernie_tokenizer' version 1
|
||||||
I1019 09:41:15.375987 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1022] loading: ernie_seqcls:1
|
I1019 09:41:15.375987 2823 model_repository_manager.cc:1022] loading: ernie_seqcls:1
|
||||||
@@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ Attention: The proxy need turning off when executing client requests. The ip add
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
python seq_cls_grpc_client.py
|
python seq_cls_grpc_client.py
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
输出打印如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
{'label': array([5, 9]), 'confidence': array([0.6425664 , 0.66534853], dtype=float32)}
|
{'label': array([5, 9]), 'confidence': array([0.6425664 , 0.66534853], dtype=float32)}
|
||||||
{'label': array([4]), 'confidence': array([0.53198355], dtype=float32)}
|
{'label': array([4]), 'confidence': array([0.53198355], dtype=float32)}
|
||||||
@@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ Attention: The proxy need turning off when executing client requests. The ip add
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
python token_cls_grpc_client.py
|
python token_cls_grpc_client.py
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
输出打印如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
input data: 北京的涮肉,重庆的火锅,成都的小吃都是极具特色的美食。
|
input data: 北京的涮肉,重庆的火锅,成都的小吃都是极具特色的美食。
|
||||||
The model detects all entities:
|
The model detects all entities:
|
||||||
@@ -173,5 +173,5 @@ entity: 玛雅 label: LOC pos: [2, 3]
|
|||||||
entity: 华夏 label: LOC pos: [14, 15]
|
entity: 华夏 label: LOC pos: [14, 15]
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 配置修改
|
## Configuration Modification
|
||||||
The current classification task (ernie_seqcls_model/config.pbtxt) is by default configured to run the OpenVINO engine on CPU; the sequence labelling task is by default configured to run the Paddle engine on GPU. If you want to run on CPU/GPU or other inference engines, you should modify the configuration. please refer to the [configuration document.](../../../../serving/docs/zh_CN/model_configuration.md)
|
The current classification task (ernie_seqcls_model/config.pbtxt) is by default configured to run the OpenVINO engine on CPU; the sequence labelling task is by default configured to run the Paddle engine on GPU. If you want to run on CPU/GPU or other inference engines, you should modify the configuration. please refer to the [configuration document.](../../../../serving/docs/zh_CN/model_configuration.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
本目录存放ERNIE 3.0模型
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
This directory contains ERNIE 3.0 models.
|
||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
本目录存放ERNIE 3.0模型
|
||||||
@@ -1 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
本目录存放ERNIE 3.0模型
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
This directory contains ERNIE 3.0 models
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
本目录存放ERNIE 3.0模型
|
||||||
@@ -6,8 +6,8 @@ This directory provides `infer.cc` quickly complete the example on CPU/GPU by [U
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Before deployment, two steps need to be confirmed.
|
Before deployment, two steps need to be confirmed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. The software and hardware environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. The software and hardware environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [Environment requirements for FastDeploy](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
- 2. Download precompiled deployment library and samples code based on the develop environment. Please refer to [FastDeploy预编译库](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. Download precompiled deployment library and samples code based on the develop environment. Please refer to [FastDeploy pre-compiled libraries](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## A Quick Start
|
## A Quick Start
|
||||||
Take uie-base model inference on Linux as an example, execute the following command in this directory to complete the compilation test. FastDeploy version 0.7.0 or above is required to support this model (x.x.x>=0.7.0).
|
Take uie-base model inference on Linux as an example, execute the following command in this directory to complete the compilation test. FastDeploy version 0.7.0 or above is required to support this model (x.x.x>=0.7.0).
|
||||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Take uie-base model inference on Linux as an example, execute the following comm
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
# Download FastDeploy precompiled library. Users can choose proper versions in the `FastDeploy预编译库` mentioned above.
|
# Download FastDeploy precompiled library. Users can choose proper versions in the `FastDeploy pre-compiled libraries` mentioned above.
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
@@ -73,10 +73,10 @@ std::string param_path = model_dir + sep + "inference.pdiparams";
|
|||||||
std::string vocab_path = model_dir + sep + "vocab.txt";
|
std::string vocab_path = model_dir + sep + "vocab.txt";
|
||||||
using fastdeploy::text::SchemaNode;
|
using fastdeploy::text::SchemaNode;
|
||||||
using fastdeploy::text::UIEResult;
|
using fastdeploy::text::UIEResult;
|
||||||
// 定义uie result对象
|
// Define the uie result object
|
||||||
std::vector<std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<UIEResult>>> results;
|
std::vector<std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<UIEResult>>> results;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 初始化UIE模型
|
// Initialize UIE model
|
||||||
auto predictor =
|
auto predictor =
|
||||||
fastdeploy::text::UIEModel(model_path, param_path, vocab_path, 0.5, 128,
|
fastdeploy::text::UIEModel(model_path, param_path, vocab_path, 0.5, 128,
|
||||||
{"时间", "选手", "赛事名称"}, option);
|
{"时间", "选手", "赛事名称"}, option);
|
||||||
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ predictor.Predict({"2月8日上午北京冬奥会自由式滑雪女子大跳台
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 赛事名称:
|
// 赛事名称:
|
||||||
// text: 北京冬奥会自由式滑雪女子大跳台决赛
|
// text: 北京冬奥会自由式滑雪女子大跳台决赛
|
||||||
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ predictor.Predict({"(右肝肿瘤)肝细胞性肝癌(II-"
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 脉管内癌栓分级:
|
// 脉管内癌栓分级:
|
||||||
// text: M0级
|
// text: M0级
|
||||||
@@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ predictor.Predict(
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 竞赛名称:
|
// 竞赛名称:
|
||||||
// text: 2022语言与智能技术竞赛
|
// text: 2022语言与智能技术竞赛
|
||||||
@@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ predictor.Predict(
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 地震触发词:
|
// 地震触发词:
|
||||||
// text: 地震
|
// text: 地震
|
||||||
@@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ predictor.Predict(
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 评价维度:
|
// 评价维度:
|
||||||
// text: 店面
|
// text: 店面
|
||||||
@@ -332,7 +332,7 @@ predictor.Predict({"这个产品用起来真的很流畅,我非常喜欢"}, &r
|
|||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 情感倾向[正向,负向]:
|
// 情感倾向[正向,负向]:
|
||||||
// text: 正向
|
// text: 正向
|
||||||
@@ -355,7 +355,7 @@ predictor.Predict({"北京市海淀区人民法院\n民事判决书\n(199x)"
|
|||||||
&results);
|
&results);
|
||||||
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
std::cout << results << std::endl;
|
||||||
results.clear();
|
results.clear();
|
||||||
// 示例输出
|
// An output example
|
||||||
// The result:
|
// The result:
|
||||||
// 被告:
|
// 被告:
|
||||||
// text: B公司
|
// text: B公司
|
||||||
@@ -433,7 +433,7 @@ UIEModel(
|
|||||||
SchemaLanguage schema_language = SchemaLanguage::ZH);
|
SchemaLanguage schema_language = SchemaLanguage::ZH);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
UIEModel loading and initialization. Among them, model_file, params_file are Paddle inference documents exported by trained models. Please refer to [模型导出](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2)。
|
UIEModel loading and initialization. Among them, model_file, params_file are Paddle inference documents exported by trained models. Please refer to [Model export](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Parameter**
|
**Parameter**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -472,8 +472,8 @@ void Predict(
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Related Documents
|
## Related Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE模型详细介绍](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md)
|
[Details for UIE model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE模型导出方法](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2)
|
[How to export a UIE model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE Python部署方法](../python/README.md)
|
[UIE Python deployment](../python/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -4,8 +4,8 @@ English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Before deployment, two steps need to be confirmed.
|
Before deployment, two steps need to be confirmed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. The software and hardware environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. The software and hardware environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [Environment requirements for FastDeploy](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl pacakage needs installation. Please refer to [FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl pacakage needs installation. Please refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This directory provides an example that `infer.py` quickly complete CPU deployment conducted by the UIE model with OpenVINO acceleration on CPU/GPU and CPU.
|
This directory provides an example that `infer.py` quickly complete CPU deployment conducted by the UIE model with OpenVINO acceleration on CPU/GPU and CPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ The extraction schema: ['肿瘤的大小', '肿瘤的个数', '肝癌级别', '
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Description of command line arguments
|
### Description of command line arguments
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`infer.py` 除了以上示例的命令行参数,还支持更多命令行参数的设置。以下为各命令行参数的说明。
|
`infer.py` supports more command line parameters than the above example. The following is a description of each command line parameter.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Argument | Description |
|
| Argument | Description |
|
||||||
|----------|--------------|
|
|----------|--------------|
|
||||||
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ vocab_path = os.path.join(model_dir, "vocab.txt")
|
|||||||
runtime_option = fastdeploy.RuntimeOption()
|
runtime_option = fastdeploy.RuntimeOption()
|
||||||
schema = ["时间", "选手", "赛事名称"]
|
schema = ["时间", "选手", "赛事名称"]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 初始化UIE模型
|
# Initialise UIE model
|
||||||
uie = UIEModel(
|
uie = UIEModel(
|
||||||
model_path,
|
model_path,
|
||||||
param_path,
|
param_path,
|
||||||
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ The initialization stage sets the schema```["time", "player", "event name"]``` t
|
|||||||
["2月8日上午北京冬奥会自由式滑雪女子大跳台决赛中中国选手谷爱凌以188.25分获得金牌!"], return_dict=True)
|
["2月8日上午北京冬奥会自由式滑雪女子大跳台决赛中中国选手谷爱凌以188.25分获得金牌!"], return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'时间': {'end': 6,
|
# [{'时间': {'end': 6,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9857379794120789,
|
# 'probability': 0.9857379794120789,
|
||||||
# 'start': 0,
|
# 'start': 0,
|
||||||
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ For example, if the target entity types are "肿瘤的大小", "肿瘤的个数"
|
|||||||
return_dict=True)
|
return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'肝癌级别': {'end': 20,
|
# [{'肝癌级别': {'end': 20,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9243271350860596,
|
# 'probability': 0.9243271350860596,
|
||||||
# 'start': 13,
|
# 'start': 13,
|
||||||
@@ -181,7 +181,7 @@ For example, if we take "contest name" as the extracted entity, and the relation
|
|||||||
return_dict=True)
|
return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'竞赛名称': {'end': 13,
|
# [{'竞赛名称': {'end': 13,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.7825401425361633,
|
# 'probability': 0.7825401425361633,
|
||||||
# 'relation': {'主办方': [{'end': 22,
|
# 'relation': {'主办方': [{'end': 22,
|
||||||
@@ -229,7 +229,7 @@ For example, if the targets are"地震强度", "时间", "震中位置" and "引
|
|||||||
return_dict=True)
|
return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'地震触发词': {'end': 58,
|
# [{'地震触发词': {'end': 58,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9977425932884216,
|
# 'probability': 0.9977425932884216,
|
||||||
# 'relation': {'地震强度': [{'end': 56,
|
# 'relation': {'地震强度': [{'end': 56,
|
||||||
@@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ For example, if the extraction target is the evaluation dimensions and their cor
|
|||||||
["店面干净,很清静,服务员服务热情,性价比很高,发现收银台有排队"], return_dict=True)
|
["店面干净,很清静,服务员服务热情,性价比很高,发现收银台有排队"], return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'评价维度': {'end': 20,
|
# [{'评价维度': {'end': 20,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9817039966583252,
|
# 'probability': 0.9817039966583252,
|
||||||
# 'relation': {'情感倾向[正向,负向]': [{'end': 0,
|
# 'relation': {'情感倾向[正向,负向]': [{'end': 0,
|
||||||
@@ -290,7 +290,7 @@ Sentence-level sentiment classification, i.e., determining a sentence has a "pos
|
|||||||
>>> results = uie.predict(["这个产品用起来真的很流畅,我非常喜欢"], return_dict=True)
|
>>> results = uie.predict(["这个产品用起来真的很流畅,我非常喜欢"], return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'情感倾向[正向,负向]': {'end': 0,
|
# [{'情感倾向[正向,负向]': {'end': 0,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9990023970603943,
|
# 'probability': 0.9990023970603943,
|
||||||
# 'start': 0,
|
# 'start': 0,
|
||||||
@@ -311,7 +311,7 @@ For example, in a legal scenario where both entity extraction and relation extra
|
|||||||
],
|
],
|
||||||
return_dict=True)
|
return_dict=True)
|
||||||
>>> pprint(results)
|
>>> pprint(results)
|
||||||
# 示例输出
|
# An output example
|
||||||
# [{'原告': {'end': 37,
|
# [{'原告': {'end': 37,
|
||||||
# 'probability': 0.9949813485145569,
|
# 'probability': 0.9949813485145569,
|
||||||
# 'relation': {'委托代理人': [{'end': 46,
|
# 'relation': {'委托代理人': [{'end': 46,
|
||||||
@@ -348,7 +348,7 @@ fd.text.uie.UIEModel(model_file,
|
|||||||
schema_language=SchemaLanguage.ZH)
|
schema_language=SchemaLanguage.ZH)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
UIEModel loading and initialization. Among them, `model_file`, `params_file` are Paddle inference documents exported by trained models. Please refer to [模型导出](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2).`vocab_file`refers to the vocabulary file. The vocabulary of the UIE model UIE can be downloaded in [UIE配置文件](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/5401f01af85f1c73d8017c6b3476242fce1e6d52/model_zoo/uie/utils.py)
|
UIEModel loading and initialization. Among them, `model_file`, `params_file` are Paddle inference documents exported by trained models. Please refer to [Model export](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2).`vocab_file`refers to the vocabulary file. The vocabulary of the UIE model UIE can be downloaded in [UIE configuration file](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/5401f01af85f1c73d8017c6b3476242fce1e6d52/model_zoo/uie/utils.py)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Parameter**
|
**Parameter**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -393,8 +393,8 @@ UIEModel loading and initialization. Among them, `model_file`, `params_file` are
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Related Documents
|
## Related Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE模型详细介绍](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md)
|
[Details for UIE model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE模型导出方法](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2)
|
[How to export a UIE model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/uie/README.md#%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[UIE C++部署方法](../cpp/README.md)
|
[UIE C++ deployment](../cpp/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Before serving deployment, you need to confirm:
|
Before serving deployment, you need to confirm:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. You can refer to [FastDeploy服务化部署](../../../../../serving/README_CN.md) for hardware and software environment requirements and image pull commands for serving images.
|
- 1. You can refer to [FastDeploy serving deployment](../../../../../serving/README_CN.md) for hardware and software environment requirements and image pull commands for serving images.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Prepare models
|
## Prepare models
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -143,4 +143,4 @@ results:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Configuration Modification
|
## Configuration Modification
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The current configuration is by default to run the paddle engine on CPU. If you want to run on CPU/GPU or other inference engines, modifying the configuration is needed.Please refer to [配置文档](../../../../serving/docs/zh_CN/model_configuration.md)
|
The current configuration is by default to run the paddle engine on CPU. If you want to run on CPU/GPU or other inference engines, modifying the configuration is needed.Please refer to [Configuration Document](../../../../serving/docs/zh_CN/model_configuration.md).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleDetection SOPHGO部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleDetection SOPHGO Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 支持模型列表
|
## Supporting Model List
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
目前FastDeploy支持的如下模型的部署[ResNet系列模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/zh_CN/models/ResNet_and_vd.md)
|
Currently FastDeploy supports the following model deployment: [ResNet series model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/en/models/ResNet_and_vd_en.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 准备ResNet部署模型以及转换模型
|
## Preparing ResNet Model Deployment and Conversion
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
Before deploying SOPHGO-TPU model, you need to first convert Paddle model to bmodel. Specific steps are as follows:
|
||||||
- Paddle动态图模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[Paddle2ONNX模型转换](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/tree/develop/model_zoo/classification)
|
- Convert Paddle dynamic map model to ONNX model, please refer to [Paddle2ONNX model conversion](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/tree/develop/model_zoo/classification).
|
||||||
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)。
|
- For the process of converting ONNX model to bmodel, please refer to [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型转换example
|
## Model Converting Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
下面以[ResNet50_vd](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz)为例子,教大家如何转换Paddle模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型。
|
Here we take [ResNet50_vd](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz) as an example to show you how to convert Paddle model to SOPHGO-TPU model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 导出ONNX模型
|
## Export ONNX Model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 下载Paddle ResNet50_vd静态图模型并解压
|
### Download and Unzip Paddle ResNet50_vd Static Map Model
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
tar xvf ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 静态图转ONNX模型,注意,这里的save_file请和压缩包名对齐
|
### Convert Static Map Model to ONNX Model, note that the save_file here aligns with the zip name
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
paddle2onnx --model_dir ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
paddle2onnx --model_dir ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
||||||
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||||
@@ -30,32 +31,32 @@ paddle2onnx --model_dir ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
|||||||
--save_file ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
--save_file ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
||||||
--enable_dev_version True
|
--enable_dev_version True
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
### 导出bmodel模型
|
### Export bmodel
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以转化BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
Take converting BM1684x model to bmodel as an example. You need to download [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir) project. For the process of installation, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
### 1. 安装
|
### 1. Installation
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
# myname1234 is just an example, you can customize your own name.
|
||||||
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
source ./envsetup.sh
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
./build.sh
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
### 2. Convert ONNX model to bmodel
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
mkdir ResNet50_vd_infer && cd ResNet50_vd_infer
|
mkdir ResNet50_vd_infer && cd ResNet50_vd_infer
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步转换好的ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
# Put the test image in this file, and put the ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx into this folder.
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
# 放入onnx模型文件ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx
|
# Put in the onnx model file ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
# Convert ONNX model to mlir model, the parameter --output_names can be viewed via NETRON.
|
||||||
model_transform.py \
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
--model_name ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
--model_name ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
||||||
--model_def ../ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
--model_def ../ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
||||||
@@ -69,7 +70,7 @@ model_transform.py \
|
|||||||
--test_result ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_result ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir
|
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
# Convert mlir model to BM1684x F32 bmodel.
|
||||||
model_deploy.py \
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir \
|
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir \
|
||||||
--quantize F32 \
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
@@ -78,7 +79,7 @@ model_deploy.py \
|
|||||||
--test_reference ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_reference ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--model ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
--model ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
The final bmodel, ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel, can run on BM1684x. If you want to further accelerate the model, you can convert ONNX model to INT8 bmodel. For details, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其他链接
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
- [Cpp Deployment](./cpp)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleDetection SOPHGO部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 支持模型列表
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
目前FastDeploy支持的如下模型的部署[ResNet系列模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/zh_CN/models/ResNet_and_vd.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 准备ResNet部署模型以及转换模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
||||||
|
- Paddle动态图模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[Paddle2ONNX模型转换](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX/tree/develop/model_zoo/classification)
|
||||||
|
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型转换example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下面以[ResNet50_vd](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz)为例子,教大家如何转换Paddle模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 导出ONNX模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 下载Paddle ResNet50_vd静态图模型并解压
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf ResNet50_vd_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 静态图转ONNX模型,注意,这里的save_file请和压缩包名对齐
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
paddle2onnx --model_dir ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
||||||
|
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||||
|
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
|
||||||
|
--save_file ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--enable_dev_version True
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
### 导出bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以转化BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
### 1. 安装
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
||||||
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
mkdir ResNet50_vd_infer && cd ResNet50_vd_infer
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步转换好的ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
|
# 放入onnx模型文件ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
||||||
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
|
--model_name ResNet50_vd_infer \
|
||||||
|
--model_def ../ResNet50_vd_infer.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--input_shapes [[1,3,224,224]] \
|
||||||
|
--mean 0.0,0.0,0.0 \
|
||||||
|
--scale 0.0039216,0.0039216,0.0039216 \
|
||||||
|
--keep_aspect_ratio \
|
||||||
|
--pixel_format rgb \
|
||||||
|
--output_names save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_1 \
|
||||||
|
--test_input ../image/dog.jpg \
|
||||||
|
--test_result ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
|
--mlir ResNet50_vd_infer.mlir \
|
||||||
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
|
--chip bm1684x \
|
||||||
|
--test_input ResNet50_vd_infer_in_f32.npz \
|
||||||
|
--test_reference ResNet50_vd_infer_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--model ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型ResNet50_vd_infer_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其他链接
|
||||||
|
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
||||||
@@ -1,48 +1,49 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleClas C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleClas C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成ResNet50_vd模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
`infer.cc` in this directory provides a quick example of accelerated deployment of the ResNet50_vd model on SOPHGO BM1684x.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Before deployment, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Compile the FastDeploy repository from scratch according to the development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
For the above steps, please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate Basic Directory Files
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
The routine consists of the following parts:
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile Folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # Folder for images
|
||||||
├── infer.cc
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
├── preprocess_config.yaml #示例前处理配置文件
|
├── preprocess_config.yaml # Preprocessing configuration sample file.
|
||||||
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
└── model # Folder for models
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and Copy SDK to folder thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
Please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md) to compile SDK.After compiling, the fastdeploy-0.0.3 directory will be created in the build directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy model and configuration files to folder Model
|
||||||
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
Convert Paddle model to SOPHGO bmodel model. For the conversion steps, please refer to [Document](../README.md).
|
||||||
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
Please copy the converted SOPHGO bmodel to folder model.
|
||||||
将前处理配置文件也拷贝到model中
|
Copy the preprocessing configuration file to folder model as well.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cp preprocess_config.yaml ./model
|
cp preprocess_config.yaml ./model
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare Test Images to folder image
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
cp ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg ./images
|
cp ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg ./images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compile example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -50,12 +51,12 @@ cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
|||||||
make
|
make
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running Routines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
./infer_demo model images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
./infer_demo model images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
- [Model Description](../../)
|
||||||
- [模型转换](../)
|
- [Model Conversion](../)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleClas C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成ResNet50_vd模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
|
├── preprocess_config.yaml #示例前处理配置文件
|
||||||
|
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
||||||
|
将前处理配置文件也拷贝到model中
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cp preprocess_config.yaml ./model
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
cp ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg ./images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
||||||
|
make
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo model images/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
||||||
|
- [模型转换](../)
|
||||||
@@ -1,29 +1,30 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleClas Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleClas Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before deployment, the following step need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirement](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 ResNet50_vd 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
`infer.py` in this directory provides a quick example of deployment of the ResNet50_vd model on SOPHGO TPU. Please run the following script:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the sample deployment code.
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/classification/paddleclas/sophgo/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/classification/paddleclas/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images.
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference.
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/resnet50_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ResNet50_vd_infer/inference_cls.yaml --image ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/resnet50_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ResNet50_vd_infer/inference_cls.yaml --image ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
# The returned result.
|
||||||
ClassifyResult(
|
ClassifyResult(
|
||||||
label_ids: 153,
|
label_ids: 153,
|
||||||
scores: 0.684570,
|
scores: 0.684570,
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [ResNet50_vd C++部署](../cpp)
|
- [ResNet50_vd C++ Deployment](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [转换ResNet50_vd SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Converting ResNet50_vd SOPHGO model](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleClas Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 ResNet50_vd 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/classification/paddleclas/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas/raw/release/2.4/deploy/images/ImageNet/ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/resnet50_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ResNet50_vd_infer/inference_cls.yaml --image ILSVRC2012_val_00000010.jpeg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
||||||
|
ClassifyResult(
|
||||||
|
label_ids: 153,
|
||||||
|
scores: 0.684570,
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
- [ResNet50_vd C++部署](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [转换ResNet50_vd SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,52 +1,53 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv5 SOPHGO部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 SOPHGO Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 支持模型列表
|
## Supporting Model List
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
YOLOv5 v6.0部署模型实现来自[YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v6.0),和[基于COCO的预训练模型](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.0)
|
For YOLOv5 v6.0 model deployment, please refer to [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v6.0) and [Pretrained model based on COCO](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.0).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 准备YOLOv5部署模型以及转换模型
|
## Preparing YOLOv5 Model Deployment and Conversion
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
Before deploying SOPHGO-TPU model, you need to first convert Paddle model to bmodel. Specific steps are as follows:
|
||||||
- 下载预训练ONNX模型,请参考[YOLOv5准备部署模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/vision/detection/yolov5)
|
- Download the pre-trained ONNX model. Please refer to [YOLOv5 Ready-to-deploy Model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/vision/detection/yolov5).
|
||||||
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)
|
- Convert ONNX model to bmodel. Please refer to [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型转换example
|
## Model conversion example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
下面以YOLOv5s为例子,教大家如何转换ONNX模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型
|
Here we take YOLOv5s as an example to show you how to convert ONNX model to SOPHGO-TPU model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 下载YOLOv5s模型
|
## Download YOLOv5s Model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 下载ONNX YOLOv5s静态图模型
|
### Download ONNX YOLOv5s Static Map Model
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov5s.onnx
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
### 导出bmodel模型
|
### Export bmodel Model
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以转化BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
Here we take BM1684x bmodel as an example. You need to download [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir) project. For the installing process, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
### 1. 安装
|
### 1. Installation
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
# myname1234 is just an example, you can customize your own name.
|
||||||
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
source ./envsetup.sh
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
./build.sh
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
### 2. Convert ONNX model to bmodel
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
mkdir YOLOv5s && cd YOLOv5s
|
mkdir YOLOv5s && cd YOLOv5s
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步下载的yolov5s.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
# Put the test image in this file, and put the yolov5s.onnx into this folder.
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
# 放入onnx模型文件yolov5s.onnx
|
# Put in the onnx model file yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
# Convert ONNX model to mlir model, the parameter --output_names can be viewed via NETRON.
|
||||||
model_transform.py \
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
--model_name yolov5s \
|
--model_name yolov5s \
|
||||||
--model_def ../yolov5s.onnx \
|
--model_def ../yolov5s.onnx \
|
||||||
@@ -60,7 +61,7 @@ model_transform.py \
|
|||||||
--test_result yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_result yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--mlir yolov5s.mlir
|
--mlir yolov5s.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
# Convert mlir model to BM1684x F32 bmodel.
|
||||||
model_deploy.py \
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
--mlir yolov5s.mlir \
|
--mlir yolov5s.mlir \
|
||||||
--quantize F32 \
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
@@ -69,7 +70,7 @@ model_deploy.py \
|
|||||||
--test_reference yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_reference yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--model yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
--model yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
The final bmodel, yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel, can run on BM1684x. If you want to further accelerate the model, you can convert ONNX model to INT8 bmodel. For details, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其他链接
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
- [Cpp Deployment](./cpp)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
76
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/README_CN.md
Normal file
76
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 SOPHGO部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 支持模型列表
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
YOLOv5 v6.0部署模型实现来自[YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v6.0),和[基于COCO的预训练模型](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.0)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 准备YOLOv5部署模型以及转换模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
||||||
|
- 下载预训练ONNX模型,请参考[YOLOv5准备部署模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/vision/detection/yolov5)
|
||||||
|
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型转换example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下面以YOLOv5s为例子,教大家如何转换ONNX模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 下载YOLOv5s模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 下载ONNX YOLOv5s静态图模型
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
### 导出bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以转化BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
### 1. 安装
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
||||||
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
mkdir YOLOv5s && cd YOLOv5s
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步下载的yolov5s.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
|
# 放入onnx模型文件yolov5s.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
||||||
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
|
--model_name yolov5s \
|
||||||
|
--model_def ../yolov5s.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--input_shapes [[1,3,640,640]] \
|
||||||
|
--mean 0.0,0.0,0.0 \
|
||||||
|
--scale 0.0039216,0.0039216,0.0039216 \
|
||||||
|
--keep_aspect_ratio \
|
||||||
|
--pixel_format rgb \
|
||||||
|
--output_names output,350,498,646 \
|
||||||
|
--test_input ../image/dog.jpg \
|
||||||
|
--test_result yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--mlir yolov5s.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
|
--mlir yolov5s.mlir \
|
||||||
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
|
--chip bm1684x \
|
||||||
|
--test_input yolov5s_in_f32.npz \
|
||||||
|
--test_reference yolov5s_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--model yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其他链接
|
||||||
|
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
||||||
@@ -1,43 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv5 C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成yolov5s模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
`infer.cc` in this directory provides a quick example of accelerated deployment of the yolov5s model on SOPHGO BM1684x.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Before deployment, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Compile the FastDeploy repository from scratch according to the development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
For the above steps, please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate Basic Directory Files
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
The routine consists of the following parts:
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile Folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # Folder for images
|
||||||
├── infer.cc
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
└── model # Folder for models
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and Copy SDK to folder thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
Please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md) to compile SDK.After compiling, the fastdeploy-0.0.3 directory will be created in the build directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy model and configuration files to folder Model
|
||||||
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
Convert Paddle model to SOPHGO bmodel model. For the conversion steps, please refer to [Document](../README.md).
|
||||||
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
Please copy the converted SOPHGO bmodel to folder model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare Test Images to folder image
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compile example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -45,12 +46,12 @@ cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
|||||||
make
|
make
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running Routines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
./infer_demo model images/000000014439.jpg
|
./infer_demo model images/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
- [Model Description](../../)
|
||||||
- [模型转换](../)
|
- [Model Conversion](../)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
57
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
57
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/cpp/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成yolov5s模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
|
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
cp 000000014439.jpg ./images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
||||||
|
make
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo model images/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
||||||
|
- [模型转换](../)
|
||||||
@@ -1,23 +1,24 @@
|
|||||||
# YOLOv5 Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before deployment, the following step need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirement](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 YOLOv5 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
`infer.py` in this directory provides a quick example of deployment of the YOLOv5 model on SOPHGO TPU. Please run the following script:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the sample deployment code.
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images.
|
||||||
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference.
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel --image 000000014439.jpg
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel --image 000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
# The returned result.
|
||||||
DetectionResult: [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, score, label_id]
|
DetectionResult: [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, score, label_id]
|
||||||
268.480255,81.053055, 298.694794, 169.439026, 0.896569, 0
|
268.480255,81.053055, 298.694794, 169.439026, 0.896569, 0
|
||||||
104.731163,45.661972, 127.583824, 93.449387, 0.869531, 0
|
104.731163,45.661972, 127.583824, 93.449387, 0.869531, 0
|
||||||
@@ -41,6 +42,6 @@ DetectionResult: [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, score, label_id]
|
|||||||
101.406250,152.562500, 118.890625, 169.140625, 0.253891, 24
|
101.406250,152.562500, 118.890625, 169.140625, 0.253891, 24
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [YOLOv5 C++部署](../cpp)
|
- [YOLOv5 C++ Deployment](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [转换YOLOv5 SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Converting YOLOv5 SOPHGO model](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
47
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
47
examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/python/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv5 Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 YOLOv5 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/detection/yolov5/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleDetection/raw/release/2.4/demo/000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/yolov5s_1684x_f32.bmodel --image 000000014439.jpg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
||||||
|
DetectionResult: [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, score, label_id]
|
||||||
|
268.480255,81.053055, 298.694794, 169.439026, 0.896569, 0
|
||||||
|
104.731163,45.661972, 127.583824, 93.449387, 0.869531, 0
|
||||||
|
378.909363,39.750137, 395.608643, 84.243454, 0.868430, 0
|
||||||
|
158.552979,80.361511, 199.185760, 168.181915, 0.842988, 0
|
||||||
|
414.375305,90.948090, 506.321899, 280.405182, 0.835842, 0
|
||||||
|
364.003448,56.608932, 381.978607, 115.968216, 0.815136, 0
|
||||||
|
351.725128,42.635330, 366.910309, 98.048386, 0.808936, 0
|
||||||
|
505.888306,114.366791, 593.124878, 275.995270, 0.801361, 0
|
||||||
|
327.708618,38.363693, 346.849915, 80.893021, 0.794725, 0
|
||||||
|
583.493408,114.532883, 612.354614, 175.873535, 0.760649, 0
|
||||||
|
186.470657,44.941360, 199.664505, 61.037643, 0.632591, 0
|
||||||
|
169.615891,48.014603, 178.141556, 60.888596, 0.613938, 0
|
||||||
|
25.810200,117.199692, 59.888783, 152.850128, 0.590614, 0
|
||||||
|
352.145294,46.712723, 381.946075, 106.752151, 0.505329, 0
|
||||||
|
1.875000,150.734375, 37.968750, 173.781250, 0.404573, 24
|
||||||
|
464.657288,15.901413, 472.512939, 34.116409, 0.346033, 0
|
||||||
|
64.625000,135.171875, 84.500000, 154.406250, 0.332831, 24
|
||||||
|
57.812500,151.234375, 103.000000, 174.156250, 0.332566, 24
|
||||||
|
165.906250,88.609375, 527.906250, 339.953125, 0.259424, 33
|
||||||
|
101.406250,152.562500, 118.890625, 169.140625, 0.253891, 24
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
- [YOLOv5 C++部署](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [转换YOLOv5 SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# PP-LiteSeg 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PP-LiteSeg Quantized Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型在 A311D 上的部署推理加速。
|
`infer.cc` in this directory can help you quickly complete the inference acceleration of PP-LiteSeg quantization model deployment on A311D.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Deployment Preparations
|
||||||
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Cross-compile Environment Preparations
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/a311d.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
1. For the software and hardware environment, and the cross-compile environment, please refer to [FastDeploy Cross-compile environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/a311d.md#Cross-compilation-environment-construction)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 模型准备
|
### Model Preparations
|
||||||
1. 用户可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署。
|
1. You can directly use the quantized model provided by FastDeploy for deployment.
|
||||||
2. 用户可以使用 FastDeploy 提供的一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的 deploy.yaml 文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此 yaml 文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
2. You can use one-click automatical compression tool provided by FastDeploy to quantize model by yourself, and use the generated quantized model for deployment.(Note: The quantized classification model still needs the deploy.yaml file in the FP32 model folder. Self-quantized model folder does not contain this yaml file, you can copy it from the FP32 model folder to the quantized model folder.)
|
||||||
3. 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
3. The model requires heterogeneous computation. Please refer to: [Heterogeneous Computation](./../../../../../../docs/en/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md). Since the model is already provided, you can test the heterogeneous file we provide first to verify whether the accuracy meets the requirements.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
For more information, please refer to [Model Quantization](../../quantize/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 在 A311D 上部署量化后的 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型
|
## Deploying the Quantized PP-LiteSeg Segmentation model on A311D
|
||||||
请按照以下步骤完成在 A311D 上部署 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型:
|
Please follow these steps to complete the deployment of the PP-LiteSeg quantization model on A311D.
|
||||||
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/a311d.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
1. Cross-compile the FastDeploy library as described in [Cross-compile FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/a311d.md#FastDeploy-cross-compilation-library-compilation-based-on-Paddle-Lite)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
2. Copy the compiled library to the current directory. You can run this line:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
3. Download the model and example images required for deployment in current path.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
@@ -33,26 +34,26 @@ wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
|||||||
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
4. Compile the deployment example. You can run the following lines:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
mkdir build && cd build
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=arm64 ..
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=arm64 ..
|
||||||
make -j8
|
make -j8
|
||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
# After success, an install folder will be created with a running demo and libraries required for deployment.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型到晶晨 A311D,可使用如下命令:
|
5. Deploy the PP-LiteSeg segmentation model to A311D based on adb. You can run the following lines:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 进入 install 目录
|
# Go to the install directory.
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp/build/install/
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
# The following line represents: bash run_with_adb.sh, demo needed to run, model path, image path, DEVICE ID.
|
||||||
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
部署成功后运行结果如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
需要特别注意的是,在 A311D 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
Please note that the model deployed on A311D needs to be quantized. You can refer to [Model Quantization](../../../../../../docs/en/quantize.md).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PP-LiteSeg 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型在 A311D 上的部署推理加速。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/a311d.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 模型准备
|
||||||
|
1. 用户可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署。
|
||||||
|
2. 用户可以使用 FastDeploy 提供的一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的 deploy.yaml 文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此 yaml 文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
||||||
|
3. 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 在 A311D 上部署量化后的 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型
|
||||||
|
请按照以下步骤完成在 A311D 上部署 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型:
|
||||||
|
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/a311d.md#基于-paddle-lite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/rk1/ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
cp -r ppliteseg models
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp
|
||||||
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=arm64 ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型到晶晨 A311D,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 进入 install 目录
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/a311d/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
|
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
部署成功后运行结果如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
需要特别注意的是,在 A311D 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,97 +1,98 @@
|
|||||||
# 目标检测 PaddleSeg Android Demo 使用文档
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Android Demo for Target Detection
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在 Android 上实现实时的人像分割功能,此 Demo 有很好的的易用性和开放性,如在 Demo 中跑自己训练好的模型等。
|
For real-time portrait segmentation on Android, this demo has good ease of use and openness. You can run your own training model in the demo.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 环境准备
|
## Environment Preparations
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 在本地环境安装好 Android Studio 工具,详细安装方法请见[Android Stuido 官网](https://developer.android.com/studio)。
|
1. Install the Android Studio tool locally, for details see [Android Stuido official website](https://developer.android.com/studio).
|
||||||
2. 准备一部 Android 手机,并开启 USB 调试模式。开启方法: `手机设置 -> 查找开发者选项 -> 打开开发者选项和 USB 调试模式`
|
2. Get an Android phone and turn on USB debugging mode. How to turn on: ` Phone Settings -> Find Developer Options -> Turn on Developer Options and USB Debug Mode`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署步骤
|
## Deployment Steps
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 目标检测 PaddleSeg Demo 位于 `fastdeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/android` 目录
|
1. Target detection PaddleSeg Demo is located in `fastdeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/android` directory.
|
||||||
2. 用 Android Studio 打开 paddleseg/android 工程
|
2. Please use Android Studio to open paddleseg/android project.
|
||||||
3. 手机连接电脑,打开 USB 调试和文件传输模式,并在 Android Studio 上连接自己的手机设备(手机需要开启允许从 USB 安装软件权限)
|
3. Connect your phone to your computer, turn on USB debugging and file transfer mode, and connect your own mobile device on Android Studio (your phone needs to be enabled to allow software installation from USB).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center">
|
<p align="center">
|
||||||
<img width="1440" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203257262-71b908ab-bb2b-47d3-9efb-67631687b774.png">
|
<img width="1440" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203257262-71b908ab-bb2b-47d3-9efb-67631687b774.png">
|
||||||
</p>
|
</p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> **注意:**
|
> **Notes:**
|
||||||
>> 如果您在导入项目、编译或者运行过程中遇到 NDK 配置错误的提示,请打开 ` File > Project Structure > SDK Location`,修改 `Andriod SDK location` 为您本机配置的 SDK 所在路径。
|
>> If you encounter an NDK configuration error during importing, compiling or running the program, please open ` File > Project Structure > SDK Location` and change `Andriod SDK location` to your locally configured SDK path.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. 点击 Run 按钮,自动编译 APP 并安装到手机。(该过程会自动下载预编译的 FastDeploy Android 库 以及 模型文件,需要联网)
|
4. Click the Run button to automatically compile the APP and install it to your phone. (The process will automatically download the pre-compiled FastDeploy Android library and model files, internet connection required.)
|
||||||
成功后效果如下,图一:APP 安装到手机;图二: APP 打开后的效果,会自动识别图片中的人物并绘制mask;图三:APP设置选项,点击右上角的设置图片,可以设置不同选项进行体验。
|
The success interface is as follows. Figure 1: Install APP on phone; Figure 2: The opening interface, it will automatically recognize the person in the picture and draw the mask; Figure 3: APP setting options, click setting in the upper right corner, and you can set different options.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| APP 图标 | APP 效果 | APP设置项
|
| APP icon | APP effect | APP setting options
|
||||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||||
| <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203268599-c94018d8-3683-490a-a5c7-a8136a4fa284.jpg"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203267867-7c51b695-65e6-402e-9826-5d6d5864da87.gif"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/197332983-afbfa6d5-4a3b-4c54-a528-4a3e58441be1.jpg"> |
|
| <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203268599-c94018d8-3683-490a-a5c7-a8136a4fa284.jpg"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203267867-7c51b695-65e6-402e-9826-5d6d5864da87.gif"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/197332983-afbfa6d5-4a3b-4c54-a528-4a3e58441be1.jpg"> |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## PaddleSegModel Java API 说明
|
## PaddleSegModel Java API Introduction
|
||||||
- 模型初始化 API: 模型初始化API包含两种方式,方式一是通过构造函数直接初始化;方式二是,通过调用init函数,在合适的程序节点进行初始化。PaddleSegModel初始化参数说明如下:
|
- Model initialization API: Model initialization API contains two methods, you can initialize directly through the constructor, or call init function at the appropriate program node. PaddleSegModel initialization parameters are described as follows:
|
||||||
- modelFile: String, paddle格式的模型文件路径,如 model.pdmodel
|
- modelFile: String, path to the model file in paddle format, e.g. model.pdmodel.
|
||||||
- paramFile: String, paddle格式的参数文件路径,如 model.pdiparams
|
- paramFile: String, path to the parameter file in paddle format, e.g. model.pdiparams.
|
||||||
- configFile: String, 模型推理的预处理配置文件,如 deploy.yml
|
- configFile: String, preprocessing configuration file of model inference, e.g. deploy.yml.
|
||||||
- option: RuntimeOption,可选参数,模型初始化option。如果不传入该参数则会使用默认的运行时选项。
|
- option: RuntimeOption, optional, model initialization option. If this parameter is not passed, the default runtime option will be used.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
// 构造函数: constructor w/o label file
|
// Constructor w/o label file
|
||||||
public PaddleSegModel(); // 空构造函数,之后可以调用init初始化
|
public PaddleSegModel(); // An empty constructor, which can be initialised by calling init function later.
|
||||||
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile);
|
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile);
|
||||||
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
||||||
// 手动调用init初始化: call init manually w/o label file
|
// Call init manually w/o label file
|
||||||
public boolean init(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
public boolean init(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
- 模型预测 API:模型预测API包含直接预测的API以及带可视化功能的API。直接预测是指,不保存图片以及不渲染结果到Bitmap上,仅预测推理结果。预测并且可视化是指,预测结果以及可视化,并将可视化后的图片保存到指定的途径,以及将可视化结果渲染在Bitmap(目前支持ARGB8888格式的Bitmap), 后续可将该Bitmap在camera中进行显示。
|
- Model prediction API: Model prediction API includes direct prediction API and API with visualization function. Direct prediction means that no image is saved and no result is rendered to Bitmap, but only the inference result is predicted. Prediction and visualization means to predict the result and visualize it, and save the visualized image to the specified path, and render the result to Bitmap (currently supports Bitmap in format ARGB8888), which can be displayed in camera later.
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
// 直接预测:不保存图片以及不渲染结果到Bitmap上
|
// Directly predict: do not save images or render result to Bitmap.
|
||||||
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap);
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap);
|
||||||
// 预测并且可视化:预测结果以及可视化,并将可视化后的图片保存到指定的途径,以及将可视化结果渲染在Bitmap上
|
// Predict and visualize: predict the result and visualize it, and save the visualized image to the specified path, and render the result to Bitmap.
|
||||||
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
||||||
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, boolean rendering, float weight); // 只渲染 不保存图片
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, boolean rendering, float weight); // Only rendering images without saving.
|
||||||
// 修改result,而非返回result,关注性能的用户可以将以下接口与SegmentationResult的CxxBuffer一起使用
|
// Modify result, but not return it. Concerning performance, you can use the following interface with CxxBuffer in SegmentationResult.
|
||||||
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result);
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result);
|
||||||
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
||||||
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, boolean rendering, float weight);
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, boolean rendering, float weight);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
- 设置竖屏或横屏模式: 对于 PP-HumanSeg系列模型,必须要调用该方法设置竖屏模式为true.
|
- Set vertical or horizontal mode: For PP-HumanSeg series model, you should call this method to set the vertical mode to true.
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
public void setVerticalScreenFlag(boolean flag);
|
public void setVerticalScreenFlag(boolean flag);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
- 模型资源释放 API:调用 release() API 可以释放模型资源,返回true表示释放成功,false表示失败;调用 initialized() 可以判断模型是否初始化成功,true表示初始化成功,false表示失败。
|
- Model resource release API: Calling function release() API can release model resources, and true means successful release, false means failure. Calling function initialized() can determine whether the model is initialized successfully, and true means successful initialization, false means failure.
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
public boolean release(); // 释放native资源
|
public boolean release(); // Release native resources.
|
||||||
public boolean initialized(); // 检查是否初始化成功
|
public boolean initialized(); // Check if initialization is successful.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- RuntimeOption设置说明
|
- Runtime Option Setting
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
public void enableLiteFp16(); // 开启fp16精度推理
|
public void enableLiteFp16(); // Enable fp16 precision inference
|
||||||
public void disableLiteFP16(); // 关闭fp16精度推理
|
public void disableLiteFP16(); // Disable fp16 precision inference
|
||||||
public void setCpuThreadNum(int threadNum); // 设置线程数
|
public void setCpuThreadNum(int threadNum); // Set number of threads.
|
||||||
public void setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode mode); // 设置能耗模式
|
public void setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode mode); // Set power mode.
|
||||||
public void setLitePowerMode(String modeStr); // 通过字符串形式设置能耗模式
|
public void setLitePowerMode(String modeStr); // Set power mode by string.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 模型结果SegmentationResult说明
|
- Segmentation Result
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
public class SegmentationResult {
|
public class SegmentationResult {
|
||||||
public int[] mLabelMap; // 预测到的label map 每个像素位置对应一个label HxW
|
public int[] mLabelMap; // The predicted label map, each pixel position corresponds to a label HxW.
|
||||||
public float[] mScoreMap; // 预测到的得分 map 每个像素位置对应一个score HxW
|
public float[] mScoreMap; // The predicted score map, each pixel position corresponds to a score HxW.
|
||||||
public long[] mShape; // label map实际的shape (H,W)
|
public long[] mShape; // The real shape(H,W) of label map.
|
||||||
public boolean mContainScoreMap = false; // 是否包含 score map
|
public boolean mContainScoreMap = false; // Whether score map is included.
|
||||||
// 用户可以选择直接使用CxxBuffer,而非通过JNI拷贝到Java层,
|
// You can choose to use CxxBuffer directly instead of copying it to JAVA layer through JNI.
|
||||||
// 该方式可以一定程度上提升性能
|
// This method can improve performance to some extent.
|
||||||
public void setCxxBufferFlag(boolean flag); // 设置是否为CxxBuffer模式
|
public void setCxxBufferFlag(boolean flag); // Set whether the mode is CxxBuffer.
|
||||||
public boolean releaseCxxBuffer(); // 手动释放CxxBuffer!!!
|
public boolean releaseCxxBuffer(); // Release CxxBuffer manually!!!
|
||||||
public boolean initialized(); // 检测结果是否有效
|
public boolean initialized(); // Check if the result is valid.
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
其他参考:C++/Python对应的SegmentationResult说明: [api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md)
|
Other reference: C++/Python corresponding SegmentationResult description: [api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 模型调用示例1:使用构造函数以及默认的RuntimeOption
|
- Model calling example 1: Using constructor and the default RuntimeOption:
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
|
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
|
||||||
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
|
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
|
||||||
@@ -100,77 +101,77 @@ import android.opengl.GLES20;
|
|||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 初始化模型
|
// Initialise model.
|
||||||
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel(
|
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel(
|
||||||
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel",
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel",
|
||||||
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams",
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams",
|
||||||
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml");
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 如果摄像头为竖屏模式,PP-HumanSeg系列需要设置改标记
|
// If the camera is in portrait mode, the PP-HumanSeg series needs to change the mark.
|
||||||
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 读取图片: 以下仅为读取Bitmap的伪代码
|
// Read Bitmaps: The following is the pseudo code of reading the Bitmap.
|
||||||
ByteBuffer pixelBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(width * height * 4);
|
ByteBuffer pixelBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(width * height * 4);
|
||||||
GLES20.glReadPixels(0, 0, width, height, GLES20.GL_RGBA, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixelBuffer);
|
GLES20.glReadPixels(0, 0, width, height, GLES20.GL_RGBA, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixelBuffer);
|
||||||
Bitmap ARGB8888ImageBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
|
Bitmap ARGB8888ImageBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
|
||||||
ARGB8888ImageBitmap.copyPixelsFromBuffer(pixelBuffer);
|
ARGB8888ImageBitmap.copyPixelsFromBuffer(pixelBuffer);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 模型推理
|
// Model inference.
|
||||||
SegmentationResult result = new SegmentationResult();
|
SegmentationResult result = new SegmentationResult();
|
||||||
result.setCxxBufferFlag(true);
|
result.setCxxBufferFlag(true);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap, result);
|
model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap, result);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 释放CxxBuffer
|
// Release CxxBuffer.
|
||||||
result.releaseCxxBuffer();
|
result.releaseCxxBuffer();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 或直接预测返回 SegmentationResult
|
// Or return SegmentationResult directly.
|
||||||
SegmentationResult result = model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap);
|
SegmentationResult result = model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 释放模型资源
|
// Release model resources.
|
||||||
model.release();
|
model.release();
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 模型调用示例2: 在合适的程序节点,手动调用init,并自定义RuntimeOption
|
- Model calling example 2: Call init function manually at the appropriate program node and customize RuntimeOption.
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
// import 同上 ...
|
// import id.
|
||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.RuntimeOption;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.RuntimeOption;
|
||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.LitePowerMode;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.LitePowerMode;
|
||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
||||||
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
||||||
// 新建空模型
|
// Create empty model.
|
||||||
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel();
|
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel();
|
||||||
// 模型路径
|
// Model path.
|
||||||
String modelFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel";
|
String modelFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel";
|
||||||
String paramFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams";
|
String paramFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams";
|
||||||
String configFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml";
|
String configFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml";
|
||||||
// 指定RuntimeOption
|
// Specify RuntimeOption.
|
||||||
RuntimeOption option = new RuntimeOption();
|
RuntimeOption option = new RuntimeOption();
|
||||||
option.setCpuThreadNum(2);
|
option.setCpuThreadNum(2);
|
||||||
option.setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode.LITE_POWER_HIGH);
|
option.setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode.LITE_POWER_HIGH);
|
||||||
option.enableLiteFp16();
|
option.enableLiteFp16();
|
||||||
// 如果摄像头为竖屏模式,PP-HumanSeg系列需要设置改标记
|
// If the camera is in portrait mode, the PP-HumanSeg series needs to change the mark.
|
||||||
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
||||||
// 使用init函数初始化
|
// Initialise with the init function.
|
||||||
model.init(modelFile, paramFile, configFile, option);
|
model.init(modelFile, paramFile, configFile, option);
|
||||||
// Bitmap读取、模型预测、资源释放 同上 ...
|
// Read Bitmap, predict model, release resources, id.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
更详细的用法请参考 [SegmentationMainActivity](./app/src/main/java/com/baidu/paddle/fastdeploy/app/examples/segmentation/SegmentationMainActivity.java) 中的用法
|
For details, please refer to [SegmentationMainActivity](./app/src/main/java/com/baidu/paddle/fastdeploy/app/examples/segmentation/SegmentationMainActivity.java).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 替换 FastDeploy SDK和模型
|
## Replace FastDeploy SDK and model
|
||||||
替换FastDeploy预测库和模型的步骤非常简单。预测库所在的位置为 `app/libs/fastdeploy-android-sdk-xxx.aar`,其中 `xxx` 表示当前您使用的预测库版本号。模型所在的位置为,`app/src/main/assets/models/portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model`。
|
Steps to replace the FastDeploy prediction libraries and model are very simple. The location of the prediction library is `app/libs/fastdeploy-android-sdk-xxx.aar`, where `xxx` indicates the version of the prediction library you are currently using. The location of the model is, `app/src/main/assets/models/portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model`.
|
||||||
- 替换FastDeploy Android SDK: 下载或编译最新的FastDeploy Android SDK,解压缩后放在 `app/libs` 目录下;详细配置文档可参考:
|
- Replace FastDeploy Android SDK: Download or compile the latest FastDeploy Android SDK, unzip it and put it in the `app/libs` directory. For details please refer to:
|
||||||
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy Java SDK](../../../../../java/android/)
|
- [Use FastDeploy Java SDK on Android](../../../../../java/android/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 替换PaddleSeg模型的步骤:
|
- Steps for replacing the PaddleSeg model.
|
||||||
- 将您的PaddleSeg模型放在 `app/src/main/assets/models` 目录下;
|
- Put your PaddleSeg model in `app/src/main/assets/models`;
|
||||||
- 修改 `app/src/main/res/values/strings.xml` 中模型路径的默认值,如:
|
- Modify the model path in `app/src/main/res/values/strings.xml`, such as:
|
||||||
```xml
|
```xml
|
||||||
<!-- 将这个路径指修改成您的模型,如 models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model -->
|
<!-- Modify this path for your model, e.g. models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model -->
|
||||||
<string name="SEGMENTATION_MODEL_DIR_DEFAULT">models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model</string>
|
<string name="SEGMENTATION_MODEL_DIR_DEFAULT">models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model</string>
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 更多参考文档
|
## Other Documenets
|
||||||
如果您想知道更多的FastDeploy Java API文档以及如何通过JNI来接入FastDeploy C++ API感兴趣,可以参考以下内容:
|
If you are interested in more FastDeploy Java API documents and how to access the FastDeploy C++ API via JNI, you can refer to the following:
|
||||||
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy Java SDK](../../../../../java/android/)
|
- [Use FastDeploy Java SDK on Android](../../../../../java/android/)
|
||||||
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy C++ SDK](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/use_cpp_sdk_on_android.md)
|
- [Use FastDeploy C++ SDK on Android](../../../../../docs/en/faq/use_cpp_sdk_on_android.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
177
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/android/README_CN.md
Normal file
177
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/android/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# 目标检测 PaddleSeg Android Demo 使用文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在 Android 上实现实时的人像分割功能,此 Demo 有很好的的易用性和开放性,如在 Demo 中跑自己训练好的模型等。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 环境准备
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 在本地环境安装好 Android Studio 工具,详细安装方法请见[Android Stuido 官网](https://developer.android.com/studio)。
|
||||||
|
2. 准备一部 Android 手机,并开启 USB 调试模式。开启方法: `手机设置 -> 查找开发者选项 -> 打开开发者选项和 USB 调试模式`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 目标检测 PaddleSeg Demo 位于 `fastdeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/android` 目录
|
||||||
|
2. 用 Android Studio 打开 paddleseg/android 工程
|
||||||
|
3. 手机连接电脑,打开 USB 调试和文件传输模式,并在 Android Studio 上连接自己的手机设备(手机需要开启允许从 USB 安装软件权限)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<p align="center">
|
||||||
|
<img width="1440" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203257262-71b908ab-bb2b-47d3-9efb-67631687b774.png">
|
||||||
|
</p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> **注意:**
|
||||||
|
>> 如果您在导入项目、编译或者运行过程中遇到 NDK 配置错误的提示,请打开 ` File > Project Structure > SDK Location`,修改 `Andriod SDK location` 为您本机配置的 SDK 所在路径。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4. 点击 Run 按钮,自动编译 APP 并安装到手机。(该过程会自动下载预编译的 FastDeploy Android 库 以及 模型文件,需要联网)
|
||||||
|
成功后效果如下,图一:APP 安装到手机;图二: APP 打开后的效果,会自动识别图片中的人物并绘制mask;图三:APP设置选项,点击右上角的设置图片,可以设置不同选项进行体验。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| APP 图标 | APP 效果 | APP设置项
|
||||||
|
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||||
|
| <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203268599-c94018d8-3683-490a-a5c7-a8136a4fa284.jpg"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/203267867-7c51b695-65e6-402e-9826-5d6d5864da87.gif"> | <img width="300" height="500" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/31974251/197332983-afbfa6d5-4a3b-4c54-a528-4a3e58441be1.jpg"> |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PaddleSegModel Java API 说明
|
||||||
|
- 模型初始化 API: 模型初始化API包含两种方式,方式一是通过构造函数直接初始化;方式二是,通过调用init函数,在合适的程序节点进行初始化。PaddleSegModel初始化参数说明如下:
|
||||||
|
- modelFile: String, paddle格式的模型文件路径,如 model.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
- paramFile: String, paddle格式的参数文件路径,如 model.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
- configFile: String, 模型推理的预处理配置文件,如 deploy.yml
|
||||||
|
- option: RuntimeOption,可选参数,模型初始化option。如果不传入该参数则会使用默认的运行时选项。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 构造函数: constructor w/o label file
|
||||||
|
public PaddleSegModel(); // 空构造函数,之后可以调用init初始化
|
||||||
|
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile);
|
||||||
|
public PaddleSegModel(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
||||||
|
// 手动调用init初始化: call init manually w/o label file
|
||||||
|
public boolean init(String modelFile, String paramsFile, String configFile, RuntimeOption option);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
- 模型预测 API:模型预测API包含直接预测的API以及带可视化功能的API。直接预测是指,不保存图片以及不渲染结果到Bitmap上,仅预测推理结果。预测并且可视化是指,预测结果以及可视化,并将可视化后的图片保存到指定的途径,以及将可视化结果渲染在Bitmap(目前支持ARGB8888格式的Bitmap), 后续可将该Bitmap在camera中进行显示。
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 直接预测:不保存图片以及不渲染结果到Bitmap上
|
||||||
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap);
|
||||||
|
// 预测并且可视化:预测结果以及可视化,并将可视化后的图片保存到指定的途径,以及将可视化结果渲染在Bitmap上
|
||||||
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
||||||
|
public SegmentationResult predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, boolean rendering, float weight); // 只渲染 不保存图片
|
||||||
|
// 修改result,而非返回result,关注性能的用户可以将以下接口与SegmentationResult的CxxBuffer一起使用
|
||||||
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result);
|
||||||
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, String savedImagePath, float weight);
|
||||||
|
public boolean predict(Bitmap ARGB8888Bitmap, SegmentationResult result, boolean rendering, float weight);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
- 设置竖屏或横屏模式: 对于 PP-HumanSeg系列模型,必须要调用该方法设置竖屏模式为true.
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
public void setVerticalScreenFlag(boolean flag);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
- 模型资源释放 API:调用 release() API 可以释放模型资源,返回true表示释放成功,false表示失败;调用 initialized() 可以判断模型是否初始化成功,true表示初始化成功,false表示失败。
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
public boolean release(); // 释放native资源
|
||||||
|
public boolean initialized(); // 检查是否初始化成功
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- RuntimeOption设置说明
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
public void enableLiteFp16(); // 开启fp16精度推理
|
||||||
|
public void disableLiteFP16(); // 关闭fp16精度推理
|
||||||
|
public void setCpuThreadNum(int threadNum); // 设置线程数
|
||||||
|
public void setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode mode); // 设置能耗模式
|
||||||
|
public void setLitePowerMode(String modeStr); // 通过字符串形式设置能耗模式
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 模型结果SegmentationResult说明
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
public class SegmentationResult {
|
||||||
|
public int[] mLabelMap; // 预测到的label map 每个像素位置对应一个label HxW
|
||||||
|
public float[] mScoreMap; // 预测到的得分 map 每个像素位置对应一个score HxW
|
||||||
|
public long[] mShape; // label map实际的shape (H,W)
|
||||||
|
public boolean mContainScoreMap = false; // 是否包含 score map
|
||||||
|
// 用户可以选择直接使用CxxBuffer,而非通过JNI拷贝到Java层,
|
||||||
|
// 该方式可以一定程度上提升性能
|
||||||
|
public void setCxxBufferFlag(boolean flag); // 设置是否为CxxBuffer模式
|
||||||
|
public boolean releaseCxxBuffer(); // 手动释放CxxBuffer!!!
|
||||||
|
public boolean initialized(); // 检测结果是否有效
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
其他参考:C++/Python对应的SegmentationResult说明: [api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 模型调用示例1:使用构造函数以及默认的RuntimeOption
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
|
||||||
|
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
|
||||||
|
import android.opengl.GLES20;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 初始化模型
|
||||||
|
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel(
|
||||||
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel",
|
||||||
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams",
|
||||||
|
"portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 如果摄像头为竖屏模式,PP-HumanSeg系列需要设置改标记
|
||||||
|
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 读取图片: 以下仅为读取Bitmap的伪代码
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer pixelBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(width * height * 4);
|
||||||
|
GLES20.glReadPixels(0, 0, width, height, GLES20.GL_RGBA, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixelBuffer);
|
||||||
|
Bitmap ARGB8888ImageBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
|
||||||
|
ARGB8888ImageBitmap.copyPixelsFromBuffer(pixelBuffer);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 模型推理
|
||||||
|
SegmentationResult result = new SegmentationResult();
|
||||||
|
result.setCxxBufferFlag(true);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap, result);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 释放CxxBuffer
|
||||||
|
result.releaseCxxBuffer();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 或直接预测返回 SegmentationResult
|
||||||
|
SegmentationResult result = model.predict(ARGB8888ImageBitmap);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 释放模型资源
|
||||||
|
model.release();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 模型调用示例2: 在合适的程序节点,手动调用init,并自定义RuntimeOption
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// import 同上 ...
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.RuntimeOption;
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.LitePowerMode;
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.SegmentationResult;
|
||||||
|
import com.baidu.paddle.fastdeploy.vision.segmentation.PaddleSegModel;
|
||||||
|
// 新建空模型
|
||||||
|
PaddleSegModel model = new PaddleSegModel();
|
||||||
|
// 模型路径
|
||||||
|
String modelFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdmodel";
|
||||||
|
String paramFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/model.pdiparams";
|
||||||
|
String configFile = "portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model/deploy.yml";
|
||||||
|
// 指定RuntimeOption
|
||||||
|
RuntimeOption option = new RuntimeOption();
|
||||||
|
option.setCpuThreadNum(2);
|
||||||
|
option.setLitePowerMode(LitePowerMode.LITE_POWER_HIGH);
|
||||||
|
option.enableLiteFp16();
|
||||||
|
// 如果摄像头为竖屏模式,PP-HumanSeg系列需要设置改标记
|
||||||
|
model.setVerticalScreenFlag(true);
|
||||||
|
// 使用init函数初始化
|
||||||
|
model.init(modelFile, paramFile, configFile, option);
|
||||||
|
// Bitmap读取、模型预测、资源释放 同上 ...
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
更详细的用法请参考 [SegmentationMainActivity](./app/src/main/java/com/baidu/paddle/fastdeploy/app/examples/segmentation/SegmentationMainActivity.java) 中的用法
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 替换 FastDeploy SDK和模型
|
||||||
|
替换FastDeploy预测库和模型的步骤非常简单。预测库所在的位置为 `app/libs/fastdeploy-android-sdk-xxx.aar`,其中 `xxx` 表示当前您使用的预测库版本号。模型所在的位置为,`app/src/main/assets/models/portrait_pp_humansegv2_lite_256x144_inference_model`。
|
||||||
|
- 替换FastDeploy Android SDK: 下载或编译最新的FastDeploy Android SDK,解压缩后放在 `app/libs` 目录下;详细配置文档可参考:
|
||||||
|
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy Java SDK](../../../../../java/android/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 替换PaddleSeg模型的步骤:
|
||||||
|
- 将您的PaddleSeg模型放在 `app/src/main/assets/models` 目录下;
|
||||||
|
- 修改 `app/src/main/res/values/strings.xml` 中模型路径的默认值,如:
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<!-- 将这个路径指修改成您的模型,如 models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model -->
|
||||||
|
<string name="SEGMENTATION_MODEL_DIR_DEFAULT">models/human_pp_humansegv1_lite_192x192_inference_model</string>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 更多参考文档
|
||||||
|
如果您想知道更多的FastDeploy Java API文档以及如何通过JNI来接入FastDeploy C++ API感兴趣,可以参考以下内容:
|
||||||
|
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy Java SDK](../../../../../java/android/)
|
||||||
|
- [在 Android 中使用 FastDeploy C++ SDK](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/use_cpp_sdk_on_android.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,36 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg 量化模型部署
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
FastDeploy已支持部署量化模型,并提供一键模型自动化压缩的工具.
|
# PaddleSeg Quantized Model Deployment
|
||||||
用户可以使用一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行对模型量化后部署, 也可以直接下载FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
FastDeploy already supports the deployment of quantitative models and provides a tool to automatically compress model with just one click.
|
||||||
|
You can use the one-click automatical model compression tool to quantify and deploy the models, or directly download the quantified models provided by FastDeploy for deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## FastDeploy一键模型自动化压缩工具
|
## FastDeploy One-Click Automation Model Compression Tool
|
||||||
FastDeploy 提供了一键模型自动化压缩工具, 能够简单地通过输入一个配置文件, 对模型进行量化.
|
FastDeploy provides an one-click automatical model compression tool that can quantify a model simply by entering configuration file.
|
||||||
详细教程请见: [一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/)
|
For details, please refer to [one-click automatical compression tool](../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/).
|
||||||
注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可。
|
Note: The quantized classification model still needs the deploy.yaml file in the FP32 model folder. Self-quantized model folder does not contain this yaml file, you can copy it from the FP32 model folder to the quantized model folder.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 下载量化完成的PaddleSeg模型
|
## Download the Quantized PaddleSeg Model
|
||||||
用户也可以直接下载下表中的量化模型进行部署.(点击模型名字即可下载)
|
You can also directly download the quantized models in the following table for deployment (click model name to download).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Benchmark表格说明:
|
Note:
|
||||||
- Runtime时延为模型在各种Runtime上的推理时延,包含CPU->GPU数据拷贝,GPU推理,GPU->CPU数据拷贝时间. 不包含模型各自的前后处理时间.
|
- Runtime latency is the inference latency of the model on various Runtimes, including CPU->GPU data copy, GPU inference, and GPU->CPU data copy time. It does not include the respective pre and post processing time of the models.
|
||||||
- 端到端时延为模型在实际推理场景中的时延, 包含模型的前后处理.
|
- The end-to-end latency is the latency of the model in the actual inference scenario, including the pre and post processing of the model.
|
||||||
- 所测时延均为推理1000次后求得的平均值, 单位是毫秒.
|
- The measured latencies are averaged over 1000 inferences, in milliseconds.
|
||||||
- INT8 + FP16 为在推理INT8量化模型的同时, 给Runtime 开启FP16推理选项
|
- INT8 + FP16 is to enable the FP16 inference option for Runtime while inferring the INT8 quantization model.
|
||||||
- INT8 + FP16 + PM, 为在推理INT8量化模型和开启FP16的同时, 开启使用Pinned Memory的选项,可加速GPU->CPU数据拷贝的速度
|
- INT8 + FP16 + PM is the option to use Pinned Memory while inferring INT8 quantization model and turning on FP16, which can speed up the GPU->CPU data copy speed.
|
||||||
- 最大加速比, 为FP32时延除以INT8推理的最快时延,得到最大加速比.
|
- The maximum speedup ratio is obtained by dividing the FP32 latency by the fastest INT8 inference latency.
|
||||||
- 策略为量化蒸馏训练时, 采用少量无标签数据集训练得到量化模型, 并在全量验证集上验证精度, INT8精度并不代表最高的INT8精度.
|
- The strategy is quantitative distillation training, using a small number of unlabeled data sets to train the quantitative model, and verify the accuracy on the full validation set, INT8 accuracy does not represent the highest INT8 accuracy.
|
||||||
- CPU为Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6271C, 所有测试中固定CPU线程数为1. GPU为Tesla T4, TensorRT版本8.4.15.
|
- The CPU is Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6271C with a fixed CPU thread count of 1 in all tests. The GPU is Tesla T4, TensorRT version 8.4.15.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Runtime Benchmark
|
#### Runtime Benchmark
|
||||||
| 模型 |推理后端 |部署硬件 | FP32 Runtime时延 | INT8 Runtime时延 | INT8 + FP16 Runtime时延 | INT8+FP16+PM Runtime时延 | 最大加速比 | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | 量化方式 |
|
| Model |Inference Backends | Hardware | FP32 Runtime Latency | INT8 Runtime Latency | INT8 + FP16 Runtime Latency | INT8+FP16+PM Runtime Latency | Max Speedup | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | Method |
|
||||||
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
||||||
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar)) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 1138.04| 602.62 |None|None | 1.89 |77.37 | 71.62 |量化蒸馏训练 |
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 1138.04| 602.62 |None|None | 1.89 |77.37 | 71.62 |Quantaware Distillation Training |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### 端到端 Benchmark
|
#### End to End Benchmark
|
||||||
| 模型 |推理后端 |部署硬件 | FP32 End2End时延 | INT8 End2End时延 | INT8 + FP16 End2End时延 | INT8+FP16+PM End2End时延 | 最大加速比 | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | 量化方式 |
|
| Model |Inference Backends | Hardware | FP32 End2End Latency | INT8 End2End Latency | INT8 + FP16 End2End Latency | INT8+FP16+PM End2End Latency | Max Speedup | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | Method |
|
||||||
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
||||||
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar)) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 4726.65| 4134.91|None|None | 1.14 |77.37 | 71.62 |量化蒸馏训练 |
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 4726.65| 4134.91|None|None | 1.14 |77.37 | 71.62 |Quantaware Distillation Training|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 详细部署文档
|
## Detailed Deployment Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [Python部署](python)
|
- [Python Deployment](python)
|
||||||
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
- [C++ Deployment](cpp)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
37
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/quantize/README_CN.md
Normal file
37
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/quantize/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg 量化模型部署
|
||||||
|
FastDeploy已支持部署量化模型,并提供一键模型自动化压缩的工具.
|
||||||
|
用户可以使用一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行对模型量化后部署, 也可以直接下载FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## FastDeploy一键模型自动化压缩工具
|
||||||
|
FastDeploy 提供了一键模型自动化压缩工具, 能够简单地通过输入一个配置文件, 对模型进行量化.
|
||||||
|
详细教程请见: [一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/)
|
||||||
|
注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 下载量化完成的PaddleSeg模型
|
||||||
|
用户也可以直接下载下表中的量化模型进行部署.(点击模型名字即可下载)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Benchmark表格说明:
|
||||||
|
- Runtime时延为模型在各种Runtime上的推理时延,包含CPU->GPU数据拷贝,GPU推理,GPU->CPU数据拷贝时间. 不包含模型各自的前后处理时间.
|
||||||
|
- 端到端时延为模型在实际推理场景中的时延, 包含模型的前后处理.
|
||||||
|
- 所测时延均为推理1000次后求得的平均值, 单位是毫秒.
|
||||||
|
- INT8 + FP16 为在推理INT8量化模型的同时, 给Runtime 开启FP16推理选项
|
||||||
|
- INT8 + FP16 + PM, 为在推理INT8量化模型和开启FP16的同时, 开启使用Pinned Memory的选项,可加速GPU->CPU数据拷贝的速度
|
||||||
|
- 最大加速比, 为FP32时延除以INT8推理的最快时延,得到最大加速比.
|
||||||
|
- 策略为量化蒸馏训练时, 采用少量无标签数据集训练得到量化模型, 并在全量验证集上验证精度, INT8精度并不代表最高的INT8精度.
|
||||||
|
- CPU为Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6271C, 所有测试中固定CPU线程数为1. GPU为Tesla T4, TensorRT版本8.4.15.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Runtime Benchmark
|
||||||
|
| 模型 |推理后端 |部署硬件 | FP32 Runtime时延 | INT8 Runtime时延 | INT8 + FP16 Runtime时延 | INT8+FP16+PM Runtime时延 | 最大加速比 | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | 量化方式 |
|
||||||
|
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 1138.04| 602.62 |None|None | 1.89 |77.37 | 71.62 |量化蒸馏训练 |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 端到端 Benchmark
|
||||||
|
| 模型 |推理后端 |部署硬件 | FP32 End2End时延 | INT8 End2End时延 | INT8 + FP16 End2End时延 | INT8+FP16+PM End2End时延 | 最大加速比 | FP32 mIoU | INT8 mIoU | 量化方式 |
|
||||||
|
| ------------------- | -----------------|-----------| -------- |-------- |-------- | --------- |-------- |----- |----- |----- |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT_new.tar) | Paddle Inference | CPU | 4726.65| 4134.91|None|None | 1.14 |77.37 | 71.62 |量化蒸馏训练 |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 详细部署文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](python)
|
||||||
|
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
||||||
@@ -1,31 +1,32 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg 量化模型 C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成PaddleSeg量化模型在CPU上的部署推理加速.
|
# PaddleSeg Quantitative Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
`infer.cc` in this directory can help you quickly complete the inference acceleration of PaddleSeg quantization model deployment on CPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Deployment Preparations
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparations
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. For the software and hardware requirements, please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. For the installation of FastDeploy Python whl package, please refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Quantized Model Preparations
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. You can directly use the quantized model provided by FastDeploy for deployment.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
- 2. You can use [one-click automatical compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to quantize model by yourself, and use the generated quantized model for deployment.(Note: The quantized classification model still needs the deploy.yaml file in the FP32 model folder. Self-quantized model folder does not contain this yaml file, you can copy it from the FP32 model folder to the quantized model folder.)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Take the Quantized PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes Model as an example for Deployment
|
||||||
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
Run the following commands in this directory to compile and deploy the quantized model. FastDeploy version 0.7.0 or higher is required (x.x.x>=0.7.0).
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
# Download pre-compiled FastDeploy libraries. You can choose the appropriate version from `pre-compiled FastDeploy libraries` mentioned above.
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
make -j
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download the PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes quantized model and test images provided by FastDeloy.
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用Paddle-Inference推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-Inference inference quantization model on CPU.
|
||||||
./infer_demo PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ cityscapes_demo.png 1
|
./infer_demo PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ cityscapes_demo.png 1
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg 量化模型 C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成PaddleSeg量化模型在CPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
在本目录执行如下命令即可完成编译,以及量化模型部署.支持此模型需保证FastDeploy版本0.7.0以上(x.x.x>=0.7.0)
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
# 下载FastDeploy预编译库,用户可在上文提到的`FastDeploy预编译库`中自行选择合适的版本使用
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/release/cpp/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x.tgz
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-linux-x64-x.x.x
|
||||||
|
make -j
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载FastDeloy提供的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用Paddle-Inference推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ cityscapes_demo.png 1
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg 量化模型 Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成PaddleSeg量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
# PaddleSeg Quantitative Model Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
`infer.py` in this directory can help you quickly complete the inference acceleration of PaddleSeg quantization model deployment on CPU/GPU.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Deployment Preparations
|
||||||
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Environment Preparations
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 1. For the software and hardware requirements, please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirements](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
- 2. For the installation of FastDeploy Python whl package, please refer to [FastDeploy Python Installation](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 量化模型准备
|
### Quantized Model Preparations
|
||||||
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
- 1. You can directly use the quantized model provided by FastDeploy for deployment.
|
||||||
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
- 2. You can use [one-click automatical compression tool](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/) provided by FastDeploy to quantize model by yourself, and use the generated quantized model for deployment.(Note: The quantized classification model still needs the deploy.yaml file in the FP32 model folder. Self-quantized model folder does not contain this yaml file, you can copy it from the FP32 model folder to the quantized model folder.)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 以量化后的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes模型为例, 进行部署
|
## Take the Quantized PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes Model as an example for Deployment
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
#下载部署示例代码
|
# Download sample deployment code.
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/quantize/python
|
cd examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/quantize/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#下载FastDeloy提供的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes量化模型文件和测试图片
|
# Download the PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes quantized model and test images provided by FastDeloy.
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 在CPU上使用Paddle-Inference推理量化模型
|
# Use Paddle-Inference inference quantization model on CPU.
|
||||||
python infer.py --model PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT --image cityscapes_demo.png --device cpu --backend paddle
|
python infer.py --model PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT --image cityscapes_demo.png --device cpu --backend paddle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg 量化模型 Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的`infer.py`,可以帮助用户快速完成PaddleSeg量化模型在CPU/GPU上的部署推理加速.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy环境准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
- 2. FastDeploy Python whl包安装,参考[FastDeploy Python安装](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/download_prebuilt_libraries.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 量化模型准备
|
||||||
|
- 1. 用户可以直接使用由FastDeploy提供的量化模型进行部署.
|
||||||
|
- 2. 用户可以使用FastDeploy提供的[一键模型自动化压缩工具](../../../../../../tools/common_tools/auto_compression/),自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的deploy.yaml文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此yaml文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 以量化后的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes模型为例, 进行部署
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/quantize/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载FastDeloy提供的PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes量化模型文件和测试图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_PTQ.tar
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 在CPU上使用Paddle-Inference推理量化模型
|
||||||
|
python infer.py --model PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer_QAT --image cityscapes_demo.png --device cpu --backend paddle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,33 +1,34 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg 模型部署
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Model Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型版本说明
|
## Model Version
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [PaddleSeg develop](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/develop)
|
- [PaddleSeg develop](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/develop)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
目前FastDeploy使用RKNPU2推理PPSeg支持如下模型的部署:
|
Currently FastDeploy using RKNPU2 to infer PPSeg supports the following model deployments:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| 模型 | 参数文件大小 | 输入Shape | mIoU | mIoU (flip) | mIoU (ms+flip) |
|
| Model | Parameter File Size | Input Shape | mIoU | mIoU (flip) | mIoU (ms+flip) |
|
||||||
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------|:---------|:-------|:------------|:---------------|
|
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------|:---------|:-------|:------------|:---------------|
|
||||||
| [Unet-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Unet_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 52MB | 1024x512 | 65.00% | 66.02% | 66.89% |
|
| [Unet-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Unet_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 52MB | 1024x512 | 65.00% | 66.02% | 66.89% |
|
||||||
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 31MB | 1024x512 | 77.04% | 77.73% | 77.46% |
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 31MB | 1024x512 | 77.04% | 77.73% | 77.46% |
|
||||||
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Lite(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Lite_infer.tgz) | 543KB | 192x192 | 86.2% | - | - |
|
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Lite(Universal portrait segmentation model)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Lite_infer.tgz) | 543KB | 192x192 | 86.2% | - | - |
|
||||||
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Lite(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddle2onnx/libs/PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_192x192_infer.tgz) | 12MB | 192x192 | 92.52% | - | - |
|
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Lite(Universal portrait segmentation model)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddle2onnx/libs/PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_192x192_infer.tgz) | 12MB | 192x192 | 92.52% | - | - |
|
||||||
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Mobile(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV2_Mobile_192x192_infer.tgz) | 29MB | 192x192 | 93.13% | - | - |
|
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Mobile(Universal portrait segmentation model)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV2_Mobile_192x192_infer.tgz) | 29MB | 192x192 | 93.13% | - | - |
|
||||||
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Server(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Server_infer.tgz) | 103MB | 512x512 | 96.47% | - | - |
|
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Server(Universal portrait segmentation model)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Server_infer.tgz) | 103MB | 512x512 | 96.47% | - | - |
|
||||||
| [Portait-PP-HumanSegV2_Lite(肖像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.tgz) | 3.6M | 256x144 | 96.63% | - | - |
|
| [Portait-PP-HumanSegV2_Lite(Portrait segmentation model)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.tgz) | 3.6M | 256x144 | 96.63% | - | - |
|
||||||
| [FCN-HRNet-W18-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/FCN_HRNet_W18_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 37MB | 1024x512 | 78.97% | 79.49% | 79.74% |
|
| [FCN-HRNet-W18-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/FCN_HRNet_W18_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 37MB | 1024x512 | 78.97% | 79.49% | 79.74% |
|
||||||
| [Deeplabv3-ResNet101-OS8-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Deeplabv3_ResNet101_OS8_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 150MB | 1024x512 | 79.90% | 80.22% | 80.47% |
|
| [Deeplabv3-ResNet101-OS8-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Deeplabv3_ResNet101_OS8_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 150MB | 1024x512 | 79.90% | 80.22% | 80.47% |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 准备PaddleSeg部署模型以及转换模型
|
## Prepare PaddleSeg Deployment Model and Conversion Model
|
||||||
RKNPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成RKNN模型,具体步骤如下:
|
RKNPU needs to convert the Paddle model to RKNN model before deploying, the steps are as follows:
|
||||||
* Paddle动态图模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[PaddleSeg模型导出说明](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg)
|
* For the conversion of Paddle dynamic diagram model to ONNX model, please refer to [PaddleSeg Model Export](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg).
|
||||||
* ONNX模型转换RKNN模型的过程,请参考[转换文档](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/export.md)进行转换。
|
* For the process of converting ONNX model to RKNN model, please refer to [Conversion document](../../../../../docs/en/faq/rknpu2/export.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型转换example
|
## An example of Model Conversion
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* [PPHumanSeg](./pp_humanseg.md)
|
* [PPHumanSeg](./pp_humanseg_EN.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 详细部署文档
|
## Detailed Deployment Document
|
||||||
- [RKNN总体部署教程](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/rknpu2.md)
|
- [Overall RKNN Deployment Guidance](../../../../../docs/en/faq/rknpu2/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
- [Deploy with C++](cpp)
|
||||||
- [Python部署](python)
|
- [Deploy with Python](python)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
34
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rknpu2/README_CN.md
Normal file
34
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rknpu2/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg 模型部署
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型版本说明
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [PaddleSeg develop](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/develop)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
目前FastDeploy使用RKNPU2推理PPSeg支持如下模型的部署:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| 模型 | 参数文件大小 | 输入Shape | mIoU | mIoU (flip) | mIoU (ms+flip) |
|
||||||
|
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------|:---------|:-------|:------------|:---------------|
|
||||||
|
| [Unet-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Unet_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 52MB | 1024x512 | 65.00% | 66.02% | 66.89% |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-LiteSeg-T(STDC1)-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_T_STDC1_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 31MB | 1024x512 | 77.04% | 77.73% | 77.46% |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Lite(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Lite_infer.tgz) | 543KB | 192x192 | 86.2% | - | - |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Lite(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddle2onnx/libs/PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_192x192_infer.tgz) | 12MB | 192x192 | 92.52% | - | - |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-HumanSegV2-Mobile(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV2_Mobile_192x192_infer.tgz) | 29MB | 192x192 | 93.13% | - | - |
|
||||||
|
| [PP-HumanSegV1-Server(通用人像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_HumanSegV1_Server_infer.tgz) | 103MB | 512x512 | 96.47% | - | - |
|
||||||
|
| [Portait-PP-HumanSegV2_Lite(肖像分割模型)](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.tgz) | 3.6M | 256x144 | 96.63% | - | - |
|
||||||
|
| [FCN-HRNet-W18-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/FCN_HRNet_W18_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 37MB | 1024x512 | 78.97% | 79.49% | 79.74% |
|
||||||
|
| [Deeplabv3-ResNet101-OS8-cityscapes](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Deeplabv3_ResNet101_OS8_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) | 150MB | 1024x512 | 79.90% | 80.22% | 80.47% |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 准备PaddleSeg部署模型以及转换模型
|
||||||
|
RKNPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成RKNN模型,具体步骤如下:
|
||||||
|
* Paddle动态图模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[PaddleSeg模型导出说明](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/tree/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg)
|
||||||
|
* ONNX模型转换RKNN模型的过程,请参考[转换文档](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/export.md)进行转换。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型转换example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* [PPHumanSeg](./pp_humanseg.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 详细部署文档
|
||||||
|
- [RKNN总体部署教程](../../../../../docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
- [C++部署](cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](python)
|
||||||
@@ -1,30 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Deployment Examples for C++
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下用于展示PaddleSeg系列模型在RKNPU2上的部署,以下的部署过程以PPHumanSeg为例子。
|
This directory demonstrates the deployment of PaddleSeg series models on RKNPU2. The following deployment process takes PHumanSeg as an example.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Before deployment, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Download the pre-compiled deployment repository or compile the FastDeploy repository from scratch according to the development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
For the above steps, please refer to [How to Build RKNPU2 Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/rknpu2.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate Basic Directory Files
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
The routine consists of the following parts:
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile Folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # Folder for images
|
||||||
├── infer_cpu_npu.cc
|
├── infer_cpu_npu.cc
|
||||||
├── infer_cpu_npu.h
|
├── infer_cpu_npu.h
|
||||||
├── main.cc
|
├── main.cc
|
||||||
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
├── model # Folder for models
|
||||||
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
└── thirdpartys # Folder for sdk
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
First, please build a directory structure
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
mkdir images
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
@@ -32,24 +33,23 @@ mkdir model
|
|||||||
mkdir thirdpartys
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and Copy SDK to folder thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成
|
Please refer to [How to Build RKNPU2 Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/rknpu2.md) to compile SDK.After compiling, the fastdeploy-0.0.3 directory will be created in the build directory, please move it to the thirdpartys directory.
|
||||||
fastdeploy-0.0.3目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy model and configuration files to folder Model
|
||||||
在Paddle动态图模型 -> Paddle静态图模型 -> ONNX模型的过程中,将生成ONNX文件以及对应的yaml配置文件,请将配置文件存放到model文件夹内。
|
In the process of Paddle dynamic map model -> Paddle static map model -> ONNX mdoel, ONNX file and the corresponding yaml configuration file will be generated. Please move the configuration file to the folder model.
|
||||||
转换为RKNN后的模型文件也需要拷贝至model,输入以下命令下载使用(模型文件为RK3588,RK3568需要重新[转换PPSeg RKNN模型](../README.md))。
|
After converting to RKNN, the model file also needs to be copied to folder model. Run the following command to download and use (the model file is RK3588. RK3568 needs to be [reconverted to PPSeg RKNN model](../README.md)).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare Test Images to folder image
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
||||||
unzip -qo images.zip
|
unzip -qo images.zip
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compile example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -58,17 +58,16 @@ make -j8
|
|||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running Routines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd ./build/install
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
./rknpu_test model/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/ images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
./rknpu_test model/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/ images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 注意事项
|
## Notes
|
||||||
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,
|
The input requirement for the model on RKNPU is to use NHWC format, and image normalization will be embedded into the model when converting the RKNN model, so we need to call DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++) or disable_normalize_and_permute(Python) first when deploying with FastDeploy to disable normalization and data format conversion in the preprocessing stage.
|
||||||
需要先调用DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++)或`disable_normalize_and_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
- [Model Description](../../)
|
||||||
- [Python部署](../python)
|
- [Python Deployment](../python)
|
||||||
- [转换PPSeg RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Convert PPSeg and RKNN model](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下用于展示PaddleSeg系列模型在RKNPU2上的部署,以下的部署过程以PPHumanSeg为例子。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,下载预编译部署库或者从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer_cpu_npu.cc
|
||||||
|
├── infer_cpu_npu.h
|
||||||
|
├── main.cc
|
||||||
|
├── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
└── thirdpartys # 存放sdk的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先需要先生成目录结构
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build
|
||||||
|
mkdir images
|
||||||
|
mkdir model
|
||||||
|
mkdir thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[RK2代NPU部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录,请移动它至thirdpartys目录下.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
在Paddle动态图模型 -> Paddle静态图模型 -> ONNX模型的过程中,将生成ONNX文件以及对应的yaml配置文件,请将配置文件存放到model文件夹内。
|
||||||
|
转换为RKNN后的模型文件也需要拷贝至model,输入以下命令下载使用(模型文件为RK3588,RK3568需要重新[转换PPSeg RKNN模型](../README.md))。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
||||||
|
unzip -qo images.zip
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd ./build/install
|
||||||
|
./rknpu_test model/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/ images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 注意事项
|
||||||
|
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,需要先调用DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++)或`disable_normalize_and_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
||||||
|
- [Python部署](../python)
|
||||||
|
- [转换PPSeg RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](pp_humanseg_EN.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
# PPHumanSeg模型部署
|
# PPHumanSeg模型部署
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 转换模型
|
## 转换模型
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
|||||||
|
English | [简体中文](pp_humanseg.md)
|
||||||
|
# PPHumanSeg Model Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Converting Model
|
||||||
|
The following is an example of Portait-PP-HumanSegV2_Lite (portrait segmentation model), showing how to convert PPSeg model to RKNN model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# Download Paddle2ONNX repository.
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Download the Paddle static map model and fix the input shape.
|
||||||
|
## Go to the directory where the input shape is fixed for the Paddle static map model.
|
||||||
|
cd Paddle2ONNX/tools/paddle
|
||||||
|
## Download and unzip Paddle static map model.
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
python paddle_infer_shape.py --model_dir Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/ \
|
||||||
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
|
--save_dir Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer \
|
||||||
|
--input_shape_dict="{'x':[1,3,144,256]}"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Converting static map model to ONNX model, note that the save_file here aligns with the zip name.
|
||||||
|
paddle2onnx --model_dir Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer \
|
||||||
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
|
--save_file Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--enable_dev_version True
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Convert ONNX model to RKNN model.
|
||||||
|
# Copy the ONNX model directory to the Fastdeploy root directory.
|
||||||
|
cp -r ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer /path/to/Fastdeploy
|
||||||
|
# Convert model, the model will be generated in the Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer directory.
|
||||||
|
python tools/rknpu2/export.py \
|
||||||
|
--config_path tools/rknpu2/config/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer.yaml \
|
||||||
|
--target_platform rk3588
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Modify yaml Configuration File
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In the **An example of Model Conversion** part, we fixed the shape of the model, so the corresponding yaml file needs to be modified as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**The original yaml file**
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
Deploy:
|
||||||
|
input_shape:
|
||||||
|
- -1
|
||||||
|
- 3
|
||||||
|
- -1
|
||||||
|
- -1
|
||||||
|
model: model.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
output_dtype: float32
|
||||||
|
output_op: none
|
||||||
|
params: model.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
transforms:
|
||||||
|
- target_size:
|
||||||
|
- 256
|
||||||
|
- 144
|
||||||
|
type: Resize
|
||||||
|
- type: Normalize
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**The modified yaml file**
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
Deploy:
|
||||||
|
input_shape:
|
||||||
|
- 1
|
||||||
|
- 3
|
||||||
|
- 144
|
||||||
|
- 256
|
||||||
|
model: model.pdmodel
|
||||||
|
output_dtype: float32
|
||||||
|
output_op: none
|
||||||
|
params: model.pdiparams
|
||||||
|
transforms:
|
||||||
|
- target_size:
|
||||||
|
- 256
|
||||||
|
- 144
|
||||||
|
type: Resize
|
||||||
|
- type: Normalize
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -1,36 +1,36 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Deployment Examples for Python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before deployment, the following step need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements, please refer to [Environment Requirements for FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/rknpu2.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
【注意】如你部署的为**PP-Matting**、**PP-HumanMatting**以及**ModNet**请参考[Matting模型部署](../../../../matting/)
|
【Note】If you are deploying **PP-Matting**, **PP-HumanMatting** or **ModNet**, please refer to [Matting Model Deployment](../../../../matting/).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成PPHumanseg在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
This directory provides `infer.py` for a quick example of PPHumanseg deployment on RKNPU. This can be done by running the following script.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the deploying demo code.
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images.
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
||||||
unzip images.zip
|
unzip images.zip
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference.
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer_rk3588.rknn \
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer_rk3588.rknn \
|
||||||
--config_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/deploy.yaml \
|
--config_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/deploy.yaml \
|
||||||
--image images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
--image images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 注意事项
|
## Notes
|
||||||
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,
|
The input requirement for the model on RKNPU is to use NHWC format, and image normalization will be embedded into the model when converting the RKNN model, so we need to call DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++) or disable_normalize_and_permute(Python) first when deploying with FastDeploy to disable normalization and data format conversion in the preprocessing stage.
|
||||||
需要先调用DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++)或`disable_normalize_and_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [PaddleSeg 模型介绍](..)
|
- [PaddleSeg Model Description](..)
|
||||||
- [PaddleSeg C++部署](../cpp)
|
- [PaddleSeg C++ Deployment](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
- [Description of the prediction](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
- [转换PPSeg RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Convert PPSeg and RKNN model](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rknpu2.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
【注意】如你部署的为**PP-Matting**、**PP-HumanMatting**以及**ModNet**请参考[Matting模型部署](../../../../matting/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成PPHumanseg在RKNPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/pp_humanseg_v2/images.zip
|
||||||
|
unzip images.zip
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer_rk3588.rknn \
|
||||||
|
--config_file ./Portrait_PP_HumanSegV2_Lite_256x144_infer/deploy.yaml \
|
||||||
|
--image images/portrait_heng.jpg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 注意事项
|
||||||
|
RKNPU上对模型的输入要求是使用NHWC格式,且图片归一化操作会在转RKNN模型时,内嵌到模型中,因此我们在使用FastDeploy部署时,需要先调用DisableNormalizeAndPermute(C++)或`disable_normalize_and_permute(Python),在预处理阶段禁用归一化以及数据格式的转换。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [PaddleSeg 模型介绍](..)
|
||||||
|
- [PaddleSeg C++部署](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [模型预测结果说明](../../../../../../docs/api/vision_results/)
|
||||||
|
- [转换PPSeg RKNN模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
# PP-LiteSeg 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PP-LiteSeg Quantitative Model C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型在 RV1126 上的部署推理加速。
|
`infer.cc` in this directory can help you quickly complete the inference acceleration of PP-LiteSeg quantization model deployment on RV1126.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 部署准备
|
## Deployment Preparations
|
||||||
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
### FastDeploy Cross-compile Environment Preparations
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
1. For the software and hardware environment, and the cross-compile environment, please refer to [Preparations for FastDeploy Cross-compile environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/rv1126.md#Cross-compilation-environment-construction).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 模型准备
|
### Model Preparations
|
||||||
1. 用户可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署。
|
1. You can directly use the quantized model provided by FastDeploy for deployment.
|
||||||
2. 用户可以使用 FastDeploy 提供的一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的 deploy.yaml 文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此 yaml 文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
2. You can use one-click automatical compression tool provided by FastDeploy to quantize model by yourself, and use the generated quantized model for deployment.(Note: The quantized classification model still needs the deploy.yaml file in the FP32 model folder. Self-quantized model folder does not contain this yaml file, you can copy it from the FP32 model folder to the quantized model folder.)
|
||||||
3. 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
3. The model requires heterogeneous computation. Please refer to: [Heterogeneous Computation](./../../../../../../docs/en/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md). Since the model is already provided, you can test the heterogeneous file we provide first to verify whether the accuracy meets the requirements.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
For more information, please refer to [Model Quantization](../../quantize/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 在 RV1126 上部署量化后的 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型
|
## Deploying the Quantized PP-LiteSeg Segmentation model on RV1126
|
||||||
请按照以下步骤完成在 RV1126 上部署 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型:
|
Please follow these steps to complete the deployment of the PP-LiteSeg quantization model on RV1126.
|
||||||
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
1. Cross-compile the FastDeploy library as described in [Cross-compile FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/rv1126.md#FastDeploy-cross-compilation-library-compilation-based-on-Paddle-Lite).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
2. Copy the compiled library to the current directory. You can run this line:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
3. Download the model and example images required for deployment in current path.
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/rk1/ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/rk1/ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
||||||
@@ -32,25 +33,25 @@ wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
|||||||
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
4. Compile the deployment example. You can run the following lines:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
mkdir build && cd build
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
||||||
make -j8
|
make -j8
|
||||||
make install
|
make install
|
||||||
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
# After success, an install folder will be created with a running demo and libraries required for deployment.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型到 Rockchip RV1126,可使用如下命令:
|
5. Deploy the PP-LiteSeg segmentation model to Rockchip RV1126 based on adb. You can run the following lines:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 进入 install 目录
|
# Go to the install directory.
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
# The following line represents: bash run_with_adb.sh, demo needed to run, model path, image path, DEVICE ID.
|
||||||
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
部署成功后运行结果如下:
|
The output is:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
需要特别注意的是,在 RV1126 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
Please note that the model deployed on RV1126 needs to be quantized. You can refer to [Model Quantization](../../../../../../docs/en/quantize.md).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PP-LiteSeg 量化模型 C++ 部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供的 `infer.cc`,可以帮助用户快速完成 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型在 RV1126 上的部署推理加速。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 部署准备
|
||||||
|
### FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求,以及交叉编译环境的准备,请参考:[FastDeploy 交叉编译环境准备](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#交叉编译环境搭建)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 模型准备
|
||||||
|
1. 用户可以直接使用由 FastDeploy 提供的量化模型进行部署。
|
||||||
|
2. 用户可以使用 FastDeploy 提供的一键模型自动化压缩工具,自行进行模型量化, 并使用产出的量化模型进行部署.(注意: 推理量化后的分类模型仍然需要FP32模型文件夹下的 deploy.yaml 文件, 自行量化的模型文件夹内不包含此 yaml 文件, 用户从FP32模型文件夹下复制此yaml文件到量化后的模型文件夹内即可.)
|
||||||
|
3. 模型需要异构计算,异构计算文件可以参考:[异构计算](./../../../../../../docs/cn/faq/heterogeneous_computing_on_timvx_npu.md),由于 FastDeploy 已经提供了模型,可以先测试我们提供的异构文件,验证精度是否符合要求。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
更多量化相关相关信息可查阅[模型量化](../../quantize/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 在 RV1126 上部署量化后的 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型
|
||||||
|
请按照以下步骤完成在 RV1126 上部署 PP-LiteSeg 量化模型:
|
||||||
|
1. 交叉编译编译 FastDeploy 库,具体请参考:[交叉编译 FastDeploy](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/rv1126.md#基于-paddlelite-的-fastdeploy-交叉编译库编译)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2. 将编译后的库拷贝到当前目录,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cp -r FastDeploy/build/fastdeploy-timvx/ FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3. 在当前路径下载部署所需的模型和示例图片:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir models && mkdir images
|
||||||
|
wget https://bj.bcebos.com/fastdeploy/models/rk1/ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf ppliteseg.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
cp -r ppliteseg models
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
cp -r cityscapes_demo.png images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
4. 编译部署示例,可使入如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
mkdir build && cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx/toolchain.cmake -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/../fastdeploy-timvx -DTARGET_ABI=armhf ..
|
||||||
|
make -j8
|
||||||
|
make install
|
||||||
|
# 成功编译之后,会生成 install 文件夹,里面有一个运行 demo 和部署所需的库
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
5. 基于 adb 工具部署 PP-LiteSeg 分割模型到 Rockchip RV1126,可使用如下命令:
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 进入 install 目录
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/rv1126/cpp/build/install/
|
||||||
|
# 如下命令表示:bash run_with_adb.sh 需要运行的demo 模型路径 图片路径 设备的DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
bash run_with_adb.sh infer_demo ppliteseg cityscapes_demo.png $DEVICE_ID
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
部署成功后运行结果如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30516196/205544166-9b2719ff-ed82-4908-b90a-095de47392e1.png">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
需要特别注意的是,在 RV1126 上部署的模型需要是量化后的模型,模型的量化请参考:[模型量化](../../../../../../docs/cn/quantize.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,33 +1,34 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 支持模型列表
|
## Supporting Model List
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- PP-LiteSeg部署模型实现来自[PaddleSeg PP-LiteSeg系列模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/configs/pp_liteseg/README.md)
|
- PP-LiteSeg deployment models are from [PaddleSeg PP-LiteSeg series model](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/configs/pp_liteseg/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 准备PP-LiteSeg部署模型以及转换模型
|
## PP-LiteSeg Model Deployment and Conversion Preparations
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
Befor SOPHGO-TPU model deployment, you should first convert Paddle model to bmodel model. Specific steps are as follows:
|
||||||
- 下载Paddle模型[PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz)
|
- Download Paddle model: [PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz).
|
||||||
- Pddle模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX)
|
- Convert Paddle model to ONNX model. Please refer to [Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX).
|
||||||
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)
|
- For the process of converting ONNX model to bmodel, please refer to [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型转换example
|
## Model Converting Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
下面以[PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz)为例子,教大家如何转换Paddle模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型
|
Here we take [PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz) as an example to show you how to convert Paddle model to SOPHGO-TPU model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 下载PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax模型,并转换为ONNX模型
|
### Download PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax, and convert it to ONNX
|
||||||
```shell
|
```shell
|
||||||
https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
||||||
tar xvf PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
tar xvf PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 修改PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer模型的输入shape,由动态输入变成固定输入
|
# Modify the input shape of PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer model from dynamic input to constant input.
|
||||||
python paddle_infer_shape.py --model_dir PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer \
|
python paddle_infer_shape.py --model_dir PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer \
|
||||||
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
--save_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
--save_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
||||||
--input_shape_dict="{'x':[1,3,512,512]}"
|
--input_shape_dict="{'x':[1,3,512,512]}"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#将固定输入的Paddle模型转换成ONNX模型
|
# Convert constant input Paddle model to ONNX model.
|
||||||
paddle2onnx --model_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
paddle2onnx --model_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
||||||
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
@@ -35,32 +36,32 @@ paddle2onnx --model_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
|||||||
--enable_dev_version True
|
--enable_dev_version True
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 导出bmodel模型
|
### Export bmodel
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以转换BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
Take converting BM1684x model to bmodel as an example. You need to download [TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir) project. For the process of installation, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
### 1. 安装
|
### 1. Installation
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
# myname1234 is just an example, you can customize your own name.
|
||||||
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
source ./envsetup.sh
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
./build.sh
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
### 2. Convert ONNX model to bmodel
|
||||||
``` shell
|
``` shell
|
||||||
mkdir pp_liteseg && cd pp_liteseg
|
mkdir pp_liteseg && cd pp_liteseg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步转换的pp_liteseg.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
# Put the test image in this file, and put the converted pp_liteseg.onnx into this folder.
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
#放入onnx模型文件pp_liteseg.onnx
|
# Put in the onnx model file pp_liteseg.onnx.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
# Convert ONNX model to mlir model, the parameter --output_names can be viewed via NETRON.
|
||||||
model_transform.py \
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
--model_name pp_liteseg \
|
--model_name pp_liteseg \
|
||||||
--model_def ../pp_liteseg.onnx \
|
--model_def ../pp_liteseg.onnx \
|
||||||
@@ -74,7 +75,7 @@ model_transform.py \
|
|||||||
--test_result pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_result pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir
|
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
# Convert mlir model to BM1684x F32 bmodel.
|
||||||
model_deploy.py \
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir \
|
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir \
|
||||||
--quantize F32 \
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
@@ -83,7 +84,7 @@ model_deploy.py \
|
|||||||
--test_reference pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
--test_reference pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
--model pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
--model pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
The final bmodel, pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel, can run on BM1684x. If you want to further accelerate the model, you can convert ONNX model to INT8 bmodel. For details, please refer to [TPU-MLIR Document](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其他链接
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
- [Cpp Deployment](./cpp)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
90
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/sophgo/README_CN.md
Normal file
90
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/sophgo/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 支持模型列表
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- PP-LiteSeg部署模型实现来自[PaddleSeg PP-LiteSeg系列模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/configs/pp_liteseg/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 准备PP-LiteSeg部署模型以及转换模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SOPHGO-TPU部署模型前需要将Paddle模型转换成bmodel模型,具体步骤如下:
|
||||||
|
- 下载Paddle模型[PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz)
|
||||||
|
- Paddle模型转换为ONNX模型,请参考[Paddle2ONNX](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle2ONNX)
|
||||||
|
- ONNX模型转换bmodel模型的过程,请参考[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型转换example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下面以[PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax](https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz)为例子,教大家如何转换Paddle模型到SOPHGO-TPU模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 下载PP-LiteSeg-B(STDC2)-cityscapes-without-argmax模型,并转换为ONNX模型
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
https://bj.bcebos.com/paddlehub/fastdeploy/PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
tar xvf PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer.tgz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 修改PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer模型的输入shape,由动态输入变成固定输入
|
||||||
|
python paddle_infer_shape.py --model_dir PP_LiteSeg_B_STDC2_cityscapes_without_argmax_infer \
|
||||||
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
|
--save_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
||||||
|
--input_shape_dict="{'x':[1,3,512,512]}"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#将固定输入的Paddle模型转换成ONNX模型
|
||||||
|
paddle2onnx --model_dir pp_liteseg_fix \
|
||||||
|
--model_filename model.pdmodel \
|
||||||
|
--params_filename model.pdiparams \
|
||||||
|
--save_file pp_liteseg.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--enable_dev_version True
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 导出bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以转换BM1684x的bmodel模型为例子,我们需要下载[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)工程,安装过程具体参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
### 1. 安装
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# myname1234是一个示例,也可以设置其他名字
|
||||||
|
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
source ./envsetup.sh
|
||||||
|
./build.sh
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2. ONNX模型转换为bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
``` shell
|
||||||
|
mkdir pp_liteseg && cd pp_liteseg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#在该文件中放入测试图片,同时将上一步转换的pp_liteseg.onnx放入该文件夹中
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/dataset/COCO2017 .
|
||||||
|
cp -rf ${REGRESSION_PATH}/image .
|
||||||
|
#放入onnx模型文件pp_liteseg.onnx
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#将ONNX模型转换为mlir模型,其中参数--output_names可以通过NETRON查看
|
||||||
|
model_transform.py \
|
||||||
|
--model_name pp_liteseg \
|
||||||
|
--model_def ../pp_liteseg.onnx \
|
||||||
|
--input_shapes [[1,3,512,512]] \
|
||||||
|
--mean 0.0,0.0,0.0 \
|
||||||
|
--scale 0.0039216,0.0039216,0.0039216 \
|
||||||
|
--keep_aspect_ratio \
|
||||||
|
--pixel_format rgb \
|
||||||
|
--output_names bilinear_interp_v2_6.tmp_0 \
|
||||||
|
--test_input ../image/dog.jpg \
|
||||||
|
--test_result pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#将mlir模型转换为BM1684x的F32 bmodel模型
|
||||||
|
model_deploy.py \
|
||||||
|
--mlir pp_liteseg.mlir \
|
||||||
|
--quantize F32 \
|
||||||
|
--chip bm1684x \
|
||||||
|
--test_input pp_liteseg_in_f32.npz \
|
||||||
|
--test_reference pp_liteseg_top_outputs.npz \
|
||||||
|
--model pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
最终获得可以在BM1684x上能够运行的bmodel模型pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel。如果需要进一步对模型进行加速,可以将ONNX模型转换为INT8 bmodel,具体步骤参见[TPU-MLIR文档](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir/blob/master/README.md)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其他链接
|
||||||
|
- [Cpp部署](./cpp)
|
||||||
@@ -1,43 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg C++ Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成pp_liteseg模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
`infer.cc` in this directory provides a quick example of accelerated deployment of the pp_liteseg model on SOPHGO BM1684x.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
Before deployment, the following two steps need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements.
|
||||||
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
2. Compile the FastDeploy repository from scratch according to the development environment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
For the above steps, please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 生成基本目录文件
|
## Generate Basic Directory Files
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
The routine consists of the following parts:
|
||||||
```text
|
```text
|
||||||
.
|
.
|
||||||
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
├── build # Compile Folder
|
||||||
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
├── image # Folder for images
|
||||||
├── infer.cc
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
└── model # Folder for models
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 编译
|
## Compile
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
### Compile and Copy SDK to folder thirdpartys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
Please refer to [How to Build SOPHGO Deployment Environment](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md) to compile SDK.After compiling, the fastdeploy-0.0.3 directory will be created in the build directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
### Copy model and configuration files to folder Model
|
||||||
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
Convert Paddle model to SOPHGO bmodel model. For the conversion steps, please refer to [Document](../README.md).
|
||||||
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
Please copy the converted SOPHGO bmodel to folder model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
### Prepare Test Images to folder image
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
cp cityscapes_demo.png ./images
|
cp cityscapes_demo.png ./images
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 编译example
|
### Compile example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
cd build
|
cd build
|
||||||
@@ -45,12 +46,12 @@ cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
|||||||
make
|
make
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 运行例程
|
## Running Routines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
./infer_demo model images/cityscapes_demo.png
|
./infer_demo model images/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
- [Model Description](../../)
|
||||||
- [模型转换](../)
|
- [Model Conversion](../)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg C++部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.cc`快速完成pp_liteseg模型在SOPHGO BM1684x板子上加速部署的示例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 软硬件环境满足要求
|
||||||
|
2. 根据开发环境,从头编译FastDeploy仓库
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以上步骤请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)实现
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 生成基本目录文件
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
该例程由以下几个部分组成
|
||||||
|
```text
|
||||||
|
.
|
||||||
|
├── CMakeLists.txt
|
||||||
|
├── build # 编译文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── image # 存放图片的文件夹
|
||||||
|
├── infer.cc
|
||||||
|
└── model # 存放模型文件的文件夹
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 编译
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译并拷贝SDK到thirdpartys文件夹
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
请参考[SOPHGO部署库编译](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)仓库编译SDK,编译完成后,将在build目录下生成fastdeploy-0.0.3目录.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 拷贝模型文件,以及配置文件至model文件夹
|
||||||
|
将Paddle模型转换为SOPHGO bmodel模型,转换步骤参考[文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
将转换后的SOPHGO bmodel模型文件拷贝至model中
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备测试图片至image文件夹
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
cp cityscapes_demo.png ./images
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 编译example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
cd build
|
||||||
|
cmake .. -DFASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
|
||||||
|
make
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 运行例程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./infer_demo model images/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [模型介绍](../../)
|
||||||
|
- [模型转换](../)
|
||||||
@@ -1,26 +1,27 @@
|
|||||||
# PaddleSeg Python部署示例
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Python Deployment Example
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在部署前,需确认以下两个步骤
|
Before deployment, the following step need to be confirmed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
- 1. Hardware and software environment meets the requirements. Please refer to [FastDeploy Environment Requirement](../../../../../../docs/en/build_and_install/sophgo.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 pp_liteseg 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
`infer.py` in this directory provides a quick example of deployment of the pp_liteseg model on SOPHGO TPU. Please run the following script:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
# 下载部署示例代码
|
# Download the sample deployment code.
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/sophgo/python
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 下载图片
|
# Download images.
|
||||||
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 推理
|
# Inference.
|
||||||
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ./bmodel/deploy.yaml --image cityscapes_demo.png
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ./bmodel/deploy.yaml --image cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
# The returned result.
|
||||||
运行结果保存在sophgo_img.png中
|
The result is saved as sophgo_img.png.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 其它文档
|
## Other Documents
|
||||||
- [pp_liteseg C++部署](../cpp)
|
- [pp_liteseg C++ Deployment](../cpp)
|
||||||
- [转换 pp_liteseg SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
- [Converting pp_liteseg SOPHGO model](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PaddleSeg Python部署示例
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在部署前,需确认以下步骤
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 1. 软硬件环境满足要求,参考[FastDeploy环境要求](../../../../../../docs/cn/build_and_install/sophgo.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本目录下提供`infer.py`快速完成 pp_liteseg 在SOPHGO TPU上部署的示例。执行如下脚本即可完成
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# 下载部署示例代码
|
||||||
|
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
|
||||||
|
cd FastDeploy/examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/sophgo/python
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 下载图片
|
||||||
|
wget https://paddleseg.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/demo/cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 推理
|
||||||
|
python3 infer.py --model_file ./bmodel/pp_liteseg_1684x_f32.bmodel --config_file ./bmodel/deploy.yaml --image cityscapes_demo.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 运行完成后返回结果如下所示
|
||||||
|
运行结果保存在sophgo_img.png中
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其它文档
|
||||||
|
- [pp_liteseg C++部署](../cpp)
|
||||||
|
- [转换 pp_liteseg SOPHGO模型文档](../README.md)
|
||||||
@@ -1,43 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
# PP-Humanseg v1模型前端部署
|
English | [简体中文](README_CN.md)
|
||||||
|
# PP-Humanseg v1 Model Frontend Deployment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 模型版本说明
|
## Model Version
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- [PP-HumanSeg Release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg/)
|
- [PP-HumanSeg Release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 前端部署PP-Humanseg v1模型
|
## Deploy PP-Humanseg v1 Model on Frontend
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
PP-Humanseg v1模型web demo部署及使用参考[文档](../../../../application/js/web_demo/README.md)
|
To deploy and use PP-Humanseg v1 model of web demo, please refer to [document](../../../../application/js/web_demo/README.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## PP-Humanseg v1 js接口
|
## PP-Humanseg v1 js interface
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
import * as humanSeg from "@paddle-js-models/humanseg";
|
import * as humanSeg from "@paddle-js-models/humanseg";
|
||||||
# 模型加载与初始化
|
# Load and initialise model
|
||||||
await humanSeg.load(Config);
|
await humanSeg.load(Config);
|
||||||
# 人像分割
|
# Portrait segmentation
|
||||||
const res = humanSeg.getGrayValue(input)
|
const res = humanSeg.getGrayValue(input)
|
||||||
# 提取人像与背景的二值图
|
# Extract the binary map of portrait and background
|
||||||
humanSeg.drawMask(res)
|
humanSeg.drawMask(res)
|
||||||
# 用于替换背景的可视化函数
|
# Visualization function for background replacement
|
||||||
humanSeg.drawHumanSeg(res)
|
humanSeg.drawHumanSeg(res)
|
||||||
# 背景虚化
|
# Blur background
|
||||||
humanSeg.blurBackground(res)
|
humanSeg.blurBackground(res)
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**load()函数参数**
|
**Parameters in function load()**
|
||||||
> * **Config**(dict): PP-Humanseg模型配置参数,默认为{modelpath : 'https://paddlejs.bj.bcebos.com/models/fuse/humanseg/humanseg_398x224_fuse_activation/model.json', mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], enableLightModel: false};modelPath为默认的PP-Humanseg js模型,mean,std分别为预处理的均值和标准差,enableLightModel为是否使用更轻量的模型。
|
> * **Config**(dict): Configuration parameter for PP-Humanseg model, default is {modelpath : 'https://paddlejs.bj.bcebos.com/models/fuse/humanseg/humanseg_398x224_fuse_activation/model.json', mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], enableLightModel: false};modelPath is the default PP-Humanseg js model. Mean, std respectively represent the mean and standard deviation of the preprocessing, and enableLightModel represents whether to use a lighter model.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**getGrayValue()函数参数**
|
**Parameters in function getGrayValue()**
|
||||||
> * **input**(HTMLImageElement | HTMLVideoElement | HTMLCanvasElement): 输入图像参数。
|
> * **input**(HTMLImageElement | HTMLVideoElement | HTMLCanvasElement): Input image parameter.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**drawMask()函数参数**
|
**Parameters in function drawMask()**
|
||||||
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): Input parameter, generally the result of function getGrayValue is used as input.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**blurBackground()函数参数**
|
**Parameters in function blurBackground()**
|
||||||
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): Input parameter, generally the result of function getGrayValue is used as input.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**drawHumanSeg()函数参数**
|
**Parameters in function drawHumanSeg()**
|
||||||
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): Input parameter, generally the result of function getGrayValue is used as input.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
44
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/web/README_CN.md
Normal file
44
examples/vision/segmentation/paddleseg/web/README_CN.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
|
[English](README.md) | 简体中文
|
||||||
|
# PP-Humanseg v1模型前端部署
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 模型版本说明
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [PP-HumanSeg Release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg/blob/release/2.6/contrib/PP-HumanSeg/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 前端部署PP-Humanseg v1模型
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PP-Humanseg v1模型web demo部署及使用参考[文档](../../../../application/js/web_demo/README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PP-Humanseg v1 js接口
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
import * as humanSeg from "@paddle-js-models/humanseg";
|
||||||
|
# 模型加载与初始化
|
||||||
|
await humanSeg.load(Config);
|
||||||
|
# 人像分割
|
||||||
|
const res = humanSeg.getGrayValue(input)
|
||||||
|
# 提取人像与背景的二值图
|
||||||
|
humanSeg.drawMask(res)
|
||||||
|
# 用于替换背景的可视化函数
|
||||||
|
humanSeg.drawHumanSeg(res)
|
||||||
|
# 背景虚化
|
||||||
|
humanSeg.blurBackground(res)
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**load()函数参数**
|
||||||
|
> * **Config**(dict): PP-Humanseg模型配置参数,默认为{modelpath : 'https://paddlejs.bj.bcebos.com/models/fuse/humanseg/humanseg_398x224_fuse_activation/model.json', mean: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std: [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], enableLightModel: false};modelPath为默认的PP-Humanseg js模型,mean,std分别为预处理的均值和标准差,enableLightModel为是否使用更轻量的模型。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**getGrayValue()函数参数**
|
||||||
|
> * **input**(HTMLImageElement | HTMLVideoElement | HTMLCanvasElement): 输入图像参数。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**drawMask()函数参数**
|
||||||
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**blurBackground()函数参数**
|
||||||
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**drawHumanSeg()函数参数**
|
||||||
|
> * **seg_values**(number[]): 输入参数,一般是getGrayValue函数计算的结果作为输入
|
||||||
@@ -328,7 +328,7 @@ public class SegmentationResult {
|
|||||||
public boolean initialized(); // Check if the result is valid.
|
public boolean initialized(); // Check if the result is valid.
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
Other reference:C++/Python corresponding SegmentationResult description: [api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md)
|
Other reference: C++/Python corresponding SegmentationResult description: [api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/api/vision_results/segmentation_result.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Face detection result description
|
- Face detection result description
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user